您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
哈希表,是根据关键字(Key value)而直接访问在内存存储位置的数据结构。也就是说,它通过计算一个关于键值的函数,将所需查询的数据映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,这加快了查找速度。这个映射函数称做散列函数,存放记录的数组称做散列表。(摘自维基百科)
对不同的关键字可能得到同一散列地址,即k1!=k2,而f(k1)=f(k2),这种现象称为碰撞(英语:Collision),也叫哈希冲突。
处理哈希冲突的方法有很多种:
闭散列法
开链法(哈希桶)
素数表
字符串哈希算法
在这里我们讨论最简单的闭散列法的线性探测法,学会了这种方法,就可以在线性探测法的思想基础上领会其他方法。
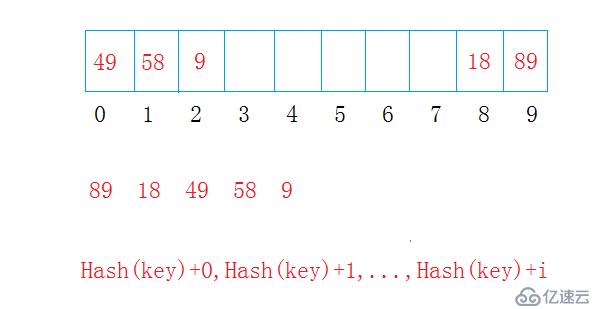
线性探测法
定义:通过散列函数hash(key),找到关键字key在线性序列中的位置,如果当前位置已经有了一个关键字,就长生了哈希冲突,就往后探测i个位置(i小于线性序列的大小),直到当前位置没有关键字存在。
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
enum State
{
EMPTY,
EXIST,
DELETE
};
template<class T>
struct DefaultFunc
{
size_t operator()(const T& data)
{
return (size_t)data;
}
};
struct StringFunc
{
size_t operator()(const string& str)
{
size_t sum = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); ++i)
{
sum += str[i];
}
return sum;
}
};
template<class K,class FuncModel=DefaultFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
HashTable();
HashTable(const size_t size);
bool Push(const K& data);//增
bool Remove(const K& data);//删
size_t Find(const K& data);//查
bool Alter(const K& data, const K& newdata);//改
void Print();//打印哈希表
protected:
size_t HashFunc(const K& data);//散列函数(哈希函数)
void Swap(HashTable<K, FuncModel>& x);
protected:
K* _table;//哈希表
State* _state;//状态表
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
FuncModel _HF;//区分默认类型的哈希函数和string类型的哈希函数
};.cpp文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"HashTable.h"
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
HashTable<K, FuncModel>::HashTable()
:_table(NULL)
, _state(NULL)
, _size(0)
, _capacity(0)
{}
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
HashTable<K, FuncModel>::HashTable(const size_t size)
:_table(new K[size])
, _state(new State[size])
, _size(0)
, _capacity(size)
{
//这里别用memset()来初始化_state,对于枚举类型的动态内存不能用memset初始化
//老老实实一个一个初始化
for (size_t i = 0; i < _capacity; i++)
{
_state[i] = EMPTY;
}
}
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
size_t HashTable<K, FuncModel>::HashFunc(const K& data)
{
return _HF(data)%_capacity;//Mod哈希表的容量,找到在哈希表中的位置,
//其实在这里最好Mod一个素数
}
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
void HashTable<K, FuncModel>::Swap(HashTable<K, FuncModel>& x)//交换两个哈希表
{
swap(_table, x._table);
swap(_state, x._state);
swap(_size, x._size);
swap(_capacity, x._capacity);
}
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
bool HashTable<K, FuncModel>::Push(const K& data)
{
if if (_size *10 >= _capacity* 8)//载荷因子不超过0.8
{
HashTable<K, FuncModel> tmp(2 * _capacity + 2);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _capacity; ++i)
{
if (_state[i] == EXIST)
{
size_t index = HashFunc(_table[i]);
while (tmp._state[index] == EXIST)
{
index++;
}
tmp._table[index] = _table[i];
tmp._state[index] = EXIST;
}
}
Swap(tmp);
}
size_t index = HashFunc(data);
while (_state[index] == EXIST)
{
index++;
}
_table[index] = data;
_state[index] = EXIST;
_size++;
return true;
}
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
void HashTable<K, FuncModel>::Print()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _capacity; ++i)
{
if (_state[i] == EXIST)
{
printf("_table[%d]:", i);
cout << _table[i] << "->存在";
}
else if (_state[i] == DELETE)
{
printf("_table[%d]:", i);
cout << _table[i] << "->删除";
}
else
{
printf("_table[%d]:空", i);
}
cout << endl;
}
}
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
bool HashTable<K, FuncModel>::Remove(const K& data)
{
if (_size > 0)
{
size_t index = Find(data);
if (index > 0)
{
_state[index] = DELETE;
_size--;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
return false;
}
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
size_t HashTable<K, FuncModel>::Find(const K& data)
{
size_t index = HashFunc(data);
size_t time = _capacity;
while (time--)
{
if (_table[index++] == data)
{
return --index;
}
if (index == _capacity)
{
index = 0;
}
}
return -1;
}
template<class K, class FuncModel = DefaultFunc<K>>
bool HashTable<K, FuncModel>::Alter(const K& data, const K& newdata)
{
size_t index = Find(data);
if (index > 0)
{
_state[index] = DELETE;
if (Push(newdata))
return true;
else
return false;
}
return false;
}在实现过程中要注意的问题有以下几点:
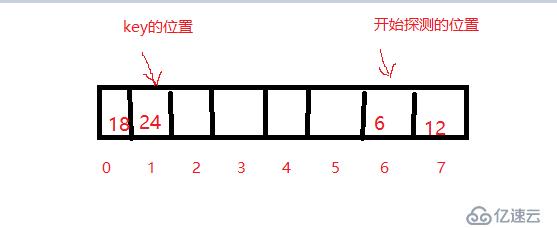
对于线性探测来说,有时候会遇到一开始探测的位置就在哈希table的最后的部分,但是因为哈希冲突key值被冲突到了哈希table的最前部分,所以探测到了table尾后将index置为0,简单又粗暴。
对于对哈希表中的数据的删除是属于弱删除,也就是说删除并没有删除数据,只是把数据的状态_state置为DELETE。
当载荷因子超过0.8时就得增容,载荷因子越高哈希冲突越多,不命中率越高。CPU缓存会大大升高。载荷因子a=填入表中元素的个数/散列表长度。
对代码的两点说明:
在这里我将模板声明与定义分开,涉及了模板的分离编译,对模板分离编译还不太清楚的可以查看博主博客http://helloleex.blog.51cto.com/10728491/1769994
并且为了增强代码的复用性,我使用了仿函数来区别调用默认类型(基本类型,自定义类型)和string类型,使调用更加灵活
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。