您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章主要介绍了Spring注解@Value及属性加载配置文件方式的示例分析,具有一定借鉴价值,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。
spring中配置属性加载文件的配置方式
<bean id="configProperties" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertiesFactoryBean"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:/properties/websit.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean>
注意
1.这里使用的configProperties必须要和定义的bean名称一致。
2.websit用来指定msgname来源于那个配置文件
3.配置的加载属性bean名称为org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertiesFactoryBean
使用这种方式,又可以有两种配置方式
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PreferencesPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="properties" ref="configProperties"/> </bean> <bean id="configProperties" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertiesFactoryBean"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:/properties/websit.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean>
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:properties/websit.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean>
当使用@Value注解bean属性时,如果没有在配置文件中配置,这时启动spring就会抛出异常。@Value提供了一种默认值的设置方式,如果在属性文件中没有配置则可以使用默认值。
形式如下
@Value("${avg.age:22}")
private int userAge;如果使用@Value注解后,数据不能正常的被注入则需要在xml的配置文件中加入下列代码
<context:annotation-config/>
为了简化读取properties文件中的配置值,spring支持@value注解的方式来获取,这种方式大大简化了项目配置,提高业务中的灵活性。
1)@Value("#{configProperties['key']}")
2)@Value("${key}")
ftp:
ftplp: 10.2.23.89
ftpPort: 21
ftpUser: uftp
ftpPwd: 12345678
ftpRemotePath: /home
说明:以上是配置文件中的信息,主要是一些账号密码等信息。
package com.dbright.dataprediction.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:ftpconfig.yml")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "ftp")
public class FtpProperties {
@Value("${ftplp}")
public String ftplp;
@Value("${ftpPort}")
public String ftpPort;
@Value("${ftpUser}")
public String ftpUser;
@Value("${ftpPwd}")
public String ftpPwd;
@Value("${ftpRemotePath}")
public String ftpRemotePath;
public String getFtplp() {
return ftplp;
}
public void setFtplp(String ftplp) {
this.ftplp = ftplp;
}
public String getFtpPort() {
return ftpPort;
}
public void setFtpPort(String ftpPort) {
this.ftpPort = ftpPort;
}
public String getFtpUser() {
return ftpUser;
}
public void setFtpUser(String ftpUser) {
this.ftpUser = ftpUser;
}
public String getFtpPwd() {
return ftpPwd;
}
public void setFtpPwd(String ftpPwd) {
this.ftpPwd = ftpPwd;
}
public String getFtpRemotePath() {
return ftpRemotePath;
}
public void setFtpRemotePath(String ftpRemotePath) {
this.ftpRemotePath = ftpRemotePath;
}
}说明:以上是使用@value注解来读取yml配置文件的代码示例
1)@component —— 把普通pojo实例化到spring容器中,相当于配置文件中的`<bean id="" class=""/>`
2) @PropertySource("classpath:ftpconfig.yml") —— 设置yml文件的路径,方便扫描到。一般我们配置文件都是放在resources包下。所以我们只需要 classpath+所需要读取的配置文件名称。
3)@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "ftp") —— 这个不需要解释太多,配置文件里面内容的前缀,我们读取的是ftp下的信息。
4)@Value("${ftplp}") —— 这是读取我们所需的配置信息,美元符号+{字段名}即可制定
5)下面定义字符串来接收所读取到的配置信息。
6)写set和get方法,方便外部类调用。
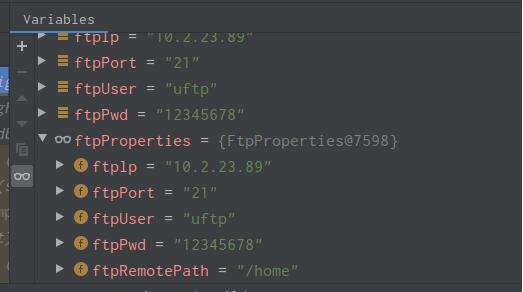
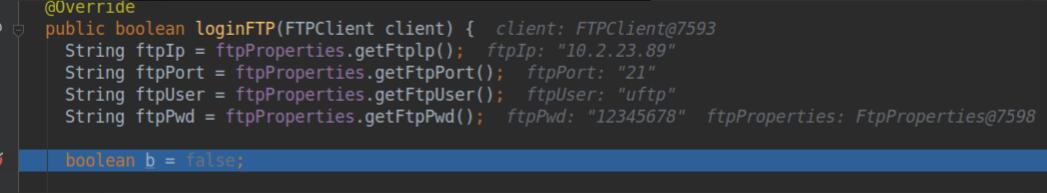
可以看到,我们成功取到了我们想要的值。
把{}外的 $ 变成 # 号,然后里面指定配置文件的信息+字段而已。大同小异,我就不贴代码上来了。
感谢你能够认真阅读完这篇文章,希望小编分享的“Spring注解@Value及属性加载配置文件方式的示例分析”这篇文章对大家有帮助,同时也希望大家多多支持亿速云,关注亿速云行业资讯频道,更多相关知识等着你来学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。