您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章主要为大家展示了“vuex如何安装使用”,内容简而易懂,条理清晰,希望能够帮助大家解决疑惑,下面让小编带领大家一起研究并学习一下“vuex如何安装使用”这篇文章吧。
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化.
先安装vuex。
npm install vuex --save
在main.js中引入后即可使用。
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
//vuex使用
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//全局变量
count: 31231
}
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
//vuex必须加入
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})<template>
<div>
老大有{{showData}}
<HelloWorld2/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld2 from './HelloWorld2'
import son from './son'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data () {
return {
message2:"",
cou
}
},
components:{
HelloWorld2,
son
},computed: {
showData(){
return this.$store.state.count;
}
}
}
</script><template>
<div>
老二有{{$store.state.count}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld2',
data() {
return {
}
}
}
</script>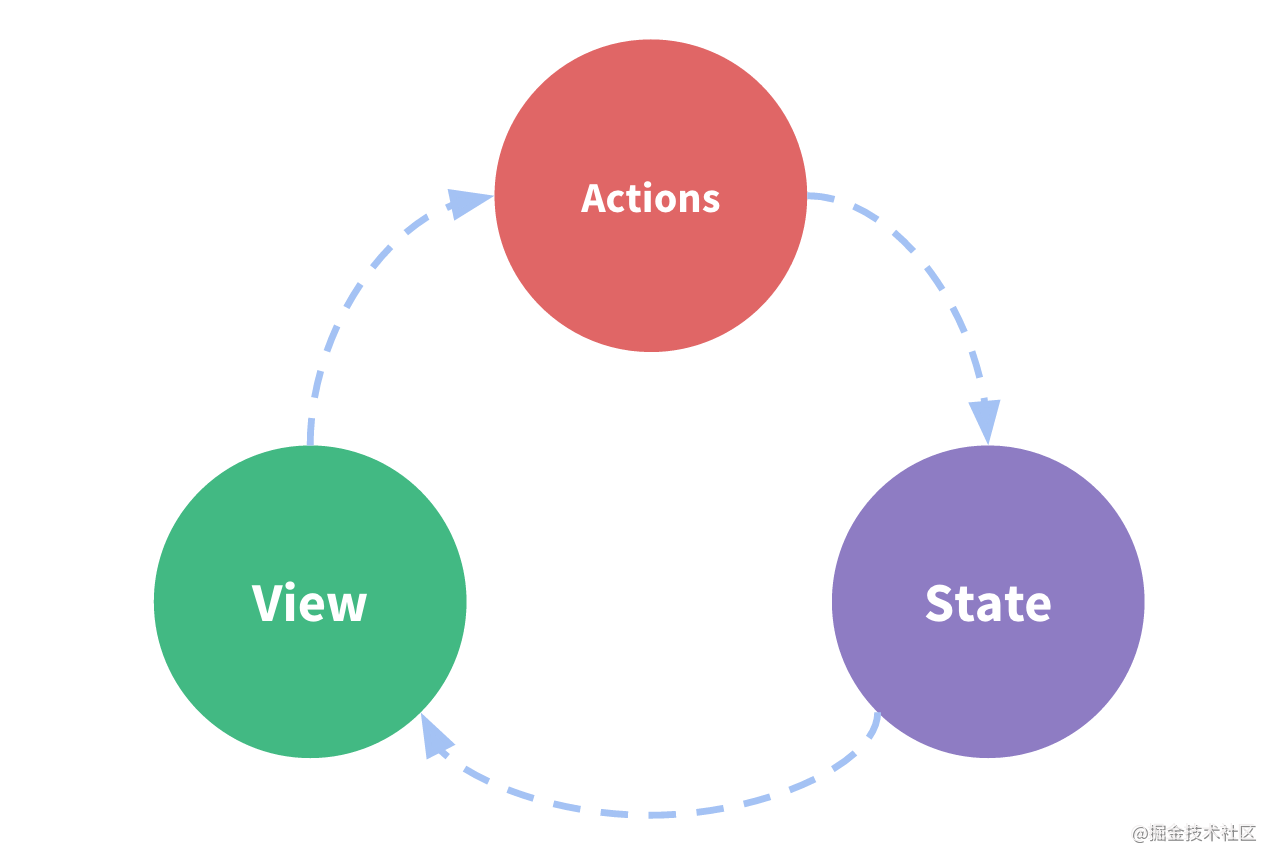
如图当没有使用vuex时流程为: view->actions->state->view
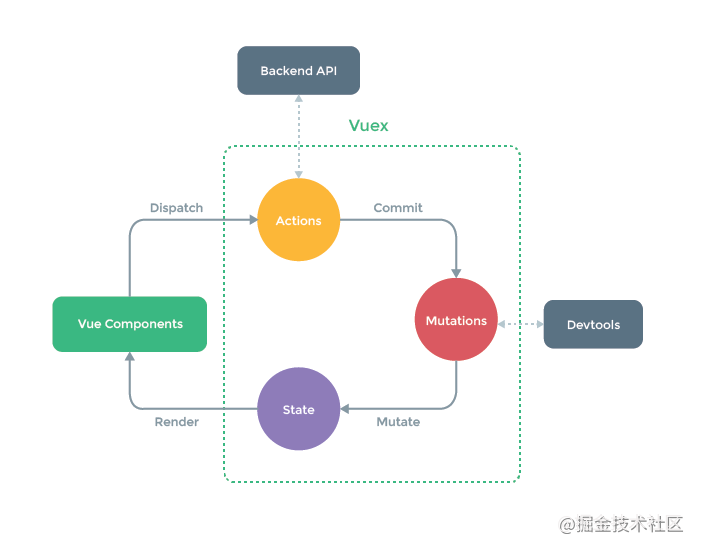
使用了vuex后流程为vuecomponent->(dispatch)actions->(commit)mutations->(mutate)state->(render)->vuecomponent
状态更改,更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type)和一个回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数。
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
//vuex使用
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//全局变量
count: 31231
},
//更改状态方法
mutations: {
//state为上面的state
addData(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
}
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
//vuex必须加入
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})然后执行更改
<template>
<div>
老大有{{showData}}
<HelloWorld2/>
<button type = "button" v-on:click = "changeData"> 修改按钮 </button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld2 from './HelloWorld2'
import son from './son'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data () {
return {
message2:"",
}
},
components:{
HelloWorld2,
son
},computed: {
showData(){
return this.$store.state.count;
}
},
methods: {
//执行更改
changeData(event){
this.$store.commit("addData");
}
}
}
</script>可以限制mutation 比如小于0就不能减少了
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
//vuex使用
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//全局变量
count: 0
},
//更改状态方法
mutations: {
//state为上面的state
addData(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
},
//过滤
getters: {
getState(state) {
if (state.count >= 5) {
return 5
} else {
return state.count
}
}
}
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
//vuex必须加入
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})调用时
<template>
<div>
老二有{{$store.getters.getState}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld2',
data() {
return {
}
}
}
</script>Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。 Action 可以包含任意异步操作。 mutation只能同步处理
main.js。示例如下:
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
//vuex使用
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//全局变量
count: 0
},
//更改状态方法
mutations: {
//state为上面的state
addData(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
},
//过滤
getters: {
getState(state) {
if (state.count >= 5) {
return 5
} else {
return state.count
}
}
},
actions: {
//action触发的mutations方法 优势是异步处理
addData(context) {
//模拟异步
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('addData')
}, 1000)
}
}
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
//vuex必须加入
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})在发送时 应该调用action。
<template>
<div>
老大有{{showData}}
<HelloWorld2/>
<button type = "button" v-on:click = "changeData"> 修改按钮 </button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld2 from './HelloWorld2'
import son from './son'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data () {
return {
message2:"",
}
},
components:{
HelloWorld2,
son
},computed: {
showData(){
return this.$store.getters.getState;
}
},
methods: {
//执行更改
changeData(event){
//操作mutations方法
//this.$store.commit("addData");
//应该操作action而不是action触发的mutations方法
this.$store.dispatch("addData");
}
}
}
</script>由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割:
如路由可以分割文件 不在main.js中放入vuex 新建store/index.js
//vuex使用
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//全局变量
count: 0
},
//更改状态方法
mutations: {
//state为上面的state
addData(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
},
//过滤
getters: {
getState(state) {
if (state.count >= 5) {
return 5
} else {
return state.count
}
}
},
actions: {
//action触发的mutations方法 优势是异步处理
addData(context) {
//模拟异步
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('addData')
}, 1000)
}
}
})修改main.js
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
//vuex必须加入
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})我们还能把main.js中的state拿出 新建store/state.js
export default {
count: 0
}然后index.js可以改成
//vuex使用
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import state from './state'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: state,
//更改状态方法
mutations: {
//state为上面的state
addData(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
},
//过滤
getters: {
getState(state) {
if (state.count >= 5) {
return 5
} else {
return state.count
}
}
},
actions: {
//action触发的mutations方法 优势是异步处理
addData(context) {
//模拟异步
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('addData')
}, 1000)
}
}
})以上是“vuex如何安装使用”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。