您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
本篇内容主要讲解“Mybatis是如何解析配置文件的”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Mybatis是如何解析配置文件的”吧!
在以前文章中,我们把Mybatis源码阅读的整个流程梳理了一遍。今天,我们来详细聊聊,Mybatis是如何解析配置文件的。
这是今天分析的流程图:
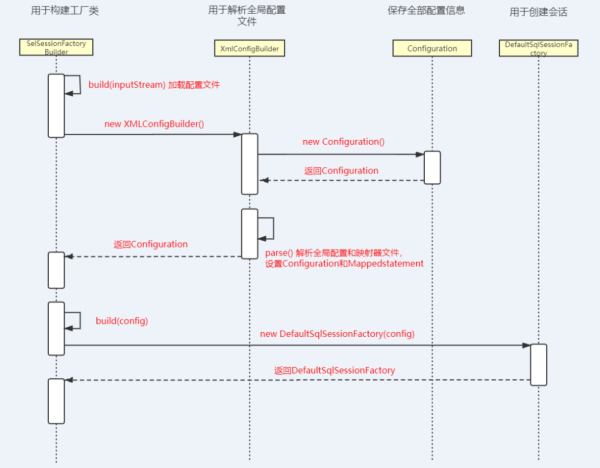
还是从案例开始。
demo案例
public static void main(String[] args) { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); System.out.println(userMapper.selectById(1)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } sqlSession.close(); } }见证奇迹
从SqlSessionFactoryBuilder开始。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类
org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
该类里全是build方法各种重载。

//这个方法啥也没干 public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) { return build(inputStream, null, null); }最终来到另外一个build方法里:
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) { try { //创建一个XMLConfigBuilder对象 XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } }XMLConfigBuilder类
该类的构造方法重载:
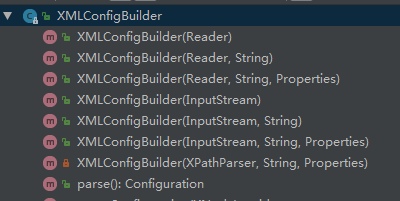
首先进入:
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) { this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props); } private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) { super(new Configuration()); ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration"); this.configuration.setVariables(props); this.parsed = false; this.environment = environment; this.parser = parser; }build(parser.parse());中的parser.parse();
mybatis-config.xml在哪里解析的呢?
请看下面这个方法:
//该方法返回一个Configuration对象 public Configuration parse() { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; //关键点 parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
终于看到开始解析配置文件了:
进入方法parseConfiguration。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //issue #117 read properties first propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); loadCustomVfs(settings); loadCustomLogImpl(settings); typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }这里就是把mybatis-config.xml内容解析,然后设置到Configuration对象中。
那么我们定义的Mapper.xml是在哪里解析的呢?
我们的Mapper.xml在mybatis-config.xml中的配置是这样的:

//1使用类路径 <mappers> <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/> <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/> <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/> </mappers> //2使用绝对url路径 <mappers> <mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/> <mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/> <mapper url="file:///var/mappers/PostMapper.xml"/> </mappers> //3使用java类名 <mappers> <mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/> <mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.BlogMapper"/> <mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.PostMapper"/> </mappers> //4自动扫描包下所有映射器 <mappers> <package name="org.mybatis.builder"/> </mappers>
继续源码分析,我们在上面mybatis-config.xml解析中可以看到:
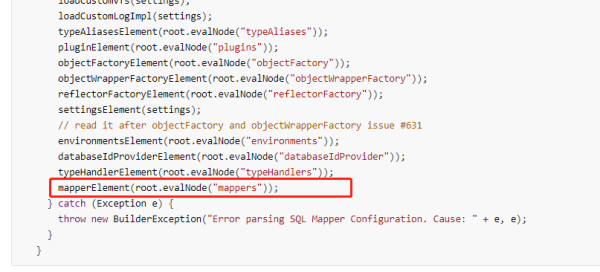
我们不妨进入这个方法看看:
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { //自动扫描包下所有映射器 if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); //放 configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage); } else { String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = child.getStringAttribute("url"); String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class"); //使用java类名 if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource); //根据文件存放目录,读取XxxMapper.xml InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //映射器比较复杂,调用XMLMapperBuilder //注意在for循环里每个mapper都重新new一个XMLMapperBuilder,来解析 XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); //使用绝对url路径 } else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(url); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url); //映射器比较复杂,调用XMLMapperBuilder XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); //使用类路径 } else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) { Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass); //直接把这个映射加入配置 configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface); } else { throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one."); } } } } }这里刚刚和我们的上面说的
到这里,配置文件mybatis-config.xml和我们定义映射文件XxxMapper.xml就全部解析完成。
回到SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类
前面讲到了XMLConfigBuilder中的parse方法,并返回了一个Configuration对象。
build(parser.parse());
这个build方法就是传入一个Configuration对象,然后构建一个DefaultSqlSession对象。
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); }继续回到我们的demo代码中这一行代码里:
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
这一行代码就相当于:
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new new DefaultSqlSessionFactory();
到这里,我们的整个流程就搞定了。
到此,相信大家对“Mybatis是如何解析配置文件的”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。