您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章主要介绍“如何理解基于自定义Unity生存期模型PerCallContextLifeTimeManager的问题”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在如何理解基于自定义Unity生存期模型PerCallContextLifeTimeManager的问题问题上存在疑惑,小编查阅了各式资料,整理出简单好用的操作方法,希望对大家解答”如何理解基于自定义Unity生存期模型PerCallContextLifeTimeManager的问题”的疑惑有所帮助!接下来,请跟着小编一起来学习吧!
PerThreadLifetimeManager的问题
使用Unity内置的PerThreadLifetimeManager生存期模型时,其基于ThreadStatic的TLS(Thread Local Storage)设计,也就是说对于每个托管的ManagedThreadId,其会缓存已生成的对象实例。
由于CLR维护了托管线程池,使用过的线程并不会立即销毁,在需要的时候会继续复用。在类似ASP.NET PerCall或WCF PerCall条件下,当Call1在线程ManagedThreadId1中处理完毕后,Call2发生,而Call2很有可能也在线程ManagedThreadId1中处理。这种条件下Call2会自动复用处理Call1时生成并缓存的对象实例。
如果我们希望每次调用(PerCall)都生成专用的对象实例,则PerThreadLifetimeManager在此种场景下不适合。
解决办法有两种:
1.继续使用PerThreadLifetimeManager模型,不适用ThreadPool,而手动创建和销毁线程。
2.自定义对象生存期模型
PerCallContextLifeTimeManager
复制代码 代码如下:
public class PerCallContextLifeTimeManager : LifetimeManager
{
private string _key =
string.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture,
"PerCallContextLifeTimeManager_{0}", Guid.NewGuid());
public override object GetValue()
{
return CallContext.GetData(_key);
}
public override void SetValue(object newValue)
{
CallContext.SetData(_key, newValue);
}
public override void RemoveValue()
{
CallContext.FreeNamedDataSlot(_key);
}
}
使用举例
复制代码 代码如下:
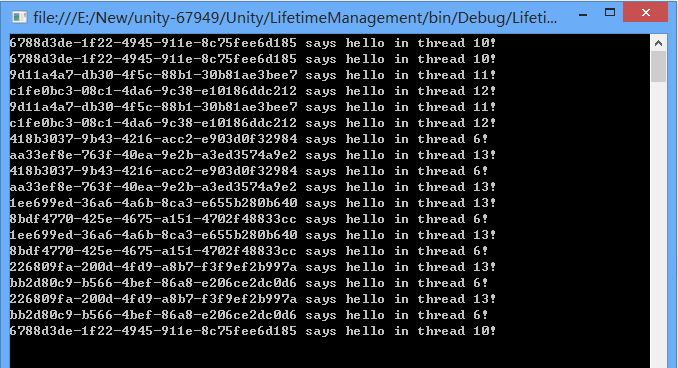
private static void TestPerCallContextLifeTimeManager()
{
IExample example;
using (IUnityContainer container = new UnityContainer())
{
container.RegisterType(typeof(IExample), typeof(Example),
new PerCallContextLifeTimeManager());
container.Resolve<IExample>().SayHello();
container.Resolve<IExample>().SayHello();
Action<int> action = delegate(int sleep)
{
container.Resolve<IExample>().SayHello();
Thread.Sleep(sleep);
container.Resolve<IExample>().SayHello();
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread((a) => action.Invoke((int)a));
Thread thread2 = new Thread((a) => action.Invoke((int)a));
thread1.Start(50);
thread2.Start(55);
thread1.Join();
thread2.Join();
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((a) => action.Invoke((int)a), 50);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((a) => action.Invoke((int)a), 55);
Thread.Sleep(100);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((a) => action.Invoke((int)a), 50);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((a) => action.Invoke((int)a), 55);
Thread.Sleep(100);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((a) => action.Invoke((int)a), 50);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((a) => action.Invoke((int)a), 55);
Thread.Sleep(100);
example = container.Resolve<IExample>();
}
example.SayHello();
Console.ReadKey();
}
到此,关于“如何理解基于自定义Unity生存期模型PerCallContextLifeTimeManager的问题”的学习就结束了,希望能够解决大家的疑惑。理论与实践的搭配能更好的帮助大家学习,快去试试吧!若想继续学习更多相关知识,请继续关注亿速云网站,小编会继续努力为大家带来更多实用的文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。