您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章主要讲解了“结合React源码如何快速掌握优先队列”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“结合React源码如何快速掌握优先队列”吧!
优先队列是数据结构中的基础概念,与队列先进先出(FIFO)的出队顺序不同的是 ,它的出队顺序与元素的优先级相关。
例如 React 的时间分片(React Fiber),它将渲染任务分了优先级,出队的顺序与任务的“重要程度”存在关系,那么满足这种情况的数据结构就是 优先队列 。
插入:在优先队列中插入元素,并使队列“有序”
删除最大/最小值:删除并返回最大/最小的元素,并使队列“有序”
查找最大/最小关键字:查找最大/最小的值
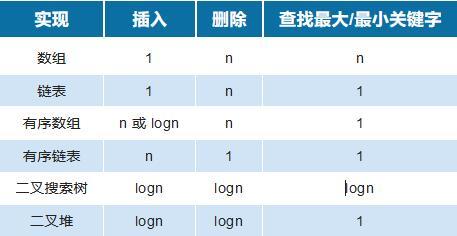
优先队列可以由以上多种方式实现,而优先队列的主要操作是插入和删除,其中二叉搜索树和二叉堆这两项操作的时间复杂度均为 logn ,但二叉树在多次删除之后容易导致树的倾斜,同时查找成本也高于二叉堆,所以最终二叉堆是比较符合实现优先队列的数据结构。
在二叉堆中数组中,要保证每个元素都小于(大于)或等于另外两个特定位置的元素。例如下图的树中,父节点总是小于或等于子节点。
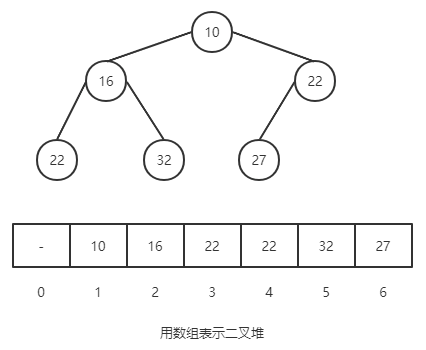
对于二叉堆有如下性质:
节点 k 的父节点下标为 k / 2(向下取整)
已某节点为根节点的子树,该节点是这颗树的极值
插入
二叉堆的插入非常简单,只需要在二叉堆的最后添加要插入的内容,并将其“上浮”到正确位置。
尝试在上面的二叉堆中插入新元素 9,过程如下:
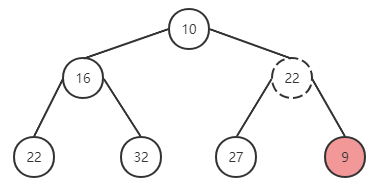
在尾部插入元素 9,与父节点进行对比,有序性被破坏,与父元素替换位置。
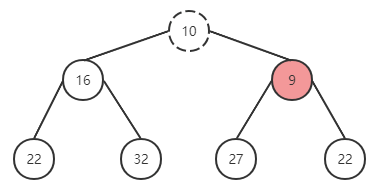
替换成功后,继续上一轮操作,与父节点进行对比,仍然无法满足有序性,继续调换位置。
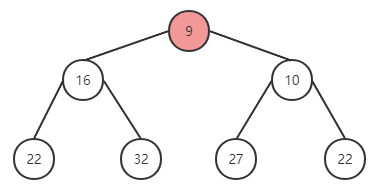
再次替换后符合。
程序框架
function push { * 在堆尾部添加元素 * 执行上浮循环 * 与父元素对比大小,将较大的放在父节点位置 return minItem }实现
function push(heap: Heap, node: Node): void { const index = heap.length; heap.push(node); // 在堆尾部添加元素 siftUp(heap, node, index); // 进行上浮操作 } function siftUp(heap, node, i) { let index = i; while (true) { const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1; // 父节点位置: parentIndex = childIndex / 2 const parent = heap[parentIndex]; if (parent !== undefined && compare(parent, node) > 0) { // The parent is larger. Swap positions. heap[parentIndex] = node; heap[index] = parent; index = parentIndex; } else { // The parent is smaller. Exit. return; } } }删除
取出根节点的值对比插入稍微复杂一点,归纳起来可以分为三步:
取出根节点的值
将最后一个元素与根节点进行替换,并删除最后一个元素
下沉
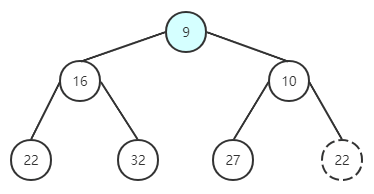
取出根节点。
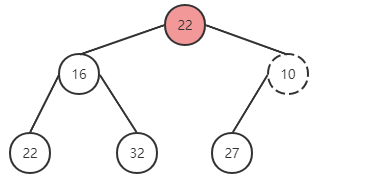
将最后一个元素与根节点调换,并删除。对比发现有序性被破坏,进行对调。
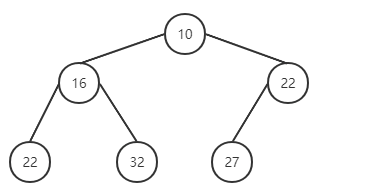
完成删除。
程序框架
function pop { * 设定 minItem 保存根节点 * 取出最后一个节点与根节点替换,并删除最后一个节点 * 执行下沉循环 * 将根元素与左右子节点对比,挑选较小的与父节点替换位置 return minItem }实现
export function pop(heap: Heap): Node | null { const first = heap[0]; // 取出根节点 if (first !== undefined) { const last = heap.pop(); // 取出最后一位元素,并删除 if (last !== first) { heap[0] = last; // 与根节点对调 siftDown(heap, last, 0); // 下沉 } return first; } else { return null; } } function siftDown(heap, node, i) { let index = i; const length = heap.length; while (index < length) { const leftIndex = (index + 1) * 2 - 1; const left = heap[leftIndex]; const rightIndex = leftIndex + 1; const right = heap[rightIndex]; // If the left or right node is smaller, swap with the smaller of those. // 寻找左右儿子较小的那一个替换 if (left !== undefined && compare(left, node) < 0) { //左子节点小于根节点 if (right !== undefined && compare(right, left) < 0) { heap[index] = right; heap[rightIndex] = node; index = rightIndex; } else { heap[index] = left; heap[leftIndex] = node; index = leftIndex; } } else if (right !== undefined && compare(right, node) < 0) { // 左子节点大于根节点,右子节点小于根节点 heap[index] = right; heap[rightIndex] = node; index = rightIndex; } else { // Neither child is smaller. Exit. return; } } }以下是 react 源码中 scheduler/src/SchedulerMinHeap.js 关于最小堆的完整实现:
/** * Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates. * * This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the * LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. * * @flow strict */ // 定义最小堆极其元素,其中 sortIndex 为最小堆对比的 key,若 sortIndex 相同,则对比 id type Heap = Array<Node>; type Node = {| id: number, sortIndex: number, |}; // 入队操作,在入队完成之后进行“上浮” export function push(heap: Heap, node: Node): void { const index = heap.length; heap.push(node); siftUp(heap, node, index); } // 查找最大值 export function peek(heap: Heap): Node | null { const first = heap[0]; return first === undefined ? null : first; } // 删除并返回最大值 export function pop(heap: Heap): Node | null { const first = heap[0]; // 取出根节点(哨兵) if (first !== undefined) { const last = heap.pop(); // 取出最后一位元素,并删除 if (last !== first) { // 头尾并没有对撞 heap[0] = last; // 与根节点对调 siftDown(heap, last, 0); // 下沉 } return first; } else { return null; } } // 上浮,调整树结构 function siftUp(heap, node, i) { let index = i; while (true) { const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1; // 父节点位置: parentIndex = childIndex / 2,此处使用位操作,右移一位 const parent = heap[parentIndex]; if (parent !== undefined && compare(parent, node) > 0) { // 对比父节点和子元素的大小 // The parent is larger. Swap positions. heap[parentIndex] = node; // 若父节点较大,则更换位置 heap[index] = parent; index = parentIndex; } else { // The parent is smaller. Exit. return; } } } // 下沉,调整树结构 function siftDown(heap, node, i) { let index = i; const length = heap.length; while (index < length) { const leftIndex = (index + 1) * 2 - 1; const left = heap[leftIndex]; const rightIndex = leftIndex + 1; const right = heap[rightIndex]; // If the left or right node is smaller, swap with the smaller of those. // 寻找左右儿子较小的那一个替换 if (left !== undefined && compare(left, node) < 0) { if (right !== undefined && compare(right, left) < 0) { // 左子节点小于根节点 heap[index] = right; heap[rightIndex] = node; index = rightIndex; } else { heap[index] = left; heap[leftIndex] = node; index = leftIndex; } } else if (right !== undefined && compare(right, node) < 0) { // 左子节点大于根节点,右子节点小于根节点 heap[index] = right; heap[rightIndex] = node; index = rightIndex; } else { // Neither child is smaller. Exit. return; } } } function compare(a, b) { // Compare sort index first, then task id. const diff = a.sortIndex - b.sortIndex; return diff !== 0 ? diff : a.id - b.id; }堆排序
利用最大/最小堆的特性,我们很容易就能实现对数组的排序,重复执行 pop 就能进行升序排列,如果要降序,使用最大堆即可,该操作时间复杂度为 nlogn 。
多叉堆
为了追求更优的时间复杂度,我们可以将二叉堆改为多叉堆实现,下图为一个三叉堆:
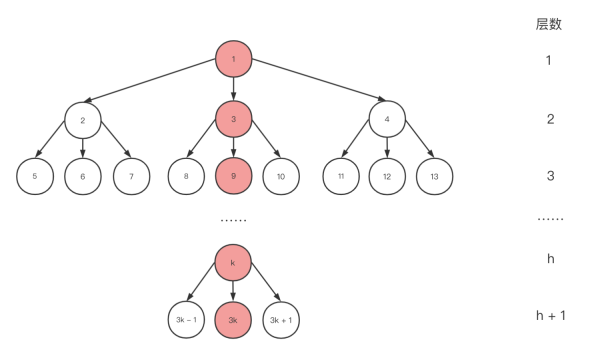
与二叉堆不同的是对于含有 N 个元素的 d 叉堆(通常情况下 d >= 2),随着 d 的增加,树高 K = logdN 的斜率会下降,然而 d 越大,删除操作的成本会更高。所以子元素不是越多越好,通常情况下三叉堆和四叉堆的应用会比较常见。
在libev中有这么一段注释 https://github.com/enki/libev/blob/master/ev.c#L2227,他提及了四叉树相比二叉堆来说缓存更加友好。 根据benchmark,在 50000+ 个 watchers 的场景下,四叉树会有 5% 的性能优势。
/* * at the moment we allow libev the luxury of two heaps, * a small-code-size 2-heap one and a ~1.5kb larger 4-heap * which is more cache-efficient. * the difference is about 5% with 50000+ watchers. */
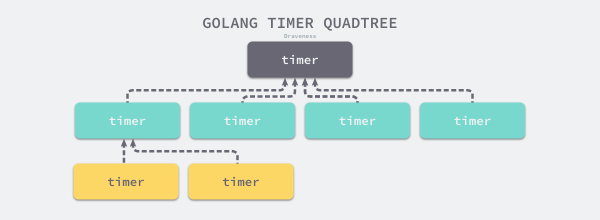
同样 Go 语言中的定时器的 timersBucket 的数据结构也采用了最小四叉堆。
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“结合React源码如何快速掌握优先队列”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对结合React源码如何快速掌握优先队列这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。