原创水平有限有误请指出
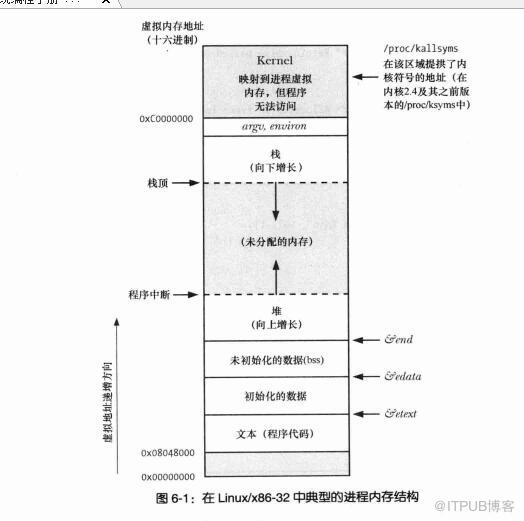
线程相比进程有着先天的数据共享的优势,如下图,线程共享了进程除栈区以外的所有内存区域如下图所示:
但是这种共享有时候也会带来问题,简单的考虑如下C++代码:
-
{
-
int b = 0;
-
b = a;
-
a = b+1;
-
return *this;
-
}
-
就是临界区代码
后面将对他们进行描述,这里我们简单实用静态互斥锁进行解决这个问题。
-
//原子操作 加锁
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
-
++test;
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
-
//原子操作 解锁
-
cout<<pthread_self() <<":";
-
test.prit()
实际上我们就是保护了操作符重载的
testc& operator++()
临界区的选择应该尽量小,避免对多线程的并发性产生较大的性能影响
具体代码如下:
-
/*************************************************************************
-
> File Name: error.cpp
-
> Author: gaopeng QQ:22389860 all right reserved
-
> Mail: gaopp_200217@163.com
-
> Created Time: Mon 15 May 2017 12:01:33 AM CST
-
************************************************************************/
-
-
#include<iostream>
-
#include <pthread.h>
-
#include <string.h>
-
#define MAXOUT 1000000
-
using namespace std;
-
-
static pthread_mutex_t mtx=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
-
-
-
class testc
-
{
-
private:
-
int a;
-
public:
-
testc()
-
{
-
a = 1;
-
}
-
testc& operator++()
-
{
-
int b = 0;
-
b = a;
-
a = b+1;
-
return *this;
-
-
}
-
void prit()
-
{
-
cout<<a<<endl;
-
}
-
};
-
-
-
testc test = test;
-
-
-
void* testp(void* arg)
-
{
-
int i = MAXOUT;
-
-
while(i--)
-
{
-
//原子操作 加锁
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
-
++test;
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
-
//原子操作 解锁
-
cout<<pthread_self() <<":";
-
test.prit();
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
int main(void)
-
{
-
pthread_t tid[3];
-
int er;
-
int i = 0;
-
-
while(i<3)
-
{
-
-
if ((er = pthread_create(tid+i,NULL,testp,NULL) )!=0 )
-
{
-
strerror(er);
-
return -1;
-
}
-
i++;
-
}
-
-
i = 0;
-
-
while(i<3)
-
{
-
pthread_join(*(tid+i),NULL);
-
i++;
-
}
-
cout<<"last numer: ";
-
test.prit();
-
}
注意:一个简单类型的i++也不一定是一个原子操作,所以在涉及到并发修改共享变量的时候一定要使用
线程同步手段。
作者微信:

免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。

