您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
作为大多数刚接触Android应用开发的人来说,在一个强大的Activity类中,就可以完成丰富多彩的UI工作,但是杂乱的屏幕分辨率,使得本来好不容易写好的UI,变得不堪入目。。。该怎么办那?
查阅了好多资料,才发现,原来我out了! 早在Android在3.0版本就引入了Fragment(碎片)功能,它非常类似于Activity,可以像Activity一样包含布局,通过将Activity 的布局分散到frament 中,可以在运行时修改activity 的外观,并且由activity 管理的back stack 中保存些变化,很巧妙的解决了不同分辨率手机上UI差异变化的问题。总结一下吧!
早在Android在3.0版本就引入了Fragment(碎片)功能,它非常类似于Activity,可以像Activity一样包含布局,通过将Activity 的布局分散到frament 中,可以在运行时修改activity 的外观,并且由activity 管理的back stack 中保存些变化,很巧妙的解决了不同分辨率手机上UI差异变化的问题。总结一下吧!
一.Fragment介绍:
官方文档:http://developer.android.com/guide/components/fragments.html

Fragment是我们在单个Activity上要切换多个UI界面时,要显示的不同内容。模块化这些UI面板可以提供给其他Acitivity来使用,因此我们可以简单地把Fragment看成类似于TextView控件一样,可以被任意的Activity进行加载。
1.静态加载:
首先,在Layout下建立两个xml
fragment1.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#000000" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是Fragment1"
/>
</LinearLayout>fragment2.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#0000ff">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是Fragment2" />
</LinearLayout>之后建立两个类:
FragmentFirst类:
package com.zhf.android_fragmentdemo;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class FragmentFirst extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false);
}
}FragmentSecond类:
package com.zhf.android_fragmentdemo;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class FragmentSecond extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
}
}最后一步就是在activity_main.xml中应用这两个布局文件:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:name="com.zhf.android_fragmentdemo.FragmentSecond"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment2"
android:name="com.zhf.android_fragmentdemo.FragmentFirst"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>主类MainActivity中不用添加其他代码,直接加载activity_main.xml即可。
效果图:
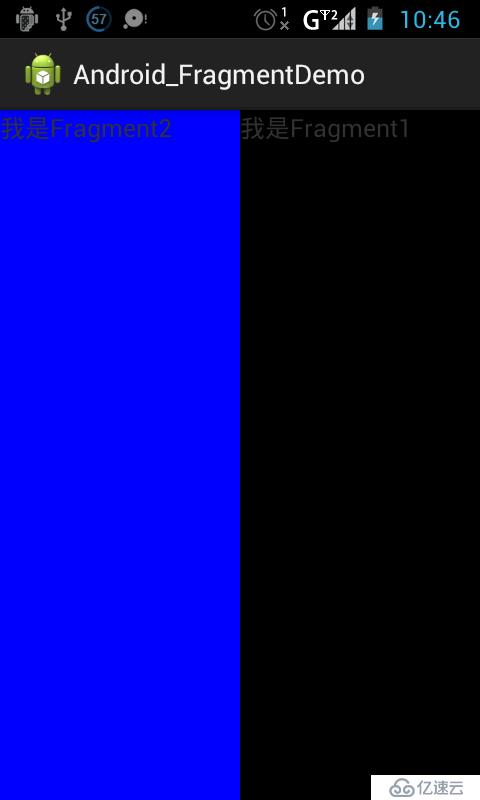
ok!简单三步就将fragment加载进去了,当然这只是fragment的一小部分功能,它的强大之处其实在于:Activity能够根据自身情况来动态的加载fragemnt,使你的UI界面变得更加多样可变!
2.动态加载:(重点)
首先,现将activity_main.xml中多余部分去掉:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/main_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
</LinearLayout> 其次,就是在MainActivity类中动态添加这两个Fragment类:
package com.zhf.android_fragmentdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Display;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
Display display = getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay();
if (display.getWidth() > display.getHeight()) {
FragmentFirst fragmentFirst = new FragmentFirst();
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.main_layout, fragmentFirst).commit();
} else {
FragmentSecond fragmentSecond = new FragmentSecond();
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.main_layout, fragmentSecond).commit();
}
}
}运行一下,效果出来了,为了体现出动态,大家可以试着把手机自动转屏打开,转一下屏试试!
 ----转屏之后--->
----转屏之后---> 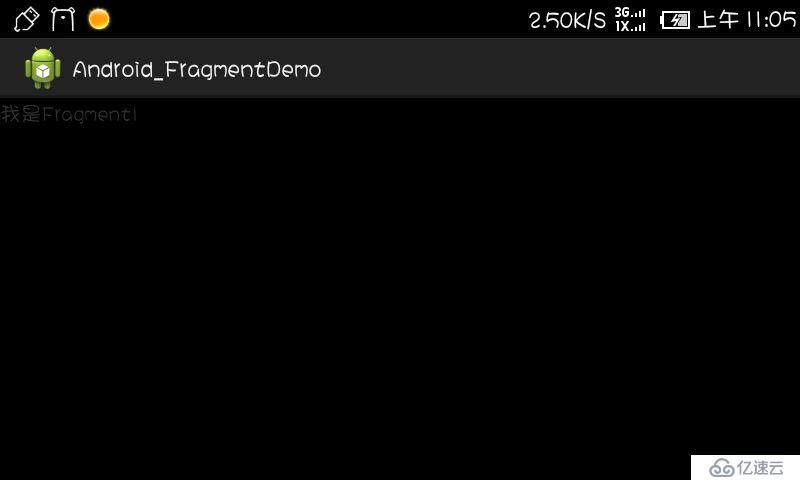
注:动态加载过程步骤
1.获取到FragmentManager,在Activity中可以直接通过getFragmentManager得到。
2.调用beginTransaction方法开启一个事务。
3.向容器内加入Fragment,一般使用replace方法实现,需要传入容器的id和Fragment的实例。
4.提交事务,调用commit方法提交。
介绍完这两种方式,大家是不是已经对其有了一些感性的认识,这里注意一下Fragment是在3.0版本引入的,如果你使用的是3.0之前的系统,需要先导入android-support-v4的jar包才能使用Fragment功能,这里可能需要继承FragmengActivity(现在建立低版本项目时,ADT会自动将libs下的android-support-v4.jar构建到项目路径)
接下来我们具体挖掘一下生命周期及其Fragment中一些主要方法的介绍!
二.Fragment类的生命周期
复写fragment中的方法,测试一下它的生命周期看看它与Activity的异同。
package com.zhf.android_fragmentdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* Fragment的生命周期
* 注意: 方法中的排列次序即为fragment全过程:启动时方法调用次序 + 退出时方法调用次序
* @author ZHF
*
*/
public class FragmentFirst extends Fragment {
/**Fragment和Activity建立关联的时候调用**/
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
super.onAttach(activity);
System.out.println("onAttach");
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
System.out.println("onCreate");
}
/**为Fragment加载布局时调用**/
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
System.out.println("onCreateView");
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false);
}
/**当Activity中的onCreate方法执行完后调用**/
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
System.out.println("onActivityCreated");
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
System.out.println("onStart");
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
System.out.println("onResume");
}
@Override
public void onPause() {
super.onPause();
System.out.println("onPause");
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
System.out.println("onStop");
}
/**Fragment中的布局被移除时调用**/
@Override
public void onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView();
System.out.println("onDestroyView");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("onDestroy");
}
/**Fragment和Activity解除关联的时候调用**/
@Override
public void onDetach() {
super.onDetach();
System.out.println("onDetach");
}
}打印结果:
1.运行一下:
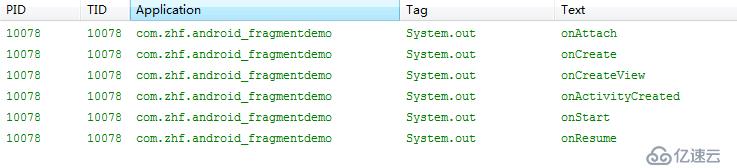
2.返回退出:
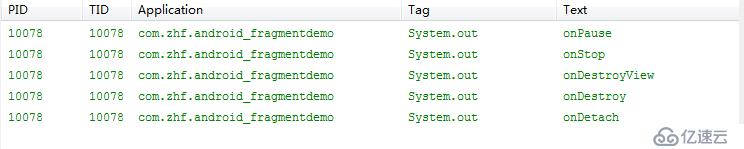
3.Home键退出:

4.再次进入:

通过打印的结果,我们应该可以清楚的了解到其实fragment和Activity的生命周期还是很相似的
(Activity生命周期博客:http://smallwoniu.blog.51cto.com/blog/3911954/1246732)
官网截图:
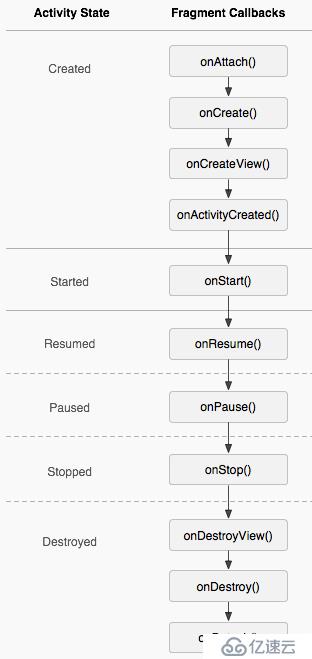
三.Fragment中有几个重要的回调方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
| onAttach() | Fragment和Activity建立关联的时候调用 |
| onCreateView() | 为Fragment加载布局时调用 |
| onActivityCreated() | 当Activity中的onCreate方法执行完后调用 |
| onDestroyView() | Fragment中的布局被移除时调用 |
| onDetach() | Fragment和Activity解除关联的时候调用 |
只有掌握了Fragment中这几个重要的方法,在使用的过程中才能更加灵活的与Activity配套使用,动态加载以适应不同屏幕分辨率的状况!
ok! 因为本人也是刚接触Fragment时间不长,这里也是查阅了许多的资料,简单总结了一番,方便以后查阅,希望能帮助到刚接触fragment的人。
在下一篇博客中我会使用Fragment+ViewPager写一个动态加载数据库的综合的案例,欢迎大家查阅!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。