您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
本篇文章为大家展示了Python中怎么定位元素,内容简明扼要并且容易理解,绝对能使你眼前一亮,通过这篇文章的详细介绍希望你能有所收获。
确定网站没有设置反爬措施,是否能直接返回待解析的内容:
import requests url = 'http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-24hours-0-0-1-1' response = requests.get(url).text print(response)
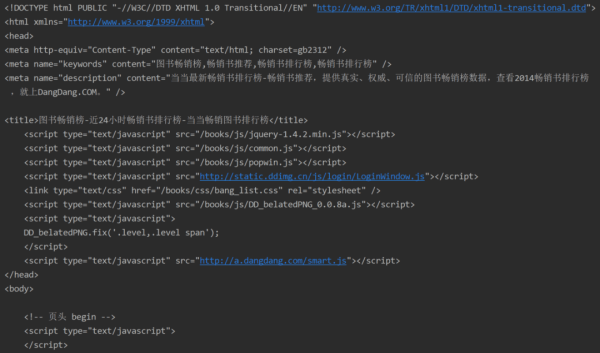
仔细检查后发现需要的数据都在返回内容中,说明不需要特别考虑反爬举措
审查网页元素后可以发现,书目信息都包含在 li 中,从属于 class 为 bang_list clearfix bang_list_mode 的 ul 中
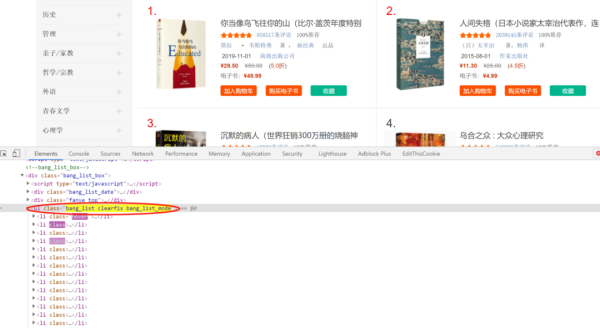
进一步审查也可以发现书名在的相应位置,这是多种解析方法的重要基础

1. 传统 BeautifulSoup 操作
经典的 BeautifulSoup 方法借助 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup,然后通过 soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml") 将文本转换为特定规范的结构,利用 find 系列方法进行解析,代码如下:
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup url = 'http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-24hours-0-0-1-1' response = requests.get(url).text def bs_for_parse(response): soup = BeautifulSoup(response, "lxml") li_list = soup.find('ul', class_='bang_list clearfix bang_list_mode').find_all('li') # 锁定ul后获取20个li for li in li_list: title = li.find('div', class_='name').find('a')['title'] # 逐个解析获取书名 print(title) if __name__ == '__main__': bs_for_parse(response)
成功获取了 20 个书名,有些书面显得冗长可以通过正则或者其他字符串方法处理,本文不作详细介绍
2. 基于 BeautifulSoup 的 CSS 选择器
这种方法实际上就是 PyQuery 中 CSS 选择器在其他模块的迁移使用,用法是类似的。关于 CSS 选择器详细语法可以参考:http://www.w3school.com.cn/cssref/css_selectors.asp由于是基于 BeautifulSoup 所以导入的模块以及文本结构转换都是一致的:
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup url = 'http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-24hours-0-0-1-1' response = requests.get(url).text def css_for_parse(response): soup = BeautifulSoup(response, "lxml") print(soup) if __name__ == '__main__': css_for_parse(response)
然后就是通过 soup.select 辅以特定的 CSS 语法获取特定内容,基础依旧是对元素的认真审查分析:
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from lxml import html url = 'http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-24hours-0-0-1-1' response = requests.get(url).text def css_for_parse(response): soup = BeautifulSoup(response, "lxml") li_list = soup.select('ul.bang_list.clearfix.bang_list_mode > li') for li in li_list: title = li.select('div.name > a')[0]['title'] print(title) if __name__ == '__main__': css_for_parse(response)3. XPath
XPath 即为 XML 路径语言,它是一种用来确定 XML 文档中某部分位置的计算机语言,如果使用 Chrome 浏览器建议安装 XPath Helper 插件,会大大提高写 XPath 的效率。
之前的爬虫文章基本都是基于 XPath,大家相对比较熟悉因此代码直接给出:
import requests from lxml import html url = 'http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-24hours-0-0-1-1' response = requests.get(url).text def xpath_for_parse(response): selector = html.fromstring(response) books = selector.xpath("//ul[@class='bang_list clearfix bang_list_mode']/li") for book in books: title = book.xpath('div[@class="name"]/a/@title')[0] print(title) if __name__ == '__main__': xpath_for_parse(response)4. 正则表达式如果对 HTML 语言不熟悉,那么之前的几种解析方法都会比较吃力。这里也提供一种万能解析大法:正则表达式,只需要关注文本本身有什么特殊构造文法,即可用特定规则获取相应内容。依赖的模块是 re
首先重新观察直接返回的内容中,需要的文字前后有什么特殊:
import requests import re url = 'http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-24hours-0-0-1-1' response = requests.get(url).text print(response)


观察几个数目相信就有答案了:<div class="name"><a href="http://product.dangdang.com/xxxxxxxx.html" target="_blank" title="xxxxxxx">
书名就藏在上面的字符串中,蕴含的网址链接中末尾的数字会随着书名而改变。
分析到这里正则表达式就可以写出来了:
import requests import re url = 'http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-24hours-0-0-1-1' response = requests.get(url).text def re_for_parse(response): reg = '<div class="name"><a href="http://product.dangdang.com/\d+.html" target="_blank" title="(.*?)">' for title in re.findall(reg, response): print(title) if __name__ == '__main__': re_for_parse(response)
可以发现正则写法是最简单的,但是需要对于正则规则非常熟练。所谓正则大法好!
当然,不论哪种方法都有它所适用的场景,在真实操作中我们也需要在分析网页结构来判断如何高效的定位元素,最后附上本文介绍的四种方法的完整代码,大家可以自行操作一下来加深体会
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from lxml import html import re url = 'http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-24hours-0-0-1-1' response = requests.get(url).text def bs_for_parse(response): soup = BeautifulSoup(response, "lxml") li_list = soup.find('ul', class_='bang_list clearfix bang_list_mode').find_all('li') for li in li_list: title = li.find('div', class_='name').find('a')['title'] print(title) def css_for_parse(response): soup = BeautifulSoup(response, "lxml") li_list = soup.select('ul.bang_list.clearfix.bang_list_mode > li') for li in li_list: title = li.select('div.name > a')[0]['title'] print(title) def xpath_for_parse(response): selector = html.fromstring(response) books = selector.xpath("//ul[@class='bang_list clearfix bang_list_mode']/li") for book in books: title = book.xpath('div[@class="name"]/a/@title')[0] print(title) def re_for_parse(response): reg = '<div class="name"><a href="http://product.dangdang.com/\d+.html" target="_blank" title="(.*?)">' for title in re.findall(reg, response): print(title) if __name__ == '__main__': # bs_for_parse(response) # css_for_parse(response) # xpath_for_parse(response) re_for_parse(response)上述内容就是Python中怎么定位元素,你们学到知识或技能了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或者丰富自己的知识储备,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。