您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有关elasticsearch Client怎么在golang中使用,可能很多人都不太了解,为了让大家更加了解,小编给大家总结了以下内容,希望大家根据这篇文章可以有所收获。
golang 是Google开发的一种静态强类型、编译型、并发型,并具有垃圾回收功能的编程语言,其语法与 C语言相近,但并不包括如枚举、异常处理、继承、泛型、断言、虚函数等功能。
elasticsearch 的client ,通过 NewClient 建立连接,通过 NewClient 中的 Set.URL设置访问的地址,SetSniff设置集群
获得连接 后,通过 Index 方法插入数据,插入后可以通过 Get 方法获得数据(最后的测试用例中会使用 elasticsearch client 的Get 方法)
func Save(item interface{}) {
client, err := elastic.NewClient(
elastic.SetURL("http://192.168.174.128:9200/"),
// Must turn off sniff in docker
elastic.SetSniff(false),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
resp, err := client.Index().
Index("dating_profile").
Type("zhenai").
BodyJson(item).
Do(context.Background()) //contex需要context 包
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%+v", resp)
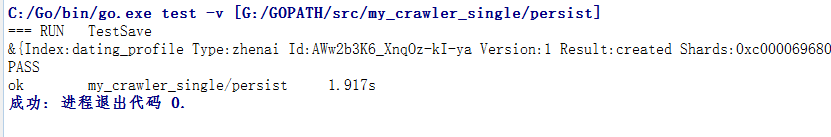
}func TestSave(t *testing.T) {
profile := model.Profile{
Age: 34,
Height: 162,
Weight: 57,
Income: "3001-5000元",
Gender: "女",
Name: "安静的雪",
XingZuo: "牡羊座",
Occupation: "人事/行政",
Marriage: "离异",
House: "已购房",
Hukou: "山东菏泽",
Education: "大学本科",
Car: "未购车",
}
Save(profile)
}
我们在test中panic,在函数中讲错误返回。在从elastisearch中 取出存入的数据,与我们定义的数据进行比较,
func Save(item interface{}) (id string, err error) {
client, err := elastic.NewClient(
elastic.SetURL("http://192.168.174.128:9200/"),
// Must turn off sniff in docker
elastic.SetSniff(false),
)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
resp, err := client.Index().
Index("dating_profile").
Type("zhenai").
BodyJson(item).
Do(context.Background())
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return resp.Id, nil
}package persist
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"my_crawler_single/model"
"testing"
elastic "gopkg.in/olivere/elastic.v5"
)
func TestSave(t *testing.T) {
expected := model.Profile{
Age: 34,
Height: 162,
Weight: 57,
Income: "3001-5000元",
Gender: "女",
Name: "安静的雪",
XingZuo: "牡羊座",
Occupation: "人事/行政",
Marriage: "离异",
House: "已购房",
Hukou: "山东菏泽",
Education: "大学本科",
Car: "未购车",
}
id, err := Save(expected)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
client, err := elastic.NewClient(
elastic.SetURL("http://192.168.174.128:9200/"),
elastic.SetSniff(false),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
resp, err := client.Get().
Index("dating_profile").
Type("zhenai").
Id(id). //查找指定id的那一条数据
Do(context.Background())
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
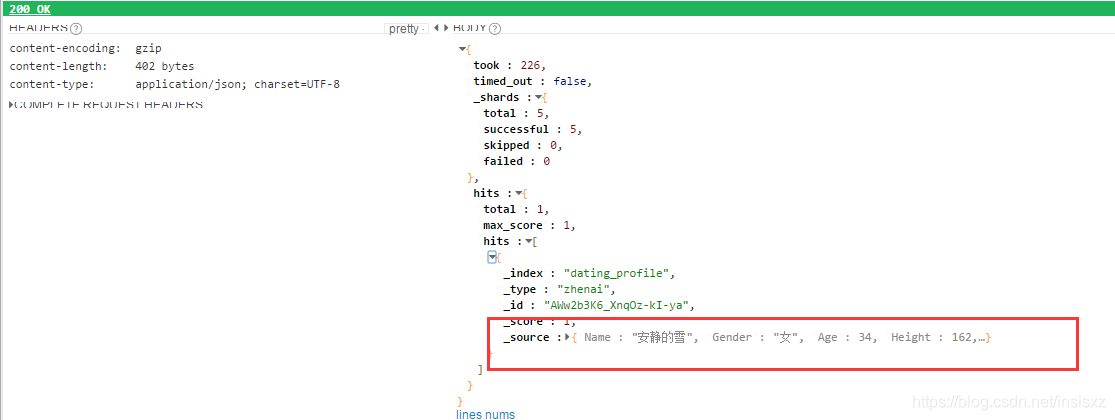
t.Logf("%+v", resp)
//从打印得知,数据在resp.Source中,从rest client的截图也可以知道
var actual model.Profile
//查看 *resp.Source 可知其数据类型为[]byte
err = json.Unmarshal(*resp.Source, &actual)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
if actual != expected {
t.Errorf("got %v;expected %v", actual, expected)
}
}补充:go-elasticsearch: Elastic官方的Go语言客户端
Elastic官方鼓励在项目中尝试用这个包,但请记住以下几点:
这个项目的工作还在进行中,并非所有计划的功能和Elasticsearch官方客户端中的标准(故障重试,节点自动发现等)都实现了。
API稳定性无法保证。 尽管公共API的设计非常谨慎,但它们可以根据进一步的探索和用户反馈以不兼容的方式进行更改。
客户端的目标是Elasticsearch 7.x版本。后续将添加对6.x和5.x版本API的支持。
用go get安装这个包:
go get -u github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch
或者将这个包添加到go.mod文件:
require github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch v0.0.0
或者克隆这个仓库:
git clone https://github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch.git \u0026amp;\u0026amp; cd go-elasticsearch
一个完整的示例:
mkdir my-elasticsearch-app \u0026amp;\u0026amp; cd my-elasticsearch-appcat \u0026gt; go.mod \u0026lt;\u0026lt;-END module my-elasticsearch-app require github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch v0.0.0ENDcat \u0026gt; main.go \u0026lt;\u0026lt;-END package main import ( \u0026quot;log\u0026quot; \u0026quot;github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch\u0026quot; ) func main() { es, _ := elasticsearch.NewDefaultClient() log.Println(es.Info()) }ENDgo run main.goelasticsearch包与另外两个包绑定在一起,esapi用于调用Elasticsearch的API,estransport通过HTTP传输数据。
使用elasticsearch.NewDefaultClient()函数创建带有以下默认设置的客户端:
es, err := elasticsearch.NewDefaultClient()if err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;Error creating the client: %s\u0026quot;, err)}res, err := es.Info()if err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;Error getting response: %s\u0026quot;, err)}log.Println(res)// [200 OK] {// \u0026quot;name\u0026quot; : \u0026quot;node-1\u0026quot;,// \u0026quot;cluster_name\u0026quot; : \u0026quot;go-elasticsearch\u0026quot;// ...注意:当导出ELASTICSEARCH_URL环境变量时,它将被用作集群端点。
使用elasticsearch.NewClient()函数(仅用作演示)配置该客户端:
cfg := elasticsearch.Config{ Addresses: []string{ \u0026quot;http://localhost:9200\u0026quot;, \u0026quot;http://localhost:9201\u0026quot;, }, Transport: \u0026amp;http.Transport{ MaxIdleConnsPerHost: 10, ResponseHeaderTimeout: time.Second, DialContext: (\u0026amp;net.Dialer{Timeout: time.Second}).DialContext, TLSClientConfig: \u0026amp;tls.Config{ MaxVersion: tls.VersionTLS11, InsecureSkipVerify: true, }, },}es, err := elasticsearch.NewClient(cfg)// ...下面的示例展示了更复杂的用法。它从集群中获取Elasticsearch版本,同时索引几个文档,并使用响应主体周围的一个轻量包装器打印搜索结果。
// $ go run _examples/main.gopackage mainimport ( \u0026quot;context\u0026quot; \u0026quot;encoding/json\u0026quot; \u0026quot;log\u0026quot; \u0026quot;strconv\u0026quot; \u0026quot;strings\u0026quot; \u0026quot;sync\u0026quot; \u0026quot;github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch\u0026quot; \u0026quot;github.com/elastic/go-elasticsearch/esapi\u0026quot;)func main() { log.SetFlags(0) var ( r map[string]interface{} wg sync.WaitGroup ) // Initialize a client with the default settings. // // An `ELASTICSEARCH_URL` environment variable will be used when exported. // es, err := elasticsearch.NewDefaultClient() if err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;Error creating the client: %s\u0026quot;, err) } // 1. Get cluster info // res, err := es.Info() if err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;Error getting response: %s\u0026quot;, err) } // Deserialize the response into a map. if err := json.NewDecoder(res.Body).Decode(\u0026amp;r); err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;Error parsing the response body: %s\u0026quot;, err) } // Print version number. log.Printf(\u0026quot;~~~~~~~\u0026gt; Elasticsearch %s\u0026quot;, r[\u0026quot;version\u0026quot;].(map[string]interface{})[\u0026quot;number\u0026quot;]) // 2. Index documents concurrently // for i, title := range []string{\u0026quot;Test One\u0026quot;, \u0026quot;Test Two\u0026quot;} { wg.Add(1) go func(i int, title string) { defer wg.Done() // Set up the request object directly. req := esapi.IndexRequest{ Index: \u0026quot;test\u0026quot;, DocumentID: strconv.Itoa(i + 1), Body: strings.NewReader(`{\u0026quot;title\u0026quot; : \u0026quot;` + title + `\u0026quot;}`), Refresh: \u0026quot;true\u0026quot;, } // Perform the request with the client. res, err := req.Do(context.Background(), es) if err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;Error getting response: %s\u0026quot;, err) } defer res.Body.Close() if res.IsError() { log.Printf(\u0026quot;[%s] Error indexing document ID=%d\u0026quot;, res.Status(), i+1) } else { // Deserialize the response into a map. var r map[string]interface{} if err := json.NewDecoder(res.Body).Decode(\u0026amp;r); err != nil { log.Printf(\u0026quot;Error parsing the response body: %s\u0026quot;, err) } else { // Print the response status and indexed document version. log.Printf(\u0026quot;[%s] %s; version=%d\u0026quot;, res.Status(), r[\u0026quot;result\u0026quot;], int(r[\u0026quot;_version\u0026quot;].(float64))) } } }(i, title) } wg.Wait() log.Println(strings.Repeat(\u0026quot;-\u0026quot;, 37)) // 3. Search for the indexed documents // // Use the helper methods of the client. res, err = es.Search( es.Search.WithContext(context.Background()), es.Search.WithIndex(\u0026quot;test\u0026quot;), es.Search.WithBody(strings.NewReader(`{\u0026quot;query\u0026quot; : { \u0026quot;match\u0026quot; : { \u0026quot;title\u0026quot; : \u0026quot;test\u0026quot; } }}`)), es.Search.WithTrackTotalHits(true), es.Search.WithPretty(), ) if err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;ERROR: %s\u0026quot;, err) } defer res.Body.Close() if res.IsError() { var e map[string]interface{} if err := json.NewDecoder(res.Body).Decode(\u0026amp;e); err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;error parsing the response body: %s\u0026quot;, err) } else { // Print the response status and error information. log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;[%s] %s: %s\u0026quot;, res.Status(), e[\u0026quot;error\u0026quot;].(map[string]interface{})[\u0026quot;type\u0026quot;], e[\u0026quot;error\u0026quot;].(map[string]interface{})[\u0026quot;reason\u0026quot;], ) } } if err := json.NewDecoder(res.Body).Decode(\u0026amp;r); err != nil { log.Fatalf(\u0026quot;Error parsing the response body: %s\u0026quot;, err) } // Print the response status, number of results, and request duration. log.Printf( \u0026quot;[%s] %d hits; took: %dms\u0026quot;, res.Status(), int(r[\u0026quot;hits\u0026quot;].(map[string]interface{})[\u0026quot;total\u0026quot;].(map[string]interface{})[\u0026quot;value\u0026quot;].(float64)), int(r[\u0026quot;took\u0026quot;].(float64)), ) // Print the ID and document source for each hit. for _, hit := range r[\u0026quot;hits\u0026quot;].(map[string]interface{})[\u0026quot;hits\u0026quot;].([]interface{}) { log.Printf(\u0026quot; * ID=%s, %s\u0026quot;, hit.(map[string]interface{})[\u0026quot;_id\u0026quot;], hit.(map[string]interface{})[\u0026quot;_source\u0026quot;]) } log.Println(strings.Repeat(\u0026quot;=\u0026quot;, 37))}// ~~~~~~~\u0026gt; Elasticsearch 7.0.0-SNAPSHOT// [200 OK] updated; version=1// [200 OK] updated; version=1// -------------------------------------// [200 OK] 2 hits; took: 7ms// * ID=1, map[title:Test One]// * ID=2, map[title:Test Two]// =====================================如上述示例所示,esapi包允许通过两种不同的方式调用Elasticsearch API:通过创建结构(如IndexRequest),并向其传递上下文和客户端来调用其Do()方法,或者通过客户端上可用的函数(如WithIndex())直接调用其上的Search()函数。更多信息请参阅包文档。
estransport包处理与Elasticsearch之间的数据传输。 目前,这个实现只占据很小的空间:它只在已配置的集群端点上进行循环。后续将添加更多功能:重试失败的请求,忽略某些状态代码,自动发现群集中的节点等等。
_examples文件夹包含许多全面的示例,可帮助你上手使用客户端,包括客户端的配置和自定义,模拟单元测试的传输,将客户端嵌入自定义类型,构建查询,执行请求和解析回应。
看完上述内容,你们对elasticsearch Client怎么在golang中使用有进一步的了解吗?如果还想了解更多知识或者相关内容,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢大家的支持。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。