您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关JavaScript的offset、client、scroll家族属性是什么,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。
偏移量(offset dimension)是javascript中的一个重要的概念。涉及到偏移量的主要是offsetLeft、offsetTop、offsetHeight、offsetWidth这四个属性。当然,还有一个偏移参照——定位父级offsetParent。本文将详细介绍该部分内容
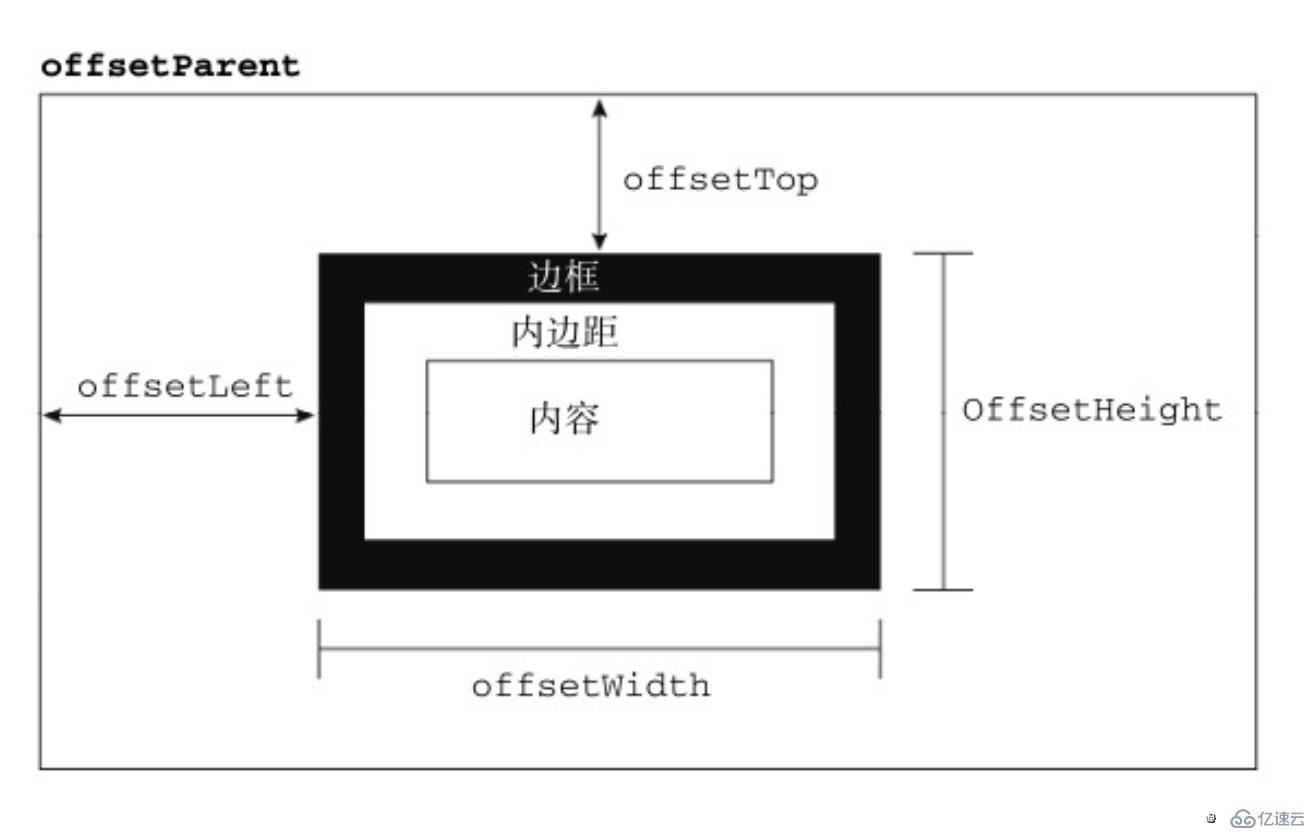
在理解偏移大小之前,首先要理解offsetParent。人们并没有把offsetParent翻译为偏移父级,而是翻译成定位父级,很大原因是offsetParent与定位有关
定位父级offsetParent的定义是:与当前元素最近的经过定位(position不等于static)的父级元素,主要分为下列几种情况
元素自身有fixed定位,offsetParent的结果为null
当元素自身有固定定位时,我们知道固定定位的元素相对于视口进行定位,此时没有定位父级,offsetParent的结果为null
[注意]firefox浏览器有兼容性问题
<p id="test" style="position:fixed"></p> <script>
var test = document.getElementById('test'); //firefox并没有考虑固定定位的问题,返回<body>,其他浏览器都返回null
console.log(test.offsetParent);</script>复制代码<p id="test"></p> <script>
var test = document.getElementById('test'); console.log(test.offsetParent);//<body></script>复制代码<p id="grandfather" style="position: relative;">
<p id="father" >
<p id="test"></p>
</p></p><script type="text/javascript">
var test = document.getElementById('test'); // 距离该子元素最近的进行过定位的父元素,如果其父元素不存在定位则offsetParent为:body元素;
console.log(test.offsetParent);</script>复制代码<body>元素的offsetParent是nullconsole.log(document.body.offsetParent);//null复制代码
偏移量共包括了offsetHeight、offsetWidth、offsetLeft、offsetTop这四个属性
offsetWidth表示元素在水平方向上占用的空间大小,无单位(以像素px计)
offsetWidth = border-left-width + padding-left + width + padding-right + border-right-width; 复制代码
offsetHeight表示元素在垂直方向上占用的空间大小,无单位(以像素px计)
offsetHeight = border-top-width + padding-top + height + padding-bottom + border-bottom-width复制代码
测试:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#box { width: 200px; height: 150px; background-color: red; padding: 10px; border: 5px solid #ddd; margin: 10px;
} </style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="box" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;"></p>
<script>
var box = document.getElementById('box'); //offsetHeight = 内容高 + 上下内边距 + 边框
console.log(box.offsetWidth,box.offsetHeight); console.log(box.style.width, box.style.height); // 可以设置大小
// box.style.width = 500 + 'px';
// 不可以设置大小
box.offsetWidth = 100 + 'px'; </script>
</body></html>复制代码注意:如果想修改盒子的大小,请使用xxx.style.width进行设置。offsetWidth和offsetHeight是只读属性
offsetTop表示元素的上外边框至offsetParent元素的上内边框之间的像素距离
offsetLeft表示元素的左外边框至offsetParent元素的左内边框之间的像素距离
测试:
<!DOCTYPE html><html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*{ padding: 0; margin: 0;
} #father{ width: 400px; height: 400px; background-color: red; /* position: relative; */
margin: 40px;
} #son { width: 200px; height: 100px; background-color: green; padding: 10px; border: 5px solid #DA70D6; margin-left: 20px;
} </style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="father">
<p id="son"></p>
</p>
<script type="text/javascript">
var box = document.getElementById('son'); //如果有父级定位元素
console.log(box.offsetLeft);//20
console.log(box.offsetTop); //0
//如果无父级定位元素
console.log(box.offsetLeft);//60
console.log(box.offsetTop); //40
</script>
</body></html>复制代码总结:相对于父元素(看父元素是否有定位,如果有定位,以父元素为基础,如果没有继续往上寻找,如果一直没有找到,则以body为基准)的左边距和上边距
要知道某个元素在页面上的偏移量,将这个元素的offsetLeft和offsetTop与其offsetParent的相同属性相加,并加上offsetParent的相应方向的边框,如此循环直到根元素,就可以得到元素到页面的偏移量
<p style="padding: 20px;border:1px solid black;position:absolute;">
<p id="test" style="width:100px; height:100px; margin:10px;background-color: red;"></p></p><script type="text/javascript">
var test = document.getElementById('test'); console.log(getElementLeft(test)); //39px
console.log(getElementTop(test)); // 39px
function getElementLeft(ele){ var actualLeft = ele.offsetLeft; var parent = ele.offsetParent; while (parent != null){
actualLeft = actualLeft + parent.offsetLeft + parent.clientLeft;
parent = parent.offsetParent;
} return actualLeft + 'px';
} function getElementTop(ele){ var actualTop = ele.offsetTop; var parent = ele.offsetParent; while (parent != null){
actualTop = actualTop + parent.offsetTop + parent.clientTop;
parent = parent.offsetParent;
} return actualTop + 'px';
}</script>复制代码关于元素尺寸,一般地,有偏移大小offset、客户端大小client和滚动大小scroll。前文已经介绍过偏移属性,后文将介绍scroll滚动大小,本文主要介绍客户区大小client。
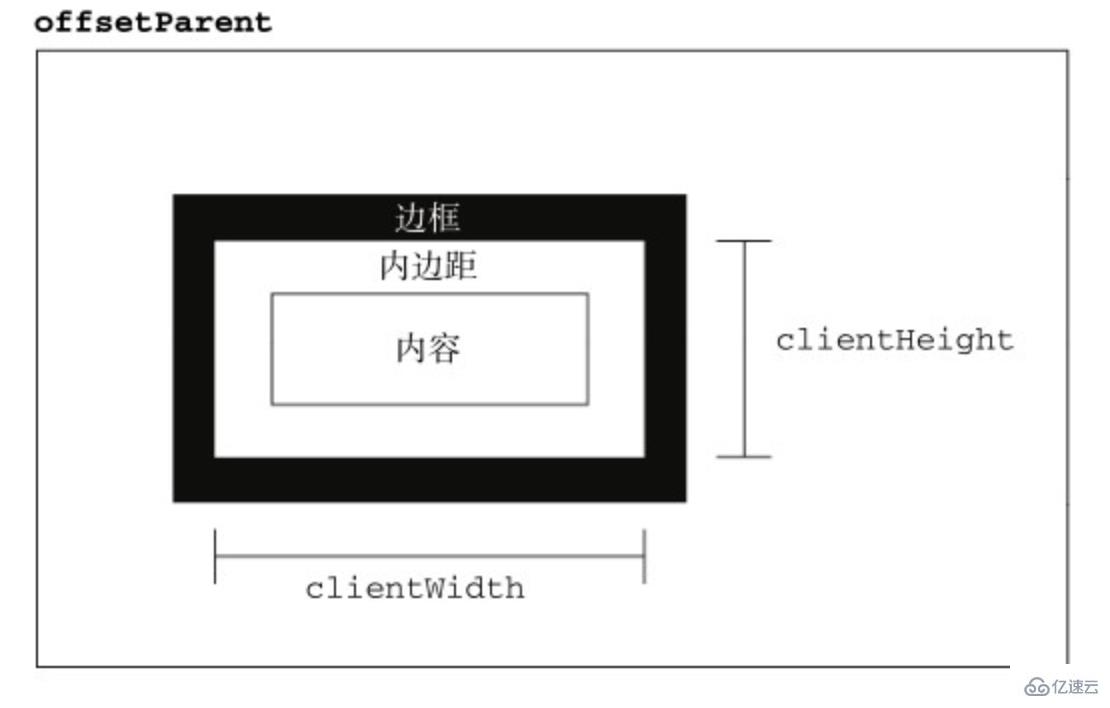
客户区大小client指的是元素内容及其内边距所占据的空间大小
clientHeight属性返回元素节点的客户区高度
clientHeight = padding-top + height + padding-bottom复制代码
clientWidth属性返回元素节点的客户区宽度
clientWidth = padding-left + width + padding-right复制代码
clientLeft属性返回左边框的宽度复制代码
clientTop属性返回上边框的宽度 复制代码
验证
<p id="box" style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: red; padding: 20px;border: 1px solid orange;"></p><script type="text/javascript">
var box = document.getElementById('box'); console.log(box.clientWidth);// 200+ 20+ 20 = 240
console.log(box.clientHeight); //200 + 20 + 20 = 240
console.log(box.clientLeft);//1
console.log(box.clientTop);//1</script>复制代码常用document.documentElement的client属性来表示页面大小(不包含滚动条宽度)
document.documentElement.clientWidth;document.documentElement.clientHeight;复制代码
1.所有的client属性都是只读的
<p id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;padding: 10px;margin: 10px;border: 1px solid black;"></p><script>
var test = document.getElementById('test'); console.log(test.clientHeight); //静态失败了
test.clientHeight = 10; console.log(test.clientHeight);</script>复制代码2.如果给元素设置了display:none,则客户区client属性都为0
<p id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;padding: 10px;margin: 10px;border: 1px solid black;display:none;"></p><script>
var test = document.getElementById('test'); console.log(test.clientHeight);//0
console.log(test.clientTop);//0</script>复制代码3.每次访问客户区client属性都需要重新计算,重复访问需要耗费大量的性能,所以要尽量避免重复访问这些属性。如果需要重复访问,则把它们的值保存在变量中,以提高性能
<p id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;padding: 10px;margin: 10px;border: 1px solid black;"></p> <script>
var test = document.getElementById('test'); console.time("time"); for(var i = 0; i < 100000; i++){ var a = test.clientHeight;
} console.timeEnd('time');//66.798ms</script>复制代码<p id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;padding: 10px;margin: 10px;border: 1px solid black;"></p>
<script>
var test = document.getElementById('test');
console.time("time");
var a = test.clientHeight;
for(var i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
var b = a;
}
console.timeEnd('time');//1.705ms
</script>复制代码scrollHeight
scrollHeight表示元素的总高度,包括由于溢出而无法展示在网页的不可见部分
scrollWidth
scrollWidth表示元素的总宽度,包括由于溢出而无法展示在网页的不可见部分
没有滚动条时,scrollHeight与clientHeight属性结果相等,scrollWidth与clientWidth属性结果相等
<p id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;padding: 10px;margin: 10px;border: 1px solid black;"></p><script>
var test = document.getElementById('test'); //120 120
console.log(test.scrollHeight,test.scrollWidth); //120 120
console.log(test.clientHeight,test.clientWidth);</script>复制代码存在滚动条时,但元素设置宽高大于等于元素内容宽高时,scroll和client属性的结果相等
<p id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;padding: 10px;margin: 10px;border: 1px solid black;"></p><script>
var test = document.getElementById('test'); //120 120
console.log(test.scrollHeight,test.scrollWidth); //120 120
console.log(test.clientHeight,test.clientWidth);</script>复制代码scrollTop
scrollTop属性表示被隐藏在内容区域上方的像素数。元素未滚动时,scrollTop的值为0,如果元素被垂直滚动了,scrollTop的值大于0,表示元素上方不可见内容的像素高度
scrollLeft
scrollLeft属性表示被隐藏在内容区域左侧的像素数。元素未滚动时,scrollLeft的值为0,如果元素被水平滚动了,scrollLeft的值大于0,且表示元素左侧不可见内容的像素宽度
当滚动条滚动到内容底部时,符合以下等式
scrollHeight = scrollTop + clientHight复制代码
与scrollHeight和scrollWidth属性不同的是,scrollLeft和scrollTop是可写的
<p id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;padding: 10px;margin: 10px;border: 1px solid black;overflow:scroll;font-size:20px;line-height:200px;">
内容<br>内容<br></p><button id="btn1">向下滚动</button><button id="btn2">向上滚动</button><script type="text/javascript">
// scrollLeft和scrollTop是可读写的
var btn1 = document.getElementById('btn1'); var btn2 = document.getElementById('btn2');
btn1.onclick = function (){
test.scrollTop += 10;
}
btn2.onclick = function (){
test.scrollTop -= 10;
}</script>复制代码理论上,大部分的浏览器通过document.documentElement.scrollTop和scrollLeft可以反映和控制页面的滚动;safari浏览器是通过document.body.scrollTop和scrollLeft来控制的
<body style="height: 2000px;width: 2000px;">
<p id="test" style="width: 100px;height: 100px;padding: 10px;margin: 10px;border: 1px solid black;overflow:scroll;font-size:20px;line-height:200px;">
内容<br>内容<br>
</p>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 页面滚动
window.onscroll = function (){ console.log(document.documentElement.scrollTop,document.documentElement.scrollLeft); console.log(document.body.scrollTop,document.body.scrollLeft);
} </script></body>复制代码所以,页面的滚动高度兼容写法是
var docScrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop复制代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body style="height: 2000px;">
<button id="backTop" style="position: fixed;">回到顶部</button>
<script type="text/javascript">
var backTop = document.getElementById('backTop');
backTop.onclick = scrollTop; function scrollTop(){ //兼容性写法
if(document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop){ document.documentElement.scrollTop = document.body.scrollTop = 0;
}
} </script>
</body></html>复制代码scrollTo(x,y)
scrollTo(x,y)方法滚动当前window中显示的文档,让文档中由坐标x和y指定的点位于显示区域的左上角
<body style="height: 2000px;">
<button id="backTop" style="position: fixed;">回到顶部</button>
<script src="scrollTop.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var backTop = document.getElementById('backTop');
backTop.onclick = scrollTop; function scrollTop(){
scrollTo(0,0);
} </script></body>复制代码关于JavaScript的offset、client、scroll家族属性是什么就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。