您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
小编这次要给大家分享的是SSM框架下如何实现登录注册,文章内容丰富,感兴趣的小伙伴可以来了解一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后能够有所收获。
基本配置:jdk1.8 tomcat 8 MyEclipse
先打好地基:
spring配置文件 application.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!-- 通过注解,将Service的生命周期纳入Spring的管理 --> <context:annotation-config /> <!-- 通过注解,将Service的生命周期纳入Spring的管理 --> <context:component-scan base-package="service"></context:component-scan> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <property name="driverClassName"> <value>com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver</value> </property> <property name="url"> <value>jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;DatabaseName=Organic </value> </property> <property name="username"> <value>sa</value> </property> <property name="password"> <value>123456</value> </property> </bean> <!-- 扫描存放SQL语句的Shop.xml --> <bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="pojo"></property> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> <property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml"></property> </bean> <!-- 扫描Mapper,并将其生命周期纳入Spring的管理 --> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <property name="basePackage" value="mapper"></property> </bean> <!--4.配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!--5.开启注解进行事务管理 transaction-manager:引用上面定义的事务管理器--> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> </beans>
springMVC配置文件 :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd">
<!-- 扫描Controller,并将其生命周期纳入Spring管理 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="controller">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
<!-- 注解驱动,以使得访问路径与方法的匹配可以通过注解配置 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!-- 静态页面,如html,css,js,images可以访问 -->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
<!-- 视图定位 -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass"
value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView" />
<property name="prefix" value="/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
</beans>web.xml 配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" version="2.5">
<display-name>OrganicShopWithSSM</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<!-- spring的配置文件-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- spring mvc核心:分发servlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- spring mvc的配置文件 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--配置由Spring 提供的针对中文乱码的编码过滤器 -->
<!-- 编码过滤器 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>开始第一层啦:
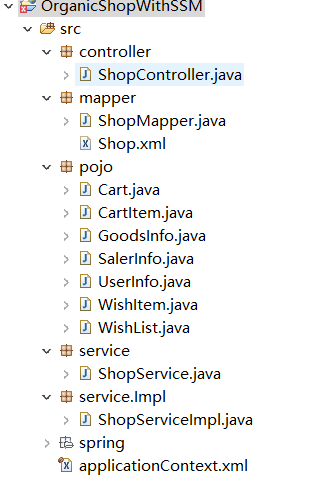
pojo包:UserInfo 类
package pojo;
public class UserInfo {
private String uid;
private String name;
private String email;
private String password;
public String getUid() {
return uid;
}
public void setUid(String uid) {
this.uid = uid;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserInfo [uid=" + uid + ", name=" + name + ", email="
+ email + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}mapper层:(注意mybatis的xml文件也要放在mapper层)
ShopMapping.java:
其中@Param注解 是为了和xml中的查询参数进行绑定
package mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import pojo.UserInfo;
public interface ShopMapper {
public void register(@Param("name")String name,@Param("email")String email,@Param("password")String password);
public UserInfo login(@Param("email")String email,@Param("password")String password);
public int findUser(@Param("email")String email);
}Shop.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="mapper.ShopMapper">
<select id="login" resultType="UserInfo" parameterType="String" >
select * from UserInfo where email=#{email} and password=#{password}
</select>
<select id="register" resultType="UserInfo">
insert into UserInfo(name,email,password) values (#{name},#{email},#{password})
</select>
<select id="findUser" resultType="int">
select count(*) from UserInfo where email=#{email}
</select>
</mapper>service层:其实在写登陆的时候用了int类型,在想登陆也只要在数据库中查询表单输入的数据就行了,在mapper层的xml的文件中也写了 select count(*) 查询个数, 但是结果并不好,因为我要做的还有设置session。
package service;
import pojo.UserInfo;
public interface ShopService {
//用户注册
void regist(String name,String email,String password);
//用户登录
UserInfo login(String email,String password);
//验证
int findUser(String email);
}service实现层:service.Impl
package service.Impl;
import mapper.ShopMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import pojo.UserInfo;
import service.ShopService;
@Service
public class ShopServiceImpl implements ShopService {
@Autowired
public ShopMapper sm;
@Override
public void regist(String name, String email, String password) {
sm.register(name, email, password);
}
@Override
public UserInfo login(String email, String password) {
UserInfo user=sm.login(email, password);
if(user!=null &&user.getPassword().equals(password)){
return user;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public int findUser(String email) {
if(sm.findUser(email)==0){
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
}controller层:
package controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import pojo.UserInfo;
import service.ShopService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("")
public class ShopController {
@Autowired
public ShopService ss;
@RequestMapping(value = "registerUser", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String registerUser(String name, String email, String password) {
int findUser = ss.findUser(email);
if (findUser == 0) {
ss.regist(name, email, password);
// System.out.println("可以注册");
return "login";
} else {
// System.out.println("注册失败");
return "register";
}
}
@RequestMapping(value = "loginUser", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String loginUser(UserInfo user, HttpSession session) {
// 调用service方法
user = ss.login(user.getEmail(), user.getPassword());
if (user != null) {
session.setAttribute("u".user);
return "index";
}
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping("/outLogin")
public String outLogin(HttpSession session){
session.invalidate();
return "index";
}
}在controller层当中,关于注册的格式要求还需要自行搜索一下,主要讲一下的是登陆。在登陆的这个方法中传递了两个形式参数,UserInfo是实体类,HttpSssion是设置session的关键,后面通过session.setAttribute()设置session,这也是在上文中提到的需要session的部分。在后来的注销中可以使用session.invalidate。
看完这篇关于SSM框架下如何实现登录注册的文章,如果觉得文章内容写得不错的话,可以把它分享出去给更多人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。