您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关Python爬虫中BeautifulSoup库剖析,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
BeautifulSoup 是一个可以从 HTML 或 XML 文件中提取数据的 Python 库,它能够将 HTML 或 XML 转化为可定位的树形结构,并提供了导航、查找、修改功能,它会自动将输入文档转换为 Unicode 编码,输出文档转换为 UTF-8 编码。
BeautifulSoup 支持 Python 标准库中的 HTML 解析器和一些第三方的解析器,默认使用 Python 标准库中的 HTML 解析器,默认解析器效率相对比较低,如果需要解析的数据量比较大或比较频繁,推荐使用更强、更快的 lxml 解析器。
1 安装
(1)BeautifulSoup 安装
如果使用 Debain 或 ubuntu 系统,可以通过系统的软件包管理来安装:apt-get install Python-bs4,如果无法使用系统包管理安装,可以使用 pip install beautifulsoup4 来安装。
(2)第三方解析器安装
如果需要使用第三方解释器 lxml 或 html5lib,可是使用如下命令进行安装:apt-get install Python-lxml(html5lib) 和 pip install lxml(html5lib)。
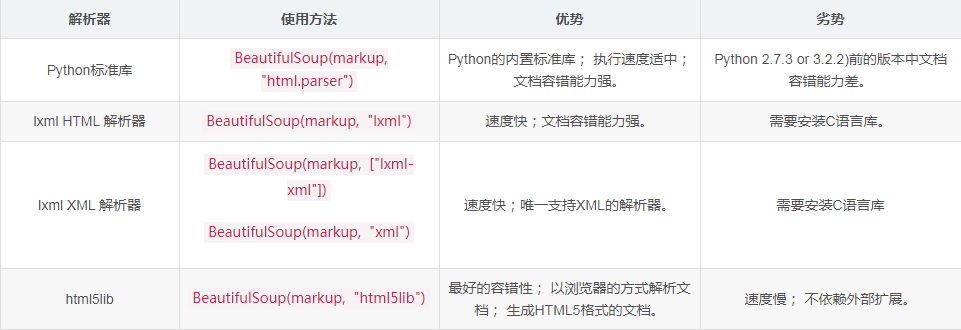
看一下主要解析器和它们的优缺点:
2 快速上手
将一段文档传入 BeautifulSoup 的构造方法,就能得到一个文档的对象,可以传入一段字符串或一个文件句柄,示例如下:
(1)使用字符串
我们以如下一段 HTML 字符串为例:
html = ''' <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>BeautifulSoup学习</title> </head> <body> Hello BeautifulSoup </body> </html> '''
使用示例如下:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #使用默认解析器 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser') #使用 lxml 解析器 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
(2)本地文件
还以上面那段 HTML 为例,将上面 HTML 字符串放在 index.html 文件中,使用示例如下:
#使用默认解析器
soup = BeautifulSoup(open('index.html'),'html.parser')
#使用 lxml 解析器
soup = BeautifulSoup(open('index.html'),'lxml')2.1 对象的种类
BeautifulSoup 将 HTML 文档转换成一个树形结构,每个节点都是 Python 对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种:Tag,NavigableString,BeautifulSoup,Comment。
(1)Tag 对象
Tag 对象与 HTML 或 XML 原生文档中的 tag 相同,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<title>BeautifulSoup学习</title>','lxml')
tag = soup.title
tp =type(tag)
print(tag)
print(tp)
#输出结果
'''
<title>BeautifulSoup学习</title>
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
'''Tag 有很多方法和属性,这里先看一下它的的两种常用属性:name 和 attributes。
我们可以通过 .name 来获取 tag 的名字,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<title>BeautifulSoup学习</title>','lxml')
tag = soup.title
print(tag.name)
#输出结果
#title我们还可以修改 tag 的 name,示例如下:
tag.name = 'title1' print(tag) #输出结果 #<title1>BeautifulSoup学习</title1>
一个 tag 可能有很多个属性,先看一它的 class 属性,其属性的操作方法与字典相同,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<title>BeautifulSoup学习</title>','lxml')
tag = soup.title
cls = tag['class']
print(cls)
#输出结果
#['tl']我们还可以使用 .attrs 来获取,示例如下:
ats = tag.attrs
print(ats)
#输出结果
#{'class': ['tl']}tag 的属性可以被添加、修改和删除,示例如下:
#添加 id 属性 tag['id'] = 1 #修改 class 属性 tag['class'] = 'tl1' #删除 class 属性 del tag['class']
(2)NavigableString 对象
NavigableString 类是用来包装 tag 中的字符串内容的,使用 .string 来获取字符串内容,示例如下:
str = tag.string
可以使用 replace_with() 方法将原有字符串内容替换成其它内容 ,示例如下:
tag.string.replace_with('BeautifulSoup')(3)BeautifulSoup 对象
BeautifulSoup 对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容,它并不是真正的 HTML 或 XML 的 tag,因此它没有 name 和 attribute 属性,为方便查看它的 name 属性,BeautifulSoup 对象包含了一个值为 [document] 的特殊属性 .name,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<title>BeautifulSoup学习</title>','lxml')
print(soup.name)
#输出结果
#[document](4)Comment 对象
Comment 对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,它会使用特殊的格式输出,看一下例子:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<title>Hello BeautifulSoup</title>','html.parser')
comment = soup.title.prettify()
print(comment)
#输出结果
'''
<title>
Hello BeautifulSoup
</title>
'''我们前面看的例子中 tag 中的字符串内容都不是注释内容,现在将字符串内容换成注释内容,我们来看一下效果:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<title><!--Hello BeautifulSoup--></title>','html.parser')
str = soup.title.string
print(str)
#输出结果
#Hello BeautifulSoup通过结果我们发现注释符号 <!----> 被自动去除了,这一点我们要注意一下。
2.2 搜索文档树
BeautifulSoup 定义了很多搜索方法,我们来具体看一下。
(1)find_all()
find_all() 方法搜索当前 tag 的所有 tag 子节点,方法详细如下:find_all(name=None, attrs={}, recursive=True, text=None,limit=None, **kwargs),来具体看一下各个参数。
name 参数可以查找所有名字为 name 的 tag,字符串对象会被自动忽略掉,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<title>Hello BeautifulSoup</title>','html.parser')
print(soup.find_all('title'))
#输出结果
#[<title>Hello BeautifulSoup</title>]attrs 参数定义一个字典参数来搜索包含特殊属性的 tag,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<title>Hello BeautifulSoup</title>','html.parser')
soup.find_all(attrs={"class": "tl"})调用 find_all() 方法时,默认会检索当前 tag 的所有子孙节点,通过设置参数 recursive=False,可以只搜索 tag 的直接子节点,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<html><head><title>Hello BeautifulSoup</title></head></html>','html.parser')
print(soup.find_all('title',recursive=False))
#输出结果
#[]通过 text 参数可以搜搜文档中的字符串内容,它接受字符串、正则表达式、列表、True,示例如下:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
soup = BeautifulSoup('<head>myHead</head><title>BeautifulSoup</title>','html.parser')
#字符串
soup.find_all(text='BeautifulSoup')
#正则表达式
soup.find_all(soup.find_all(text=re.compile('title')))
#列表
soup.find_all(soup.find_all(text=['head','title']))
#True
soup.find_all(text=True)limit 参数与 SQL 中的 limit 关键字类似,用来限制搜索的数据,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<a id="link1" href="http://example.com/elsie">Elsie</a><a id="link2" href="http://example
.com/elsie">Elsie</a>','html.parser')
soup.find_all('a', limit=1)我们经常见到 Python 中 *arg 和 **kwargs 这两种可变参数,*arg 表示非键值对的可变数量的参数,将参数打包为 tuple 传递给函数; **kwargs 表示关键字参数,参数是键值对形式的,将参数打包为 dict 传递给函数。
使用多个指定名字的参数可以同时过滤 tag 的多个属性,如:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<a id="link1" href="http://example.com/elsie">Elsie</a><a id="link2" href="http://example
.com/elsie">Elsie</a>','html.parser')
soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie"),id='link1')有些 tag 属性在搜索不能使用,如 HTML5 中的 data-* 属性,示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<div data-foo="value">foo!</div>')
soup.find_all(data-foo='value')首先当我在 Pycharm 中输入 data-foo='value' 便提示语法错误了,然后我不管提示直接执行提示 SyntaxError: keyword can't be an expression 这个结果也验证了 data-* 属性在搜索中不能使用。我们可以通过 find_all() 方法的 attrs 参数定义一个字典参数来搜索包含特殊属性的 tag,示例如下:
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'data-foo': 'value'}))(2)find()
方法详细如下:find(name=None, attrs={}, recursive=True, text=None,**kwargs),我们可以看出除了少了 limit 参数,其它参数与方法 find_all 一样,不同之处在于:find_all() 方法的返回结果是一个列表,find() 方法返回的是第一个节点,find_all() 方法没有找到目标是返回空列表,find() 方法找不到目标时,返回 None。来看个例子:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<a id="link1" href="http://example.com/elsie">Elsie</a><a id="link2" href="http://example
.com/elsie">Elsie</a>','html.parser')
print(soup.find_all('a', limit=1))
print(soup.find('a'))
#输出结果
'''
[<a href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>]
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>
'''从示例中我们也可以看出,find() 方法返回的是找到的第一个节点。
(3)find_parents() 和 find_parent()
find_all() 和 find() 用来搜索当前节点的所有子节点,find_parents() 和 find_parent() 则用来搜索当前节点的父辈节点。
(4)find_next_siblings() 和 find_next_sibling()
这两个方法通过 .next_siblings 属性对当前 tag 所有后面解析的兄弟 tag 节点进行迭代,find_next_siblings() 方法返回所有符合条件的后面的兄弟节点,find_next_sibling() 只返回符合条件的后面的第一个tag节点。
(5)find_previous_siblings() 和 find_previous_sibling()
这两个方法通过 .previous_siblings 属性对当前 tag 前面解析的兄弟 tag 节点进行迭代,find_previous_siblings() 方法返回所有符合条件的前面的兄弟节点,find_previous_sibling() 方法返回第一个符合条件的前面的兄弟节点。
(6)find_all_next() 和 find_next()
这两个方法通过 .next_elements 属性对当前 tag 之后的 tag 和字符串进行迭代,find_all_next() 方法返回所有符合条件的节点,find_next() 方法返回第一个符合条件的节点。
(7)find_all_previous() 和 find_previous()
这两个方法通过 .previous_elements 属性对当前节点前面的 tag 和字符串进行迭代,find_all_previous() 方法返回所有符合条件的节点,find_previous() 方法返回第一个符合条件的节点。
2.3 CSS选择器
BeautifulSoup 支持大部分的 CSS 选择器,在 Tag 或 BeautifulSoup 对象的 .select() 方法中传入字符串参数,即可使用 CSS 选择器的语法找到 tag,返回类型为列表。示例如下:
soup = BeautifulSoup('<body><a id="link1">Elsie</a><a id="link2">Elsie</a></body>','html.parser')
print(soup.select('a'))
#输出结果
#[<a clss="elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a clss="elsie" id="link2">Elsie</a>]通过标签逐层查找
soup.select('body a')找到某个 tag 标签下的直接子标签
soup.select('body > a')通过类名查找
soup.select('.elsie')
soup.select('[class~=elsie]')通过 id 查找
soup.select('#link1')使用多个选择器
soup.select('#link1,#link2')通过属性查找
soup.select('a[class]')通过属性的值来查找
soup.select('a[class="elsie"]')查找元素的第一个
soup.select_one('.elsie')查找兄弟节点标签
#查找所有
soup.select('#link1 ~ .elsie')
#查找第一个
soup.select('#link1 + .elsie')上述就是小编为大家分享的Python爬虫中BeautifulSoup库剖析了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。