您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
jdbc为java开发者使用数据库提供了统一的编程接口,它由一组java类和接口组成。
访问数据库的流程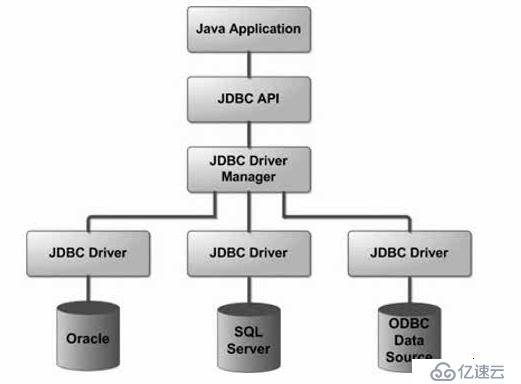
在连接这一过程中,一般初学者是MySQL和java在同一个电脑上,建立socket连接。
常用接口:- 一般针对java开发使用 Driver接口就行 ,- 在连接数据库时,需要装载特定厂商的数据驱动程序:
MySQL:Class.forname(‘com.mysql.jdbc.Driver’);
Oracle:Class.forname(‘oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver’);
建立连接:
@Test
public void getConnect(){
try {
//加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library";
String user="root";
String password="123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Statement
注意:这里Statement- 用于执行静态SQL语句并返回它所生成的结果对象,这里的Statement有三个类:
- Statement由createStatement创建,用于发送简单的SQL语句。(不带参)
- PreparedStatement:继承自Statement父类,由preparedStatement创建,用于发送含有一个或多个输入参数的SQL语句。PreparedStatement对象比Statement对象效率更高,并且可以防止SQL注入。
- CallableStatement:继承自PreparedStatement。由方法prePareCall创建,用于调用存储。
常用的Statement的方法有:
- execute():运行语句,返回是否有结果集
- executeQuery():运行select语句,返回ResultSet结果集
- executeUpdate():运行insert/update/delete操作,返回影响的行数
相关代码:
@Test
public void testStatement() throws SQLException {
//创建Statement
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql="select * from book";
boolean isNull= statement.execute(sql);
//创建PreparedStatement
sql="select * from book";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement1 = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement1.executeQuery();
//PreparedStatement防止SQL注入,这里的?表示占位符
sql="select * from book where bid = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement2 = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement2.setObject(1,2);
preparedStatement2.executeQuery();
}ResultSet
描述:ResultSet 主要是由executeQuery()方法执行返回
读取数据的流程图: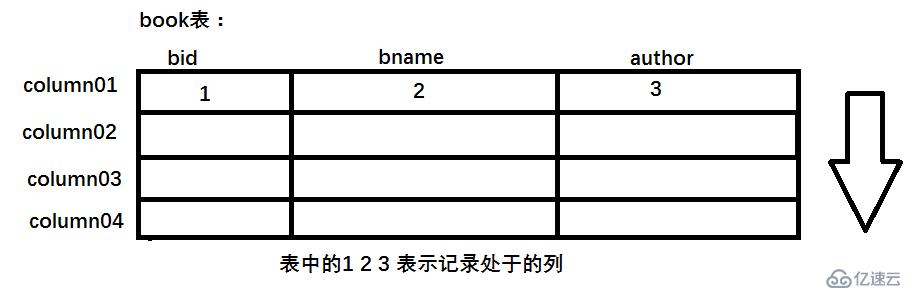
例:
@Test
public void testStatement() throws SQLException {
//创建PreparedStatement
String sql = "select * from book";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement1 = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement1.executeQuery();
while(resultSet.next()){ //表示是否还有下一个
System.out.println("bid"+resultSet.getInt(1));
System.out.println("bname"+resultSet.getString(2));
System.out.println("author"+resultSet.getString(3));
}
}jdbc的批处理
注意:如果使用大量的批处理时,建议使用statement,因为preparedstatement的预编译空间有限,当数据量特别大时,会发生异常。
例:
@Test
public void testStatement() throws SQLException {
//创建Statement
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
//获得当前的系统时间
long timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
String sql = "insert into t_date(t_time,t_id) values(" + timestamp + "," + i + ")";
//为批处理添加执行的SQL语句
statement.addBatch(sql);
}
//执行批处理
statement.executeBatch();
//提交事务
connection.commit();
}jdbc的事务
@Test
public void testTransaction() {
//取消自动提交
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//插入一条DML语句
PreparedStatement stetm1 = connection.prepareStatement("insert into book values(1001,'朝花夕拾','鲁迅')");
stetm1.execute();
//插入另条DML语句
PreparedStatement stetm2 = connection.prepareStatement("insert into book values(1001,'海贼王','尾田一郎')");
stetm2.execute();
//提交
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
try {
//失败后自动回滚
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}CLOB操作:
用于存储大量的文本数据,大字段的操作常常以流的方式处理。而非一般的字段一次读取即可。
//代码实现:
public class ReadAndWriteClob {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取数据库连接
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library",
"root",
"123456");
//clob字段插入
//表:user_info
//字段:name varchar , introduce clob
String sql = "insert into user_info values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement prepared1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//插入数据
prepared1.setObject(1, "user1");
//设置插入文本对象,第二个参数是一个输入流,直接读取文件
prepared1.setClob(2,new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("src/a.txt"))));
prepared1.execute();
//clob字段读取
sql="select * from user_info";
PreparedStatement prepared2 =conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = prepared2.executeQuery();
while(resultSet.next()){
Clob introduce = resultSet.getClob("introduce");
Reader characterStream = introduce.getCharacterStream();
int temp=0;
while((temp=characterStream.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)temp);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}BLOB操作:
用于存储大量的二进制数据,二进制可以存入任何类型的文件(音频、视频等等..)。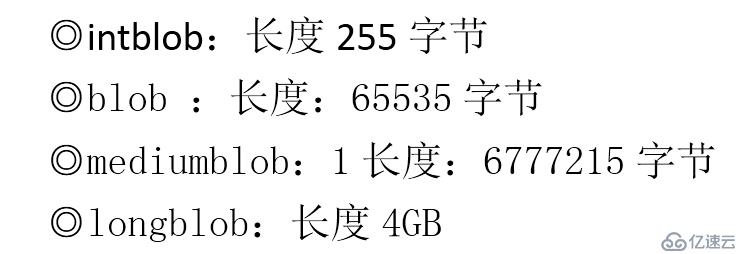
//代码实现
public class ReadAndWriteClob {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取数据库连接
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/library",
"root",
"123456");
//clob字段插入
//表:user_info
//字段:name varchar , headImg blob
String sql = "insert into user_info values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement prepared1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//插入数据
prepared1.setObject(1, "user1");
//设置插入图片对象,第二个参数是一个基本输入流
prepared1.setBlob(2,new FileInputStream("src/a.jpg"));
prepared1.execute();
//clob字段读取
sql="select * from user_info";
PreparedStatement prepared2 =conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = prepared2.executeQuery();
while(resultSet.next()){
Blob headImg = resultSet.getBlob("headImg");
//获取的是基本的流,
InputStream binaryStream = headImg.getBinaryStream();
int len=0;
byte flush []=new byte [1025];
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(new File("d:\\c.jpg"));
while((len=binaryStream.read(flush))!=-1){
os.write(flush,0,len);
os.flush();
}
os.close();
binaryStream.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}对jdbc的封装
这里需要加载配置文件:
代码实现:
public class jdbcUtils {
private static Properties pro;
static {
try {
pro = new Properties();
InputStream in = jdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbproperties.properties");
pro.load(in);
Class.forName(pro.getProperty("driver"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//建立与数据库的连接
public static Connection getMySQLConn(){
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(pro.getProperty("url"),
pro.getProperty("user"),
pro.getProperty("password"));
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 关闭顺序:resultSet --preparStatement -- Connection
* 在关闭时,不能讲这三者的close()写在同一个try{}catch{}中
*/
public static void close(Statement stem,ResultSet rs,Connection conn){
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stem!=null){
try {
stem.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。