您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章主要介绍springboot+springsecurity怎么实现动态url细粒度权限认证,文中介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们一定要看完!
@Component
//用于设置受保护资源的权限信息的数据源
public class MyFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource implements
FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource {
@Bean
public AntPathMatcher getAntPathMatcher(){
return new AntPathMatcher();
}
@Autowired
//获取数据库中的保存的url Url表只储存受保护的资源,不在表里的资源说明不受保护,任何人都可以访问
private RightsMapper rightsMapper;
@Autowired
private AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher;
@Override
/*
* @param 被调用的保护资源
* @return 返回能够访问该保护资源的角色集合,如果没有,则应返回空集合。
*/
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object)
throws IllegalArgumentException {
FilterInvocation fi = (FilterInvocation) object;
//获取用户请求的Url
String url = fi.getRequestUrl();
//先到数据库获取受权限控制的Url
List<Rights> us = rightsMapper.queryAll();
//用于储存用户请求的Url能够访问的角色
Collection<ConfigAttribute> rs=new ArrayList<ConfigAttribute>();
for(Rights u:us){
if (u.getUrl() != null) {
//逐一判断用户请求的Url是否和数据库中受权限控制的Url有匹配的
if (antPathMatcher.match(u.getUrl(), url)) {
//如果有则将可以访问该Url的角色储存到Collection<ConfigAttribute>
rs.add(rightsMapper.queryById(u.getId()));
}
}
}
if(rs.size()>0) {
return rs;
}
//没有匹配到,就说明此资源没有被控制,所有人都可以访问,返回null即可,返回null则不会进入之后的decide方法
return null;
}
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return FilterInvocation.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
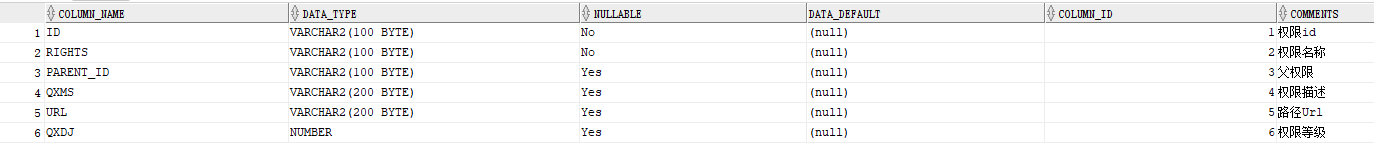
}rights表中的部分内容:
表结构
内容:

@Component
//用于设置判断当前用户是否可以访问被保护资源的逻辑
public class MyAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager {
@Override
/*
* @param 请求该保护资源的用户对象
* @param 被调用的保护资源
* @param 有权限调用该资源的集合
*/
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes)
throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException {
Iterator<ConfigAttribute> ite = configAttributes.iterator();
//遍历configAttributes,查看当前用户是否有对应的权限访问该保护资源
while (ite.hasNext()) {
ConfigAttribute ca = ite.next();
String needRole = ca.getAttribute();
for (GrantedAuthority ga : authentication.getAuthorities()) {
if (ga.getAuthority().equals(needRole)) {
// 匹配到有对应角色,则允许通过
return;
}
}
}
// 该url有配置权限,但是当前登录用户没有匹配到对应权限,则禁止访问
throw new AccessDeniedException("not allow");
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return true;
}
}@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
MyUserDetailsService myUserDetailsService;
@Autowired
private SendSmsSecurityConfig sendSmsSecurityConfig;
@Autowired
private MyAccessDecisionManager myAccessDecisionManager;
@Autowired
private MyFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource myFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
//加密机制
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance(); // 不加密
}
//认证
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(myUserDetailsService)
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
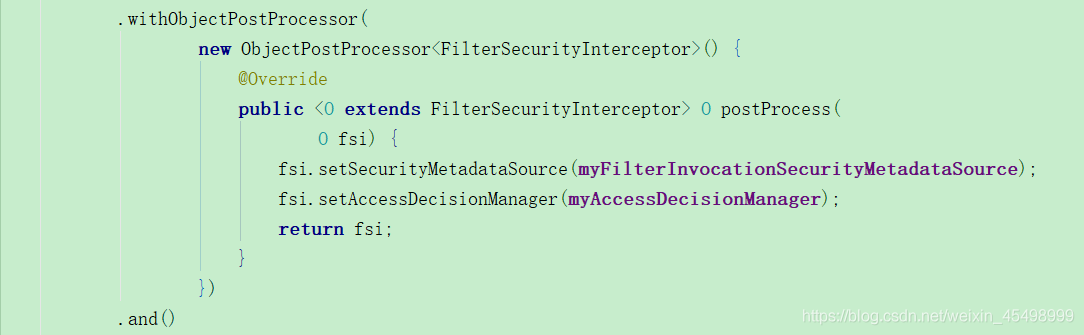
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()//对请求授权
.antMatchers("/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest()//任何请求
.authenticated()//登录后访问
.withObjectPostProcessor(
new ObjectPostProcessor<FilterSecurityInterceptor>() {
@Override
public <O extends FilterSecurityInterceptor> O postProcess(
O fsi) {
fsi.setSecurityMetadataSource(myFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource);
fsi.setAccessDecisionManager(myAccessDecisionManager);
return fsi;
}
})
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}配置如下代码:
至此完成所有配置!!!
自定义权限认证,一部分接口必须要有相应的角色权限,一部分接口面向所有访问者,一部分接口任何人都不能访问。但是在使用 SpringSecurity的过程中发现,框架会将没有指定角色列表的URL资源直接放行,不做拦截。
用户登录认证成功后,携带Token访问URL资源,spring security 根据Token(请求头Authorization中)来分辨不同用户。
用户权限数据源是一个Map:以 URL资源为Key,以有权访问的Key的角色列表为Value。
使用时发现当一个接口有Key,但是Value为空或null时,spring security 框架自动放行,导致了权限失效问题。
第一种方法:
默认rejectPublicInvocations为false。
对需要控制权限的URL资源添加标志,以防止roleList为空,跳过了权限验证.
公共权限设置为null,不进行权限验证
第二种方法:
配置rejectPublicInvocations为true
此后roleList为空,或者没有找到URL资源时,都为拒绝访问
需要控制权限的URL资源,即使对应角色为空,也会进行权限验证
公共权限设置为所有角色和匿名角色,不进行权限验证
package org.springframework.security.access.intercept;
/**
* 对安全对象(访问请求+用户主体)拦截的抽象类源码
*/
public abstract class AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements InitializingBean, ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
// ... 其他方法省略
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Security invocation attempted for object "
+ object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
// 从权限数据源获取了当前 <URL资源> 对应的 <角色列表>
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object);
// 框架在此处判断URL资源对应的角色列表是否为空
if (attributes == null || attributes.isEmpty()) {
// rejectPublicInvocations默认为false
// 可以配置为true,即角色列表为空的时候不进行放行
if (rejectPublicInvocations) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Secure object invocation "
+ object
+ " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Public object - authentication not attempted");
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes);
}
// 如果当前用户权限对象为null
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"),
object, attributes);
}
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization,此处调用accessDecisionManager 进行鉴权
try {
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authorization successful");
}
if (publishAuthorizationSuccess) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
}
// Attempt to run as a different user,这里可以另外配置或修改用户的权限对象,特殊场景使用
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object,
attributes);
if (runAs == null) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object");
}
// no further work post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false,
attributes, object);
}
else {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: " + runAs);
}
SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object);
}
}
// ... 其他方法略
}以上是“springboot+springsecurity怎么实现动态url细粒度权限认证”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!希望分享的内容对大家有帮助,更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。