您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
密码登录
登录注册
点击 登录注册 即表示同意《亿速云用户服务条款》
小编给大家分享一下怎么使用Java Stream API将List按自定义分组规则转换成Map,相信大部分人都还不怎么了解,因此分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大有收获,下面让我们一起去了解一下吧!
测试数据是List里的4个员工对象实例:
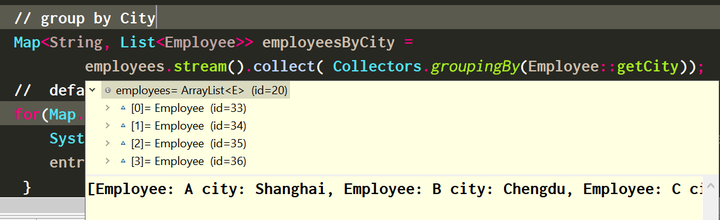
根据员工所在的城市进行分组:

结果分成了三组:
第一组的员工在上海:

第二组的员工在成都:

统计每组员工个数:


把员工进行分组,得分大于101分的在一组,小于等于101的在另一组:
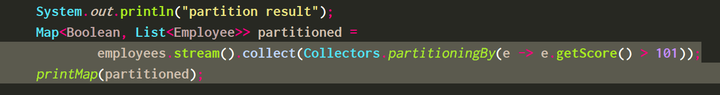
分组结果:

package java8;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Map.Entry;import java.util.function.Consumer;import java.util.stream.Collectors;class Employee {
private String city;
private String name;
private int score;
public Employee(String name, String city, int score){
this.city = city;
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
public String getCity(){
System.out.println("city: " + this.city);
return this.city;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public int getScore() {
return this.score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("Employee: " + this.name + " city: " + this.city);
}}class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("Person{name='%s', age=%d}", name, age);
}}// Jerry 2016-01-15 20:51PM ? 多用于extends generic的type,接受所有Object的sub classpublic class StreamTest {
private static void printMap(Map<? extends Object, ? extends Object> map) {
for(Entry<? extends Object, ? extends Object> entry:map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("key = " + entry.getKey() + " , Value = " + entry.getValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<Employee>();
employees.add(new Employee("A", "Shanghai",100));
employees.add(new Employee("B", "Chengdu",101));
employees.add(new Employee("C", "Shenzhen",102));
employees.add(new Employee("D", "Chengdu",104));
// group by City Map<String, List<Employee>> employeesByCity =
employees.stream().collect( Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getCity));
// default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) { for(Map.Entry<String, List<Employee>> entry:employeesByCity.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("key= " + entry.getKey() + " , Value = " + entry.getValue());
entry.getValue().forEach(System.out::println);
}
// 2016-01-15 20:37PM
Consumer<Employee> aa = a -> { System.out.println("Employee: " + a.getName() + " : " + a.getScore()); };
List<Employee> chengduEmployee = employeesByCity.get("Chengdu");
chengduEmployee.forEach(aa);
// test for counting Map<String, Long> employeesByCity2 =
employees.stream().collect( Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getCity, Collectors.counting()));
printMap(employeesByCity2);
// calculate average score Map<String, Double> employeesByCity3 =
employees.stream().collect( Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getCity,
Collectors.averagingInt(Employee::getScore)));
printMap(employeesByCity3);
/*Stream<Person> people = Stream.of(new Person("Paul", 24), new Person("Mark", 30), new Person("Will", 28)); Map<Integer, List<String>> peopleByAge = people.collect(groupingBy(p -> p.age, mapping((Person p) -> p.name, toList()))); System.out.println(peopleByAge);*/
/* * 分区是一种特殊的分组,结果 map 至少包含两个不同的分组——一个true,一个false。 * 例如,如果想找出最优秀的员工,你可以将所有雇员分为两组,一组销售量大于 N, * 另一组小于 N,使用 partitioningBy 收集器: */
System.out.println("partition result");
Map<Boolean, List<Employee>> partitioned =
employees.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(e -> e.getScore() > 101));
printMap(partitioned);
/* * 你也可以将 groupingBy 收集器传递给 partitioningBy 收集器来将联合使用分区和分组。例如,你可以统计每个分区中的每个城市的雇员人数: Map<Boolean, Map<String, Long>> result = employees.stream().collect(partitioningBy(e -> e.getNumSales() > 150, groupingBy(Employee::getCity, counting()))); 这样会生成一个二级 Map: {false={London=1}, true={New York=1, Hong Kong=1, London=1}} */
}}以上是“怎么使用Java Stream API将List按自定义分组规则转换成Map”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。