您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关使用python怎么读写修改Excel,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
pip3 install xlrd xlwt xlutils
git:https://github.com/python-excel/xlwt/tree/master/examples
实现效果
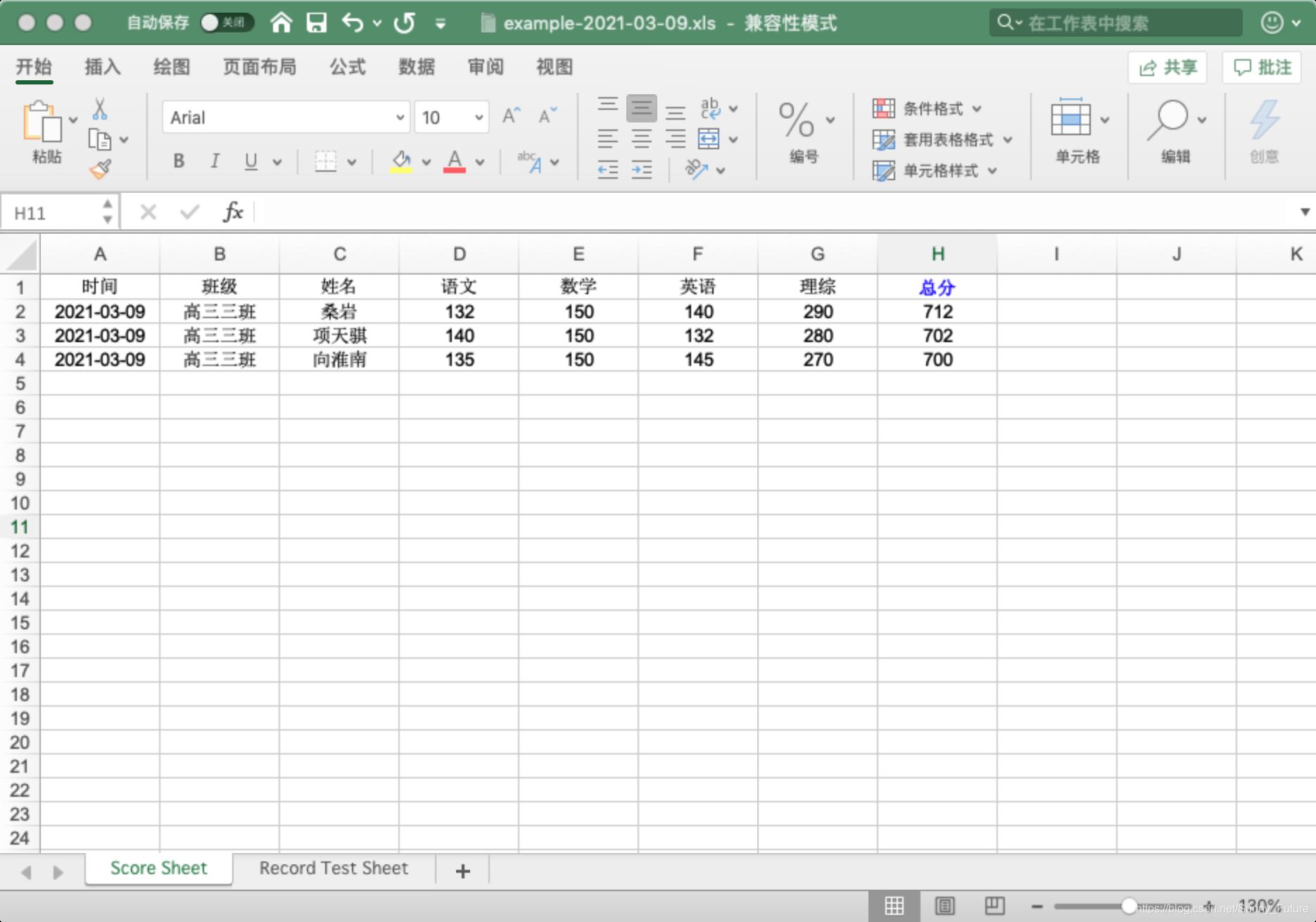
上代码
from datetime import datetime
import xlwt
font0 = xlwt.Font()
# font0.name = 'Times New Roman' # 适用于字母或数字
font0.name = '宋体' # 适用于中文,适配字体或者不指定字体才能体现出指定的颜色
# font0.colour_index = 1 # 白色
# font0.colour_index = 2 # 红色
# font0.colour_index = 3 # 绿色
# font0.colour_index = 4 # 蓝色
# font0.colour_index = 5 # 黄色
# font0.colour_index = 6 # 紫色
# font0.colour_index = 7 # 青色
# font0.colour_index = 8 # 黑色,比默认加黑,不加粗
font0.colour_index = 4 # 蓝色
font0.bold = True
style0 = xlwt.XFStyle()
style0.font = font0
# 创建样式对象:日期格式
style1 = xlwt.XFStyle()
style1.num_format_str = 'YYYY-MM-DD'
# 创建样式对象:字体居中对齐
style2 = xlwt.XFStyle()
al = xlwt.Alignment()
al.horz = 0x02 # 设置水平居中
al.vert = 0x01 # 设置垂直居中
style2.alignment = al
# 创建样式对象,设置日期格式与字体居中对齐
style3 = xlwt.XFStyle()
style3.num_format_str = 'YYYY-MM-DD'
style3.alignment = al
# 创建样式对象,设置字体居中 且 设置字体颜色
style4 = xlwt.XFStyle()
style4.alignment = al
style4.font = font0
now_time = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X')
date_time = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# 创建表格
wb = xlwt.Workbook()
# 新建一个名为 Score Sheet 的表单页
score_sheet = wb.add_sheet('Score Sheet')
# 新建一个名为 Record Test Sheet 的表单页
record_test_sheet = wb.add_sheet('Record Test Sheet')
# 1、写入 Score Sheet 表单
# 设置 表头, 第一个参数是行,第二个参数是列
score_sheet.write(0, 0, '时间', style2)
score_sheet.write(0, 1, '班级', style2)
score_sheet.write(0, 2, '姓名', style2)
score_sheet.write(0, 3, '语文', style2)
score_sheet.write(0, 4, '数学', style2)
score_sheet.write(0, 5, '英语', style2)
score_sheet.write(0, 6, '理综', style2)
score_sheet.write(0, 7, '总分', style4)
# 按照位置添加数据
score_sheet.write(1, 0, datetime.now(), style3)
score_sheet.write(1, 1, '高三三班', style2)
score_sheet.write(1, 2, '桑岩', style2)
score_sheet.write(1, 3, 132, style2)
score_sheet.write(1, 4, 150, style2)
score_sheet.write(1, 5, 140, style2)
score_sheet.write(1, 6, 290, style2)
score_sheet.write(1, 7, xlwt.Formula("D2+E2+F2+G2"), style2)
score_sheet.write(2, 0, datetime.now(), style3)
score_sheet.write(2, 1, '高三三班', style2)
score_sheet.write(2, 2, '项天骐', style2)
score_sheet.write(2, 3, 140, style2)
score_sheet.write(2, 4, 150, style2)
score_sheet.write(2, 5, 132, style2)
score_sheet.write(2, 6, 280, style2)
score_sheet.write(2, 7, xlwt.Formula("D3+E3+F3+G3"), style2)
score_sheet.write(3, 0, datetime.now(), style3)
score_sheet.write(3, 1, '高三三班', style2)
score_sheet.write(3, 2, '向淮南', style2)
score_sheet.write(3, 3, 135, style2)
score_sheet.write(3, 4, 150, style2)
score_sheet.write(3, 5, 145, style2)
score_sheet.write(3, 6, 270, style2)
score_sheet.write(3, 7, xlwt.Formula("D4+E4+F4+G4"), style2)
# 2、写入 Record Test Sheet 表单
record_test_sheet.write(0, 0, '时间')
record_test_sheet.write(0, 1, '学科', style1)
record_test_sheet.write(0, 2, '成绩', style1)
record_test_sheet.write(1, 0, datetime.now(), style1)
record_test_sheet.write(1, 1, '语文', style2)
record_test_sheet.write(1, 2, 80)
record_test_sheet.write(2, 0, datetime.now(), style3)
record_test_sheet.write(2, 1, '数学', style2)
record_test_sheet.write(2, 2, 99)
record_test_sheet.write(3, 0, now_time, style2)
record_test_sheet.write(3, 1, '英语', style2)
record_test_sheet.write(3, 2, 98)
# 保存表格,这里应该是覆盖写,注意每次都是覆盖所有表单内容,建议每次生成的表单加上时间版本区分
# wb.save('example.xls')
wb.save('example-{0}.xls'.format(date_time))git:https://github.com/python-excel/xlrd
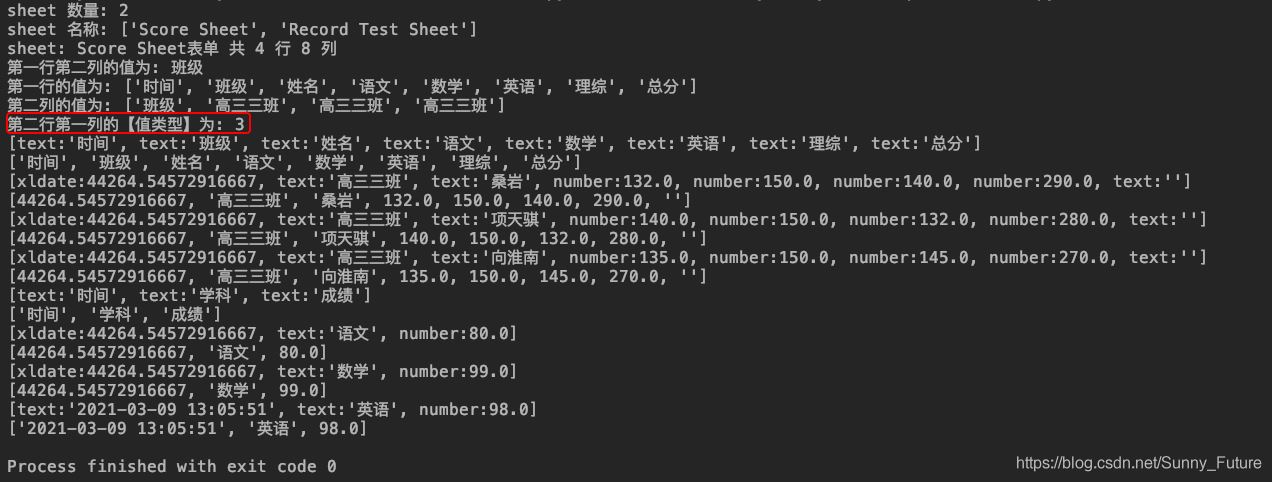
实现效果,读取sheet 表单内容
| 数值 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | empty | 空 |
| 1 | string | 字符串 |
| 2 | number | 数字 |
| 3 | date | 日期 |
| 4 | boole | 布尔值 |
| 5 | error | 错误 |
代码
import xlrd
# 打开 xls文件
wb = xlrd.open_workbook("example-2021-03-09.xls")
# 获取并打印 sheet 数量
print("sheet 数量:", wb.nsheets) # sheet 数量: 2
# 获取并打印 sheet 名称
print("sheet 名称:", wb.sheet_names()) # sheet 名称: ['Score Sheet', 'Record Test Sheet']
# 根据 sheet 索引获取内容
sh2 = wb.sheet_by_index(0)
# 或者
# 也可根据 sheet 名称获取内容
# sh = wb.sheet_by_name('Score Sheet')
# 获取并打印该 sheet 行数和列数
print(u"sheet: %s表单 共 %d 行 %d 列" % (sh2.name, sh2.nrows, sh2.ncols)) # sheet: Score Sheet表单 共 4 行 8 列
# 获取并打印某个单元格的值
print("第一行第二列的值为:", sh2.cell_value(0, 1)) # 第一行第二列的值为: 班级
# 获取整行或整列的值
row_info = sh2.row_values(0) # 获取第一行内容
col_info = sh2.col_values(1) # 获取第二列内容
# 打印获取的行列值
print("第一行的值为:", row_info) # 第一行的值为: ['时间', '班级', '姓名', '语文', '数学', '英语', '理综', '总分']
print("第二列的值为:", col_info) # 第二列的值为: ['班级', '高三三班', '高三三班', '高三三班']
# 获取单元格内容的数据类型,注意这里的值 另有含义
print("第二行第一列的【值类型】为:", sh2.cell(1, 0).ctype) # 第二行第一列的【值类型】为: 3
# 遍历所有表单内容
for sh in wb.sheets():
for r in range(sh.nrows):
# 输出指定行内容,这里包含原有类型指定,不能直接获取到指定列的值
row_val_list = sh.row(r)
print(row_val_list)
# [text:'时间', text:'班级', text:'姓名', text:'语文', text:'数学', text:'英语', text:'理综', text:'总分']
# 遍历行内,输出当前行内的所有列值
col_val_list = [col_val.value for col_val in row_val_list]
print(col_val_list)修改 Excel 是通过 xlutils 库的 copy 方法将原来的 Excel 整个复制一份,然后再做修改操作,最后再保存
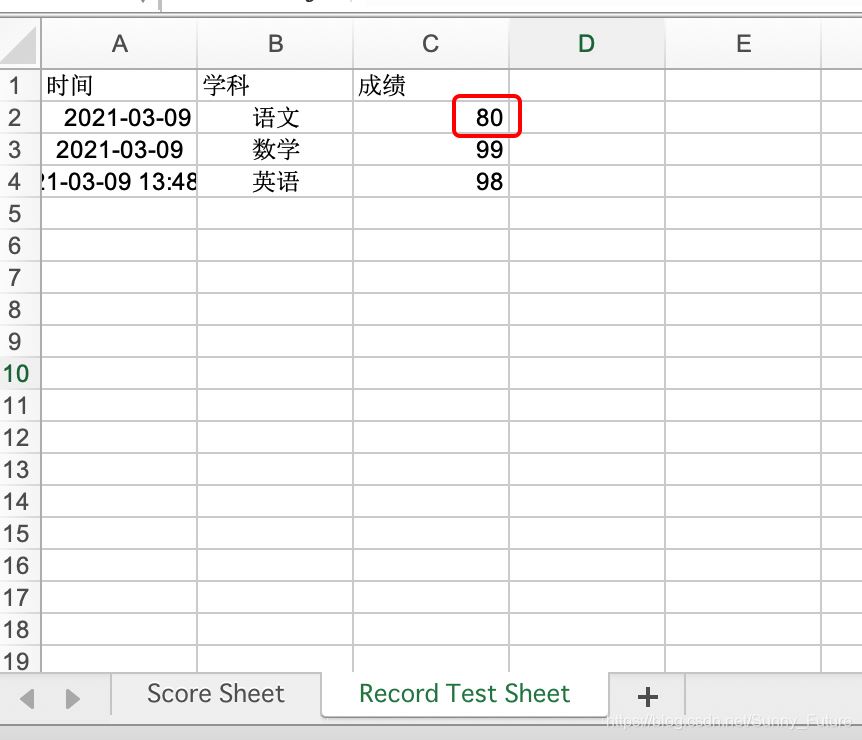
修改前
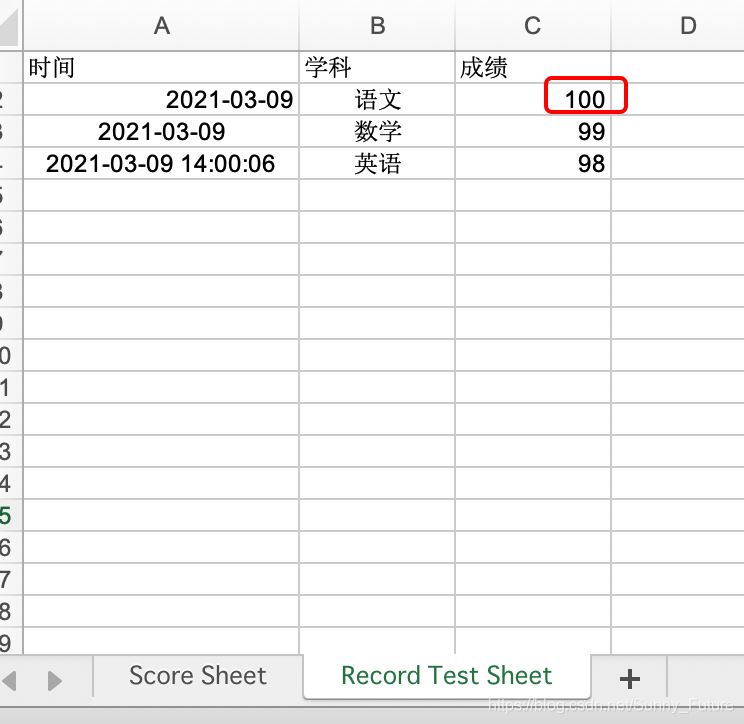
修改后
上代码
import xlrd
from xlutils.copy import copy
# 打开 excel 文件, 带格式复制
read_book = xlrd.open_workbook("example-2021-03-09.xls", formatting_info=True)
# 复制一份
wb = copy(read_book)
# 选取第一个表单
sh2 = wb.get_sheet(0)
# 在第五行新增写入数据
sh2.write(4, 0, '2020-12-16')
sh2.write(4, 1, '高三三班')
sh2.write(4, 2, '小鱼仙倌儿')
sh2.write(4, 3, 150)
sh2.write(4, 4, 150)
sh2.write(4, 5, 150)
sh2.write(4, 6, 300)
# 选取第二个表单
sh3 = wb.get_sheet(1)
# 替换总成绩数据
sh3.write(1, 2, 100)
# 保存
wb.save('example-2021-03-09.xls')1、简单易用,与C/C++、Java、C# 等传统语言相比,Python对代码格式的要求没有那么严格;2、Python属于开源的,所有人都可以看到源代码,并且可以被移植在许多平台上使用;3、Python面向对象,能够支持面向过程编程,也支持面向对象编程;4、Python是一种解释性语言,Python写的程序不需要编译成二进制代码,可以直接从源代码运行程序;5、Python功能强大,拥有的模块众多,基本能够实现所有的常见功能。
上述就是小编为大家分享的使用python怎么读写修改Excel了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。