您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
密码登录
登录注册
点击 登录注册 即表示同意《亿速云用户服务条款》
Tensorflow实现神经网络拟合线性回归?相信很多没有经验的人对此束手无策,为此本文总结了问题出现的原因和解决方法,通过这篇文章希望你能解决这个问题。
一、利用简单的一层神经网络拟合一个函数 y = x^2 ,其中加入部分噪声作为偏置值防止拟合曲线过拟合
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 生成-0.5到0.5间均匀发布的200个点,将数据变为二维,200行一列的数据
x_data = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, 200)[:, np.newaxis]
# 生成一些噪音数据
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.02, x_data.shape)
# 定义y与x的关系
y_data = np.square(x_data) + noise
# 定义两个占位符
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) # 形状为n行1列,同x_data的shape
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
# 定义神经网络
# 定义中间层,因为每个x是一维,所以只需1个神经元,定义中间层的连接神经元是10
# 矩阵:[a, b]×[b, c] = [a, c]
L1_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1, 10]))
L1_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 10]))
L1_weights_bias = tf.matmul(x, L1_weights) + L1_bias
L1 = tf.nn.tanh(L1_weights_bias)
# 定义输出层,每个x只有一个神经元
L2_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10, 1]))
L2_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 1]))
L2_weights_bias = tf.matmul(L1, L2_weights) + L2_bias
L2 = tf.nn.tanh(L2_weights_bias)
# 定义损失函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - L2))
# 梯度下降最小化损失函数
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1)
train_step = optimizer.minimize(loss)
# 全局变量初始化
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 定义会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for _ in range(2000):
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:x_data, y:y_data})
# 获取预测值
predict = sess.run(L2, feed_dict={x:x_data})
# 画图
plt.figure()
# 画出散点
plt.scatter(x_data, y_data)
# 画出拟合的曲线
plt.plot(x_data, predict)
plt.show()二、代码运行效果如下:
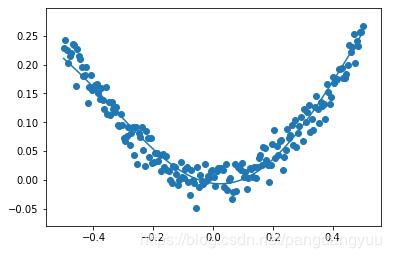
看完上述内容,你们掌握Tensorflow实现神经网络拟合线性回归的方法了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或想了解更多相关内容,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。