您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
小编这次要给大家分享的是Java中Stream流怎么实现合并操作,文章内容丰富,感兴趣的小伙伴可以来了解一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后能够有所收获。
1. 前言
Java Stream Api 提供了很多有用的 Api 让我们很方便将集合或者多个同类型的元素转换为流进行操作。今天我们来看看如何合并 Stream 流。
Stream 流合并的前提是元素的类型能够一致。
最简单合并流的方法是通过 Stream.concat() 静态方法:
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3); Stream<Integer> another = Stream.of(4, 5, 6); Stream<Integer> concat = Stream.concat(stream, another); List<Integer> collect = concat.collect(Collectors.toList()); List<Integer> expected = Lists.list(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); Assertions.assertIterableEquals(expected, collect);
这种合并是将两个流一前一后进行拼接:

多个流的合并我们也可以使用上面的方式进行“套娃操作”:
Stream.concat(Stream.concat(stream, another), more);
你可以一层一层继续套下去,如果需要合并的流多了,看上去不是很清晰。
我之前介绍过一个Stream 的 flatmap 操作 ,它的大致流程可以参考里面的这一张图:
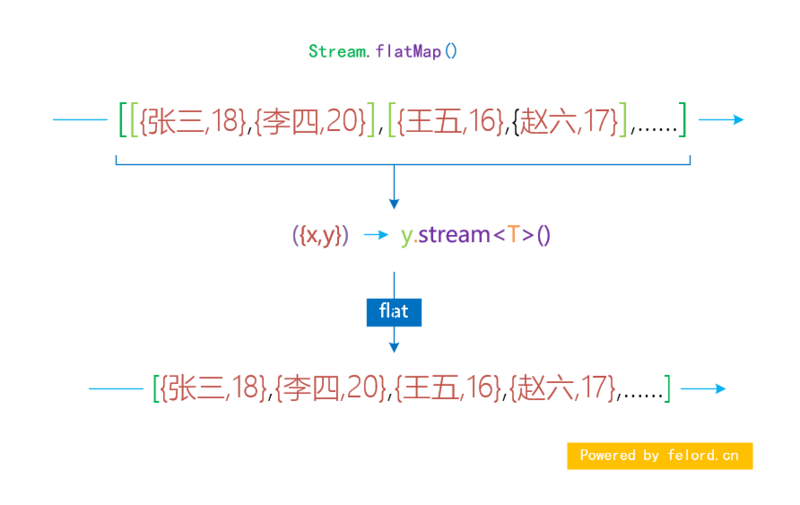
因此我们可以通过 flatmap 进行实现合并多个流:
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3); Stream<Integer> another = Stream.of(4, 5, 6); Stream<Integer> third = Stream.of(7, 8, 9); Stream<Integer> more = Stream.of(0); Stream<Integer> concat = Stream.of(stream,another,third,more). flatMap(integerStream -> integerStream); List<Integer> collect = concat.collect(Collectors.toList()); List<Integer> expected = Lists.list(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0); Assertions.assertIterableEquals(expected, collect);
这种方式是先将多个流作为元素生成一个类型为 Stream<Stream<T>> 的流,然后进行 flatmap 平铺操作合并。
有很多第三方的强化库 StreamEx 、Jooλ 都可以进行合并操作。另外反应式编程库 Reactor 3 也可以将 Stream 流合并为反应流,在某些场景下可能会有用。这里演示一下:
List<Integer> block = Flux.fromStream(stream)
.mergeWith(Flux.fromStream(another))
.collectList()
.block();看完这篇关于Java中Stream流怎么实现合并操作的文章,如果觉得文章内容写得不错的话,可以把它分享出去给更多人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。