您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有关Shiro架构和Hello World的示例分析,可能很多人都不太了解,为了让大家更加了解,小编给大家总结了以下内容,希望大家根据这篇文章可以有所收获。
Shiro 一个Apache 权限处理框架,现在更流行于security,能够指定用户的具体操作哪一个按钮,搭配接口,通过注解实现。
官网:
http://shiro.apache.org/download.html
主要涉及
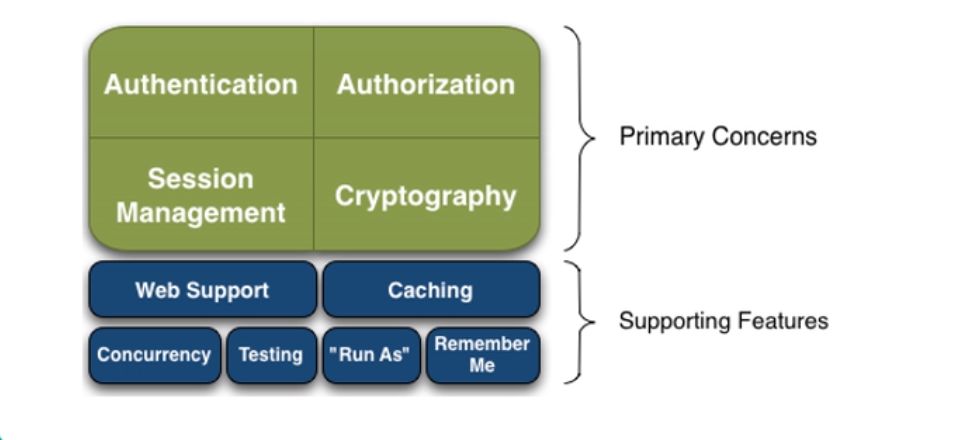
权限管理,权限认证,session管理,加密
支持web,缓存,并发,测试,记住我
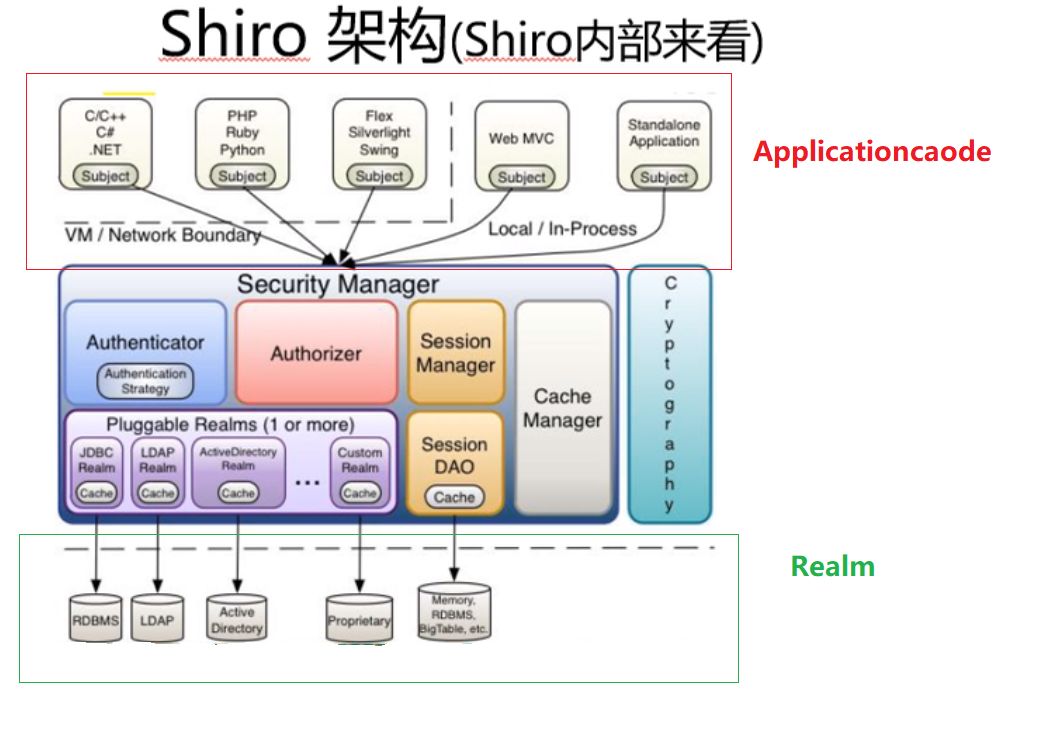
Shiro架构
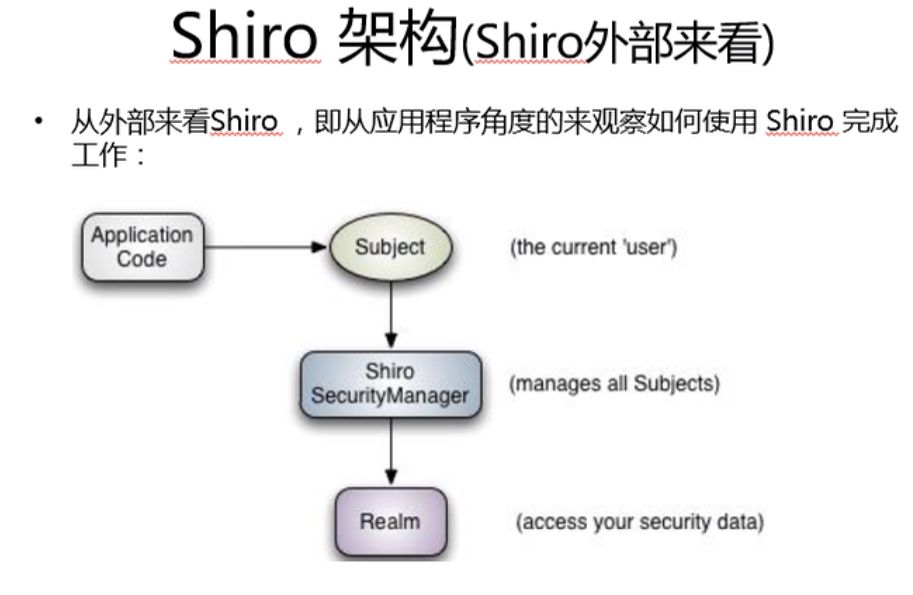
Subject 当前用户
Security 管理subject
Realm 相当于RealmDao
Hello World
找到官网下载zip包。解压后
找到samples/quickstart/QuickStart.java
并将resource下面的配置复制
QuickStart.java
注释已经写在代码内
public class Quickstart {private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Quickstart.class);public static void main(String[] args) {// The easiest way to create a Shiro SecurityManager with configured// realms, users, roles and permissions is to use the simple INI config.// We'll do that by using a factory that can ingest a .ini file and// return a SecurityManager instance:// Use the shiro.ini file at the root of the classpath// (file: and url: prefixes load from files and urls respectively):Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();// for this simple example quickstart, make the SecurityManager// accessible as a JVM singleton. Most applications wouldn't do this// and instead rely on their container configuration or web.xml for// webapps. That is outside the scope of this simple quickstart, so// we'll just do the bare minimum so you can continue to get a feel// for things.SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);// Now that a simple Shiro environment is set up, let's see what you can do:// get the currently executing user://获取当前的subject SecurityUtils.getSubject()Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();// Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)//获取sessionSession session = currentUser.getSession();//放入属性session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");//验证是否取到String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");if (value.equals("aValue")) {log.info("Retrieved the correct value! -*******[" + value + "]");}// let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions://测试是否被认证if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {//用户名密码封装UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");//记住我token.setRememberMe(true);try {//执行登录currentUser.login(token);//如果没有指定的用户} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());//密码错误} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");//用户被锁定} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");}// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application?//总的认证异常处理catch (AuthenticationException ae) {//unexpected condition? error?}}//say who they are://print their identifying principal (in this case, a username):log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully.");//test a role://测试是否有某一个角色if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");} else {log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");}//test a typed permission (not instance-level)//测试用户是否有一个行为 weild//isPermitted The 'schwartz' role can do anything (*) with any lightsaber:if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:weild")) {log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");} else {log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");}//a (very powerful) Instance Level permission://goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5 更具体的行为if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " +"Here are the keys - have fun!");} else {log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!");}//all done - log out!currentUser.logout();System.exit(0);}}
实际应用
@RequiresPermissions("risk:thirdInterface:view")@GetMapping()public String thirdInterface(ModelMap map, ThirdInterface thirdInterface) {List<ThirdInterface> thirdInterfaceList = thirdInterfaceService.selectThirdInterfaceList(thirdInterface);map.put("list", thirdInterfaceList);return prefix + "/thirdInterface";}
配合前端
var editFlag = [[${@permission.hasPermi('system:user:edit')}]];var removeFlag = [[${@permission.hasPermi('system:user:remove')}]];formatter: function(value, row, index) {var actions = [];actions.push('<a class="btn btn-success btn-xs ' + editFlag + '" href="#" onclick="$.operate.edit(\'' + row.userId + '\')"><i class="fa fa-edit"></i>编辑</a> ');actions.push('<a class="btn btn-danger btn-xs ' + removeFlag + '" href="#" onclick="$.operate.remove(\'' + row.userId + '\')"><i class="fa fa-remove"></i>删除</a> ');actions.push('<a class="btn btn-info btn-xs ' + resetPwdFlag + '" href="#" onclick="resetPwd(\'' + row.userId + '\')"><i class="fa fa-key"></i>重置</a>');return actions.join('');}
在角色的分配操作时指定是否拥有某个按钮的权限操作。
看完上述内容,你们对Shiro架构和Hello World的示例分析有进一步的了解吗?如果还想了解更多知识或者相关内容,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢大家的支持。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。