您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
一、算法描述
波雷费密码是一种对称式密码,是首种双字母取代的加密法。
下面描述算法步骤:
1、从1号二维码M05,提取明文信息和密文,M05格式:<xxx…xxx|yyy…yyy>,其中明文xxx…xxx,密钥部分信息为yyy…yyy中的提取所有英文字母信息。
2、将提取的英文字母作密匙。除去重复出现的字母。将密匙的字母逐个逐个加入5×5的矩阵内,剩下的空间将未加入的英文字母依A-Z的顺序加入。(将Q去除)
3、将要加密的讯息分成两个一组。若组内的字母相同,将X加到该组的第一个字母后,重新分组。若剩下一个字,也加入X字。
4、在每组中,找出两个字母在矩阵中的地方。
若两个字母不同行也不同列,在矩阵中找出另外两个字母,使这四个字母成为一个长方形的四个角。
若两个字母同行,取这两个字母右方的字母(若字母在最右方则取最左方的字母)。
若两个字母同列,取这两个字母下方的字母(若字母在最下方则取最上方的字母)。
5、新找到的两个字母就是原本的两个字母加密的结果。
6、取密文前3个字符与后三个字符(大写字母)作为对应6位的红外报警开启码。
二、算法过程示例
例:二维码内容为:<hidethegold|play5fair9example>。
1.明文信息hidethegold和密匙playfairexample
2.根据密钥形成5*5的矩阵。
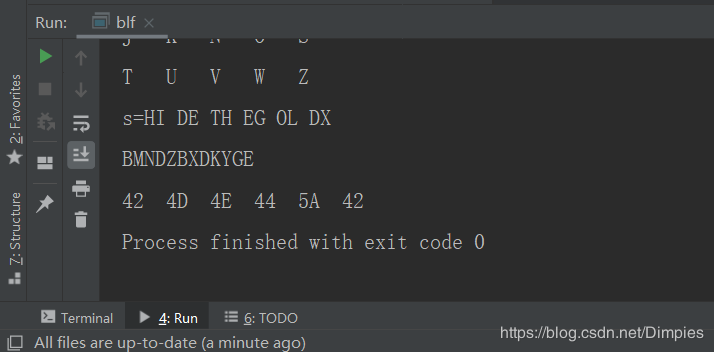
P L A Y F I R E X M B C D G H J K N O S T U V W Z
3.明文处理为:“HI DE TH EG OL DX”
4.就会得到密文:“BM ND ZB XD KY GE”,
5.取密文前6个字符(大写字母)对应6位的报警码:0X42,0X4D,0X4E,0X44, 0X5A, 0X42
三、具体代码如下:
import sun.applet.Main;
public class blf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "<hidethegold|play5fair9example>";
get_blf(s);
}
public static void get_blf(String ssss){
String eng = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPRSTUVWXYZ";
String beg = ssss.replaceAll("[<>0-9]", "");
String []ss = beg.split("\\|");
String mw = ss[0].toUpperCase();
String str = ss[1].toUpperCase();
str = removeMethod(str);
System.out.println(str);
int bs = str.length() / 5;
int ys = str.length() % 5;
System.out.println(ys);
System.out.println(bs);
char[][] arr = new char[5][5];
for (int i = 0; i < bs; i++) {
arr[i] = str.subSequence(i * 5, (i+1) * 5).toString().toCharArray();
}
String yss = str.subSequence(bs*5, (bs*5+ys)).toString();
String other = eng.replaceAll("["+ str +"]", "");
System.out.println("other=" + other);
arr[bs] = (yss + other.subSequence(0,(5-ys) )).toString().toCharArray();
int bs1 = bs + 1; //把余数补全
int oth = 25 - (bs1 * 5);//剩下的长度
other = other.subSequence((5 - ys), (oth + 5 - ys)).toString();
System.out.println("other=" + other);
int c = 5 - bs1;
System.out.println("c=" + c);
for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) {
System.out.println("bs1=" + bs1);
arr[bs1++] = other.subSequence(i * 5, (i+1) * 5).toString().toCharArray();
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
// arr[0] = one.toCharArray();
// arr[1] = two.toCharArray();
// arr[2] = three.toCharArray();
// arr[3] = four.toCharArray();
// arr[4] = five.toCharArray();
String s= "";
for (int i = 0; i < mw.length()-1; i = i + 2) {
if(mw.charAt(i) != mw.charAt(i+1)){
s += "" + mw.charAt(i) + mw.charAt(i + 1) + " ";
}
if(i == (mw.length() - 3)){
s += mw.charAt(i+2) + "X";
}
}
System.out.println("s="+s);
String []s1 = s.split(" ");
String s2 = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
s2 += resolve(arr,s1[i]);
}
System.out.println(s2);
String fin ="";
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
fin += s2.charAt(i);
}
byte[] br = fin.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < br.length; i++) {
System.out.print(decimalToHex(br[i]) + "\t");
}
}
public static String resolve(char[][] arr,String s1){
int a = 99;
int b = 99;
int a1 = 99;
int b1 = 99;
String res = "";
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
if((arr[i][j] == s1.charAt(0))){
a = i;
b = j;
}else if(arr[i][j] == s1.charAt(1)){
a1 = i;
b1 = j;
}
if((a != 99) && (b !=99) && (a1 !=99) && (b1 != 99)){
if(((a1 - a) !=0) && (((b1 - b) !=0))){
res = "" + arr[a][b1] + arr[a1][b];
}else if((a1 - a == 0) && (b1 - b != 0)){
if((b == 4)){
res = "" + arr[a][0] + arr[a1][b1+1];
}else if(b1 == 4){
res = "" + arr[a][b+1] + arr[a1][0];
}else{
res = "" + arr[a][b+1] + arr[a1][b1+1];
}
}else if((a1 - a !=0 ) && (b1 - b == 0)){
if((a == 4)){
res = "" + arr[0][b] + arr[a1+1][b1];
}else if(a1 == 4){
res = "" + arr[a+1][b] + arr[0][b1];
}else{
res = "" + arr[a+1][b] + arr[a1+1][b1];
}
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
public static String removeMethod(String s) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int len = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (s.indexOf(c) ==s.lastIndexOf(c)) {//此字符第一次位置和最后位置一致 即肯定没有重复的直接添加
sb.append(c);
} else {//同理 次字符出现过多次
int fristposition=s.indexOf(c);//次字符第一次出现的位置
if(fristposition==i){//第一次出现的位置和当前位置一致 即第一次出现添加
sb.append(c);
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static String decimalToHex(byte decimal) {
String hex = "";
while(decimal != 0) {
int hexValue = decimal % 16;
hex = toHexChar(hexValue) + hex;
decimal = (byte)(decimal / 16);
}
return hex;
}
//将0~15的十进制数转换成0~F的十六进制数
public static char toHexChar(int hexValue) {
if(hexValue <= 9 && hexValue >= 0)
return (char)(hexValue + '0');
else
return (char)(hexValue - 10 + 'A');
}
}
四、运行结果:
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持亿速云。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。