您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
本篇内容主要讲解“C语言和C++中多重继承的优缺点以及用法介绍”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“C语言和C++中多重继承的优缺点以及用法介绍”吧!
概述
优缺点
优点
缺点
声明多重继承的方法
格式
例子
二义性
两个基类有同名成员
基类和派生类有同名成员
两个基类从同一个基类派生
多重继承 (multiple inheritance): 一个派生类有两个或多个基类, 派生类从两个或多个基类中继承所需的属性. C++ 为了适应这种情况, 允许一个派生类同时继承多个基类. 这种行为称为多重继承.
自然地做到了对单继承的扩展
可以继承多个类的功能
结构复杂化
优先顺序模糊
功能冲突
多重继承的格式:
派生类构造函数名(总形式参数表列):
基类1构造函数(实际参数表列),
基类2构造函数(实际参数表列),
基类3构造函数(实际参数表列)
{
派生类中新增数成员据成员初始化语句
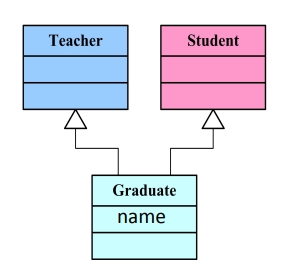
}Teacher 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
#define PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher {
protected:
string name;
int age;
string title;
public:
Teacher(string n, int a, string t);
void display_teacher();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_TEACHER_HTeacher.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Teacher.h"
using namespace std;
Teacher::Teacher(string n, int a, string t) : name(n), age(a), title(t) {}
void Teacher::display_teacher() {
cout << "Teacher name: " << name << endl;
cout << "age: " << age << endl;
cout << "title: " << title << endl;
}Student 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
#define PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student {
protected:
string name;
char gender;
double score;
public:
Student(string n, char g, double s);
void display_student();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_STUDENT_HStudent.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
Student::Student(string n, char g, double s) : name(n), gender(g), score(s) {}
void Student::display_student() {
cout << "Student name: " << name << endl;
cout << "gender: " << gender << endl;
cout << "score: " << score << endl;
}Graduate 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
#define PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
#include "Teacher.h"
#include "Student.h"
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Graduate : public Teacher, public Student{
private:
double wage;
public:
Graduate(string t_n, int t_a, string t_t, string s_n, char s_g, double s_s);
void display_graduate();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_GRADUATE_HGraduate.cpp:
#include "Graduate.h"
Graduate::Graduate(string t_n, int t_a, string t_t, string s_n, char s_g, double s_s) :
Teacher(t_n, t_a, t_t),
Student(s_n, s_g, s_s) {}
void Graduate::display_graduate() {
display_teacher();
display_student();
}main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Graduate.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Graduate graduate1("王叔叔", 18, "隔壁老王", "我是小白呀", 'f', 99);
graduate1.display_graduate();
return 0;
}输出结果:
Teacher name: 王叔叔 age: 18 title: 隔壁老王 Student name: 我是小白呀 gender: f score: 99
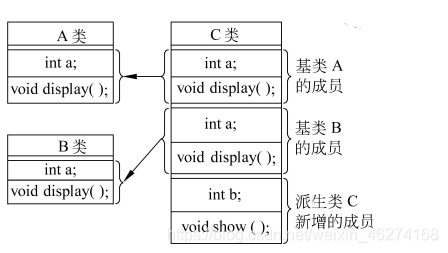
二义性 (Ambiguity) 指在多重继承中, 两个基类中的数据成员名相同.
二义性在派生类中的解决方法:
在标识符前用类名做前缀: Teacher::name 和 Student::name
基类和派生类需要有一个完整的设计, 不能随意而为
A 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_A_H
#define PROJECT5_A_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "A's num:" << num << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_A_HB 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_B_H
#define PROJECT5_B_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class B {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "B's num:" << num << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_B_HC 类:
#ifndef PROJECT5_C_H
#define PROJECT5_C_H
#include <iostream>
#include "A.h"
#include "B.h"
using namespace std;
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int c;
void display() {cout << c << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_C_Hmain:
#include <iostream>
#include "C.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
C c1;
c1.A::num = 1; // 用基类名限定
c1.B::num = 2; // 用基类名限定
c1.A::display();
c1.B::display();
return 0;
}输出结果:
A's num:1 B's num:2
错误的写法
#include <iostream>
#include "C.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
C c1;
c1.num = 1;
c1.display();
return 0;
}A 类:
class A {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "A's num:" << num << endl;};
};B 类:
class B {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "B's num:" << num << endl;};
};C 类:
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "C's num:" << num << endl;};
};main:
int main() {
C c1;
c1.num = 3;
c1.A::num = 1;
c1.B::num = 2;
c1.display();
c1.A::display();
c1.B::display();
return 0;
}输出结果:
C's num:3 A's num:1 B's num:2
同名覆盖:
基类的同名成员在派生类中被屏蔽, 成为 "不可见"的
对成员函数, 限于函数名和参数个数相同, 类型相匹配. 若只有函数名相同而参数不同, 属于函数重载
N 类:
class N {
public:
int a;
void display(){
cout << "A::a=" << a <<endl;
}
};A 类:
class A : public N {
public:
int a1;
};B 类:
class B : public N {
public:
int a2;
};C 类:
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int a3;
void display() {cout << "a3=" << a3 << endl;};
};main:
int main() {
C c1;
// 合法访问
c1.A::a = 3;
c1.A::display();
return 0;
}输出结果:
A::a=3
到此,相信大家对“C语言和C++中多重继承的优缺点以及用法介绍”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。