您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关Android开发中Dialog怎么显示图像,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
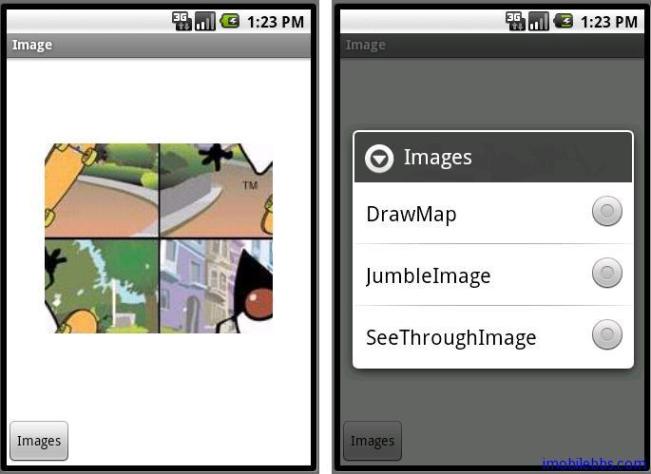
Dialog一般指可以显示在Activity前面的小窗口,当前的Activity失去焦点(Focus),Dialog将接受用户输入,一般可 以用来显示消息或接受用户输入等等。使用Dialog时一般不需要直接创建Dialog类的实例。而是可以使用 AlertDialog,ProgressDialog,DatePickerDialog,TimePickerDialog。最常用的是 AlertDialog。下面就以使用AlertDialog为例,使用AlertDialog来选择显示图像的三个例子:DrawMap, JumbleImage,SeeThroughImage。其中DrawMap暂时不介绍,将在后面介绍Internet应用显示在线地图时再说。
通常Dialog是作为Activity一部分来创建的,也就是说在Activity的onCreateDialog(int)中创建。当在 onCreateDialog(int)创建Dialog时,Android系统将自动管理Dialog的状态,并把当前Activity作为 Dialog的所有者。并且Dialog也继承当前Activity的一些属性,比如说Option Menu。
创建好Dialog后,可以使用showDialog(int) 来显示Dialog ,showDialog的参数为Dialog的ID。在显示Dialog之前,如果想对Dialog做些改动,可以 在 onPrepareDialog(int, Dialog) 添加代码。dismiss()关闭对话框。如果在Activity中则使用dismissDialog(int) 。
本例中使用一个按钮来触发Dialog,在res\layout 在添加images.xml
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android” android:orientation=”vertical” android:background=”@drawable/white” android:layout_width=”fill_parent” android:layout_height=”fill_parent”> <com.pstreets.graphics2d.GuidebeeGraphics2DView android:id=”@+id/graphics2dview” android:layout_weight=”1″ android:layout_width=”fill_parent” android:layout_height=”wrap_content”/> <LinearLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android” android:layout_width=”wrap_content” android:layout_height=”wrap_content” android:orientation=”horizontal” > <Button android:text=”Images” android:id=”@+id/btnImages” android:layout_width=”wrap_content” android:textColor=”@color/black” android:checked=”true” android:layout_height=”wrap_content”> </Button> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
修改Image.java
public class Images extends Graphics2DActivity implements OnClickListener{ private Button btnImages; private int[] imageDuke; static final private int IMAGE_DIALOG=1; int w, h; int offX, offY; int alpha = 128; FontEx font = FontEx.getSystemFont(); int fontSize = 24; Pen pen = new Pen(Color.RED, 2); char[] message = "Guidebee".toCharArray(); int widthOfMessage = 0; private int numlocs = 2; private int numcells = numlocs * numlocs; private int[] cells; int cw, ch; public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.images); graphic2dView = (GuidebeeGraphics2DView) findViewById(R.id.graphics2dview); btnImages = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnImages); btnImages.setOnClickListener(this); Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.duke_skateboard); imageDuke = new int[bitmap.getHeight() * bitmap.getWidth()]; bitmap.getPixels(imageDuke, 0, bitmap.getWidth(), 0, 0, bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight()); widthOfMessage = font.charsWidth(message, 0, message.length, fontSize); w=bitmap.getWidth(); h=bitmap.getHeight(); offX = (SharedGraphics2DInstance.CANVAS_WIDTH - w) / 2; offY = (SharedGraphics2DInstance.CANVAS_HEIGHT - h) / 2; cw = w / numlocs; ch = h / numlocs; cells = new int[numcells]; for (int i = 0; i < numcells; i++) { cells[i] = i; } } private void drawJumbleImage(){ Random rand = new Random(); int ri; for (int i = 0; i < numcells; i++) { while ((ri = rand.nextInt(numlocs)) == i) { } int tmp = cells[i]; cells[i] = cells[ri]; cells[ri] = tmp; } graphics2D.clear(Color.WHITE); graphics2D.Reset(); int dx, dy; for (int x = 0; x < numlocs; x++) { int sx = x * cw; for (int y = 0; y < numlocs; y++) { int sy = y * ch; int cell = cells[x * numlocs + y]; dx = (cell / numlocs) * cw; dy = (cell % numlocs) * ch; graphics2D.drawImage(imageDuke, w, h, dx + offX, dy + offY, sx, sy, cw, ch); } } graphic2dView.refreshCanvas(); } private void drawSeeThroughImage(){ alpha += 16; if(alpha>255) alpha=0; graphics2D.clear(Color.WHITE); graphics2D.Reset(); graphics2D.setDefaultPen(pen); graphics2D.drawChars(font, fontSize, message, 0, message.length, offX + (w - widthOfMessage) / 2, offY + h / 2); graphics2D.drawImage(imageDuke, w, h, offX, offY, 0xFFFF00FF, alpha); graphic2dView.refreshCanvas(); } protected Dialog onCreateDialog(int id) { Dialog dialog; switch(id) { case IMAGE_DIALOG: final CharSequence[] items = {"DrawMap", "JumbleImage","SeeThroughImage"}; AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this); builder.setTitle("Images"); builder.setSingleChoiceItems(items, -1, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int item) { switch(item){ case 0: break; case 1: drawJumbleImage(); break; case 2: drawSeeThroughImage(); break; } dialog.dismiss(); } }); AlertDialog alert = builder.create(); dialog=alert; break; default: dialog = null; } return dialog; } @Override protected void drawImage() { drawJumbleImage(); } @Override public void onClick(View view) { showDialog(IMAGE_DIALOG); } }从代码中看到,Dialog是通过AlertDialog.Builder 来创建的,这里Dialog显示了三个选项,通过builder.setSingleChoiceItems添加处理事件。实际AlertDialog可以有多种选项,具体请参考Android AlertDialog 文档。
上述就是小编为大家分享的Android开发中Dialog怎么显示图像了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。