您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
本篇内容主要讲解“WebWork的框架初始化过程和用户请求处理过程”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“WebWork的框架初始化过程和用户请求处理过程”吧!
一、WebWork的框架初始化过程
WebWork做的项目,在服务器启动时完成WebWork的框架初始化。具体是通过Web.xml中配置好的com.opensymphony.xwork.dispatcher.ServletDispatcher(FilterDispatcher)过滤器中的init(ServletConfig servletConfig)方法完成。
并且web.xml中配置好ServletDispatcher的映射,当用户用映射好的结尾资源请求浏览器时,ServletDispatcher会进行请求处理(ServletDispatcher是一个HttpServlet)。
具体实现是通过以下步骤:
1、通过ServletDispatcher中的init方法进行框架的初始化工作:
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException { super.init(servletConfig); DispatcherUtils.initialize(getServletContext()); }2、init方法又同时调用DispatcherUtils类的initialize方法创建DispatcherUtils实例,同时间接调用DispatcherUtils类的init方法初始化Configuration配置,创建对象创建的工厂ObjectFactory和ObjectTypeDeterminer。
至此完成WebWork框架的初始化。
二、WebWork的用户请求处理过程
所有以web.xml中映射ServletDispatcher结尾的服务请求将由ServletDispatcher进行处理。
1、从用户请求的服务名中解析出对应Action的名称。
public void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException { //.... try { request = du.wrapRequest(request, getServletContext()); } catch(IOException e) { String message = "Could not wrap servlet request with MultipartRequestWrapper!"; LOG.error(message, e); throw new ServletException(message, e); } du.serviceAction(request, response, getServletContext(), mapping); }2、遍历HttpServletRequest、HttpSession、ServletContext 中的数据,并将其复制到Webwork的Map中,为下一步创建Action实例打下基础。
实现:通过过调用DispatcherUtils的serviceAction方法中的Map extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);完成以上信息的封装。
3、以上一步封装好的信息为参数,调用ActionProxyFactory创建对应的ActionProxy实例。ActionProxyFactory 将根据Xwork 配置文件(xwork.xml)中的设定,创建ActionProxy实例,ActionProxy中包含了Action的配置信息(包括Action名称,对应实现类等等)。
实现:通过ActionProxy proxy = ActionProxyFactory.getFactory().createActionProxy(namespace, name, extraContext, true, false);//创建动态代理DefaultActionProxyFactory实现ActionProxyFactory的createActionProxy方法,返回new DefaultActionProxy(namespace, actionName, extraContext, true, true);DefaultActionProxy是对ActionProxy的默认实现,通过DefaultActionProxy类的DefaultActionProxy(namespace, actionName, extraContext, true, true)构造方法实例化DefaultActionProxy,同时得到用户请求的actionName及namespace,并通过config = ConfigurationManager.getConfiguration().getRuntimeConfiguration().getActionConfig(namespace, actionName);
ConfigurationManager的
public static synchronized Configuration getConfiguration() { if(configurationInstance == null) { configurationInstance = new DefaultConfiguration(); try { configurationInstance.reload(); } catch(ConfigurationException e) { configurationInstance = null; throw e; } } else { conditionalReload(); } return configurationInstance; }完成对xwork.xml(具体操作类是XmlConfigurationProvider)配置信息的读取。获得与此次请求相关的ActionConfig。
4、ActionProxy创建对应的Action实例,并根据配置进行一系列的处理程序。
通过DefaultActionProxy类的invocation = ActionProxyFactory.getFactory().createActionInvocation(this, extraContext);
//通过createActionInvocation方法创建动作调用类ActionInvocation,处理被Action调用的方法
privatevoid resolveMethod() { // if the method is set to null, use the one from the configuration // if the one from the configuration is also null, use "execute" if (!TextUtils.stringSet(this.method)) { this.method = config.getMethodName(); if (!TextUtils.stringSet(this.method)) { this.method = "execute"; } } }然后调用DispatcherUtils的serviceAction方法中的
if (mapping.getResult() != null) { Result result = mapping.getResult(); result.execute(proxy.getInvocation()); } else { proxy.execute(); }完成用户的最终要执行的action方法。
public String execute() throws Exception { ActionContext nestedContext = ActionContext.getContext(); ActionContext.setContext(invocation.getInvocationContext()); String retCode = null; try { retCode = invocation.invoke(); } finally { if (cleanupContext) { ActionContext.setContext(nestedContext); } } return retCode; }最终处理ActionContext对象,将Action调用提交给ActionInvocation处理。
5、 一旦Action方法返回,ActionInvocation就要查找xwork.xml文件中这个Action的结果码(Action Result Code)(一个String如success、input)所对应的result,然后执行这个result。通常情况下,result会调用JSP或FreeMarker模板来呈现页面。当呈现页面时,模板可以使用WebWork提供的一些标签,其中一些组件可以和ActionMapper一起工作来为后面的请求呈现恰当的URL。
下面我们来看action部分的定义:
<action name="loginAction" class="loginAction"> <result name="success" type="dispatcher">/common/loginedHomeAction!init.action</result> </action>
这里的result结点有一个type属性,这表示此action的结果应该怎样处理。
再来看看dispatcher类型的result是怎么定义的:
<result-type name="dispatcher" class="com.opensymphony.webwork.dispatcher.ServletDispatcherResult" default="true"/>
到这里就可以知道了处理是交给ServletDispatcherResult类来做的。
ServletDispatcherResult类继承了WebWorkResultSupport类,而WebWorkResultSupport实现了com.opensymphony.xwork.Result接口,此接口用来处理action的结果。WebWorkResultSupport类定义了一个抽象的方法——doExecute,此方法用于实现对Result的处理。
下面来看看ServletDispatcherResult是怎么处理的:
public void doExecute(String finalLocation, ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { PageContext pageContext = ServletActionContext.getPageContext(); if (pageContext != null) { pageContext.include(finalLocation); } else { HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest(); HttpServletResponse response = ServletActionContext.getResponse(); RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(finalLocation); // if the view doesn't exist, let's do a 404 if (dispatcher == null) { response.sendError(404, "result '" + finalLocation + "' not found"); return; } // If we're included, then include the view // Otherwise do forward // This allow the page to, for example, set content type if (!response.isCommitted() && (request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.include.servlet_path") == null)) { request.setAttribute("webwork.view_uri", finalLocation); request.setAttribute("webwork.request_uri", request.getRequestURI()); dispatcher.forward(request, response); } else { dispatcher.include(request, response); } } }我们看到,最终调用的是dispatcher.forward(request, response);这样就可以成功转到我们的目标页了。
以下代码为DispatcherUtils中的serviceAction方法中的:
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context, ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException { Map extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context); OgnlValueStack stack = (OgnlValueStack)request.getAttribute("webwork.valueStack"); if(stack != null) extraContext.put("com.opensymphony.xwork.util.OgnlValueStack.ValueStack", new OgnlValueStack(stack)); try { String namespace = mapping.getNamespace(); String name = mapping.getName(); String method = mapping.getMethod(); String id = request.getParameter("__continue"); if(id != null) { Map params = (Map)extraContext.get("com.opensymphony.xwork.ActionContext.parameters"); params.remove("__continue"); extraContext.put("__continue", id); } ActionProxy proxy = ActionProxyFactory.getFactory().createActionProxy(namespace, name, extraContext, true, false); proxy.setMethod(method); request.setAttribute("webwork.valueStack", proxy.getInvocation().getStack()); if(mapping.getResult() != null) { Result result = mapping.getResult(); result.execute(proxy.getInvocation()); } else { proxy.execute(); } if(stack != null) request.setAttribute("webwork.valueStack", stack); } catch(ConfigurationException e) { LOG.error("Could not find action", e); sendError(request, response, 404, e); } catch(Exception e) { String msg = "Could not execute action"; LOG.error(msg, e); throw new ServletException(msg, e); } }三、WebWork的执行流程图
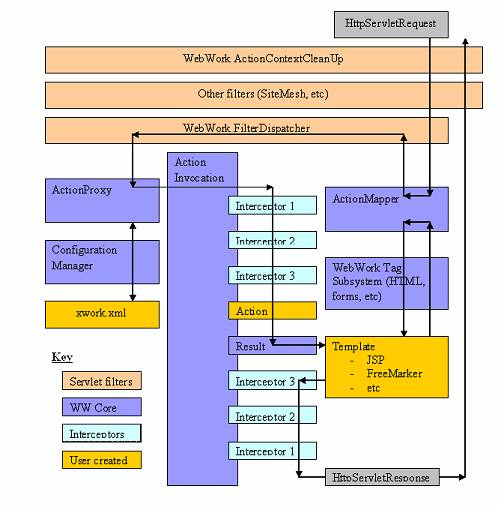
到此,相信大家对“WebWork的框架初始化过程和用户请求处理过程”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。