您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
The following table documents Unix and Linux kernel parameters that should be monitored and possibly increased after changes are made to the related init.ora parameter. Please check with your Operating System documentation for specific details on the parameter changes. 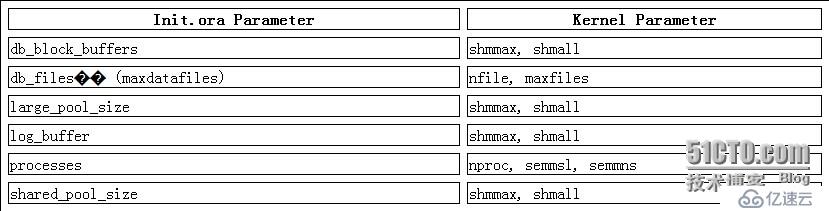 Common Kernel Parameter Definitions
Common Kernel Parameter Definitions
The following Kernel Parameters tend to be generic across most Unix and Linux platforms. However, their names may be different on your platform. Consult your Installation and Configuration Guide (ICG) for the exact names.
maxfiles - Soft file limit per process.
maxuprc - Maximum number of simultaneous user processes per userid.
nfile - Maximum number of simultaneously open files systemwide at any given time.
nproc - Maximum number of processes that can exist simultaneously in the system.
shmall - This parameter sets the total amount of shared memory pages that can be used system wide. Hence, shmall should always be at least ceil(shmmax/page_size)。##单位为页。
shmmax - The maximum size(in bytes) of a single shared memory segment。##至少为物理内存一半。
shmmin - The minimum size(in bytes) of a single shared memory segment.
shmmni - The number of shared memory identifiers.
shmseg - The maximum number of shared memory segments that can be attached by a process.
semmns - The number of semaphores in the system.
semmni - The number of semaphore set identifiers in the system; determines the number of semaphore sets that can be created at any one time.
semmsl - The maximum number of sempahores that can be in one semaphore set. It should be same size as maximum number of Oracle processes.
SHMMAX - kernel parameter controlling maximum size of one shared memory
segment
32-bit Linux Systems
Maximum: A value that is 1 byte less than 4 GB, or 4294967295
Recommended: More than half the physical memory
64-bit Linux Systems
Maximum: A value that is 1 byte less than the physical memory
Recommended: More than half the physical memory
See My Oracle Support Note 567506.1(见附件) for additional information about configuring shmmax.
SHMMNI - kernel parameter controlling maximum number of shared memory segments
in the system
SHMSEG - kernel parameter controlling maximum number of shared memory segments
a process can attach
SEMMNS - kernel parameter controlling maximum number of semphores in
the system
SEMMNI - kernel parameter controlling maximum number of semaphore
sets. Semphores in Unix are allocated in sets of 1 to SEMMSL.
SEMMSL - kernel parameter controlling maximum number of semaphores in a
semphore set.
SHMLBA - kernel parameter controlling alignment of shared memory
segments; all segments must be attached at multiples of this value.
Typically, non-tunable.
What is the maximum value of SHMMAX for a 32-bit (x86) Linux system?
Oracle Global Customer Support officially recommends a " maximum" for SHMMAX of just less than 4Gb, or 4294967295.
The maximum size of a shared memory segment is limited by the size of the available user address space. On 32-bit systems, this is a theoretical 4GB. The maximum possible value for SHMMAX is just less than 4Gb, or 4294967295. Setting SHMMAX to 4GB exactly will give you 0 bytes as max, as this value is interpreted as a 32-bit number and it wraps around.
What is the maximum value of SHMMAX for a 64-bit (x86-64) Linux system?
Oracle Global Customer Support officially recommends a " maximum" for SHMMAX of "1/2 of physical RAM".
The maximum size of a shared memory segment is limited by the size of the available user address space. On 64-bit systems, this is a theoretical 2^64bytes. So the "theoretical limit" for SHMMAX is the amount of physical RAM that you have. However, to actually attempt to use such a value could potentially lead to a situation where no system memory is available for anything else. Therefore a more realistic "physical limit" for SHMMAX would probably be "physical RAM - 2Gb".
In an Oracle RDBMS application, this "physical limit" still leaves inadequate system memory for other necessary functions. Therefore, the common "Oracle maximum" for SHMMAX that you will often see is "1/2 of physical RAM". Many Oracle customers chose a higher fraction, at their discretion.
Occasionally, Customers may erroneously think that that setting the SHMMAX as recommended in this NOTE limits the total SGA. That is not true. Setting the SHMMAX as recommended only causes a few more "shared memory segments" to be used for whatever total SGA that you subsequently configure in Oracle. For additional detail, please see
Document 15566.1, "SGA, SHMMAX, Semaphores and Shared Memory Explained"
Also to be taken into consideration for memory configuration is the kernel parameter for kernel.shmall which is the total amount of shared memory, in pages, that the system can use at one time. Review:
Document 301830.1 Upon startup of Linux database get ORA-27102: out of memory Linux-X86_64 Error: 28: No space left on device
摘自
Relationship Between Common Init.ora Parameters and Unix, Linux Kernel Parameters (文档 ID 144638.1)
Maximum SHMMAX values for Linux x86 and x86-64 (文档 ID 567506.1)
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。