жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
иҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« дё»иҰҒдёәеӨ§е®¶еұ•зӨәдәҶвҖңSpring AOPеҰӮдҪ•е®һзҺ°еӨҚжқӮзҡ„ж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•ж“ҚдҪңвҖқпјҢеҶ…е®№з®ҖиҖҢжҳ“жҮӮпјҢжқЎзҗҶжё…жҷ°пјҢеёҢжңӣиғҪеӨҹеё®еҠ©еӨ§е®¶и§ЈеҶіз–‘жғ‘пјҢдёӢйқўи®©е°Ҹзј–еёҰйўҶеӨ§е®¶дёҖиө·з ”究并еӯҰд№ дёҖдёӢвҖңSpring AOPеҰӮдҪ•е®һзҺ°еӨҚжқӮзҡ„ж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•ж“ҚдҪңвҖқиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« еҗ§гҖӮ
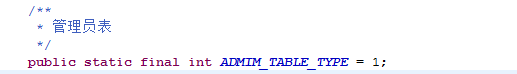
еҒҡйЎ№зӣ®дёӯпјҢдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘иҰҒжұӮеҸӘиҰҒеҜ№ж•°жҚ®еә“ж•°жҚ®иҝӣиЎҢж”№еҠЁзҡ„йғҪйңҖиҰҒи®°еҪ•ж—Ҙеҝ—пјҲеўһеҲ ж”№пјүпјҢи®°еҪ•зҡ„еҶ…е®№жңүж“ҚдҪңиҖ…гҖҒж“ҚдҪңзҡ„иЎЁеҗҚеҸҠиЎЁеҗҚз§°гҖҒе…·дҪ“зҡ„ж“ҚдҪңпјҢд»ҘеҸҠж“ҚдҪңеҜ№еә”зҡ„ж•°жҚ®гҖӮ
йҰ–е…ҲжғіеҲ°зҡ„е°ұжҳҜSpring зҡ„AOPеҠҹиғҪгҖӮеҸҜжҳҜз»ҸиҝҮдёҖз•ӘдәҶи§ЈиҝҮеҗҺпјҢеҸ‘зҺ°дёҖиҲ¬зҡ„ж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•пјҢеҸӘиғҪи®°еҪ•дёҖдәӣз®ҖеҚ•зҡ„ж“ҚдҪңпјҢдҫӢеҰӮиЎЁеҗҚгҖҒиЎЁеҗҚз§°зӯүи®°еҪ•дёҚеҲ°гҖӮ
дәҺжҳҜжғіеҲ°дәҶиҮӘе®ҡд№үжіЁи§Јзҡ„ж–№жі•пјҢжҠҠжғіиҰҒи®°еҪ•зҡ„еҶ…е®№ж”ҫеңЁжіЁи§ЈдёӯпјҢйҖҡиҝҮеҲҮе…ҘзӮ№жқҘиҺ·еҸ–жіЁи§ЈеҸӮж•°пјҢе°ұиғҪиҺ·еҸ–иҮӘе·ұжғіиҰҒзҡ„ж•°жҚ®пјҢи®°еҪ•ж•°жҚ®еә“дёӯгҖӮйЎәзқҖиҝҷдёӘжҖқи·ҜпјҢеңЁзҪ‘дёҠжҹҘжүҫдәҶдёҖдәӣзӣёе…іиө„ж–ҷпјҢжңҖз»Ҳе®һзҺ°еҠҹиғҪгҖӮиҜқдёҚеӨҡиҜҙпјҢд»ҘдёӢе°ұжҳҜе®һзҺ°зҡ„жҖқи·ҜеҸҠд»Јз Ғпјҡ
еңЁд»Јз Ғдёӯж·»еҠ иҮӘе®ҡд№үжіЁи§ЈпјҢ并且е®ҡд№үдёӨдёӘеұһжҖ§пјҢдёҖдёӘжҳҜж—Ҙеҝ—зҡ„жҸҸиҝ°пјҲdescriptionпјүпјҢиҝҳжңүдёӘжҳҜж“ҚдҪңиЎЁзұ»еһӢпјҲtableTypeпјүпјҢеұһжҖ§еҸӮж•°еҸҜжҢүйңҖжұӮж”№еҸҳгҖӮд»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢпјҡ
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* ClassName: SystemServiceLog <br/>
* Function: AOPж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•пјҢиҮӘе®ҡд№үжіЁи§Ј <br/>
* date: 2016е№ҙ6жңҲ7ж—Ҙ дёҠеҚҲ9:29:01 <br/>
* @author lcma
* @version
* @since JDK 1.7
*/
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SystemServiceLog {
/**
* ж—Ҙеҝ—жҸҸиҝ°
*/
String description() default "";
/**
* ж“ҚдҪңиЎЁзұ»еһӢ
*/
int tableType() default 0;
}е®ҡд№үеҲҮйқўзұ»пјҢиҺ·еҸ–еҲҮйқўеҸӮж•°пјҢдҝқеӯҳж•°жҚ®еә“е…·дҪ“д»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢпјҡ
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import com.iflytek.zhbs.common.annotation.SystemServiceLog;
import com.iflytek.zhbs.common.util.JacksonUtil;
import com.iflytek.zhbs.common.util.WebUtils;
import com.iflytek.zhbs.dao.BaseDaoI;
import com.iflytek.zhbs.domain.CmsAdmin;
import com.iflytek.zhbs.domain.CmsOperationLog;
@Aspect
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public class SystemLogAspect {
@Resource
private BaseDaoI<CmsOperationLog> logDao;
/**
* ж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•
*/
private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(SystemLogAspect.class);
/**
* ServiceеұӮеҲҮзӮ№
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.iflytek.zhbs.common.annotation.SystemServiceLog)")
public void serviceAspect() {
}
/**
* doServiceLog:иҺ·еҸ–жіЁи§ЈеҸӮж•°пјҢи®°еҪ•ж—Ҙеҝ—. <br/>
* @author lcma
* @param joinPoint еҲҮе…ҘзӮ№еҸӮж•°
* @since JDK 1.7
*/
@After("serviceAspect()")
public void doServiceLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
LOGGER.info("ж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•");
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
//иҺ·еҸ–з®ЎзҗҶе‘ҳз”ЁжҲ·дҝЎжҒҜ
CmsAdmin admin = WebUtils.getAdminInfo(request);
try {
//ж•°жҚ®еә“ж—Ҙеҝ—
CmsOperationLog log = new CmsOperationLog();
log.setOperationType(getServiceMthodTableType(joinPoint));
//иҺ·еҸ–ж—Ҙеҝ—жҸҸиҝ°дҝЎжҒҜ
String content = getServiceMthodDescription(joinPoint);
log.setContent(admin.getRealName() + content);
log.setRemarks(getServiceMthodParams(joinPoint));
log.setAdmin(admin);
log.setCreateTime(new Date());
logDao.save(log);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("ејӮеёёдҝЎжҒҜ:{}", e);
}
}
/**
* getServiceMthodDescription:иҺ·еҸ–жіЁи§ЈдёӯеҜ№ж–№жі•зҡ„жҸҸиҝ°дҝЎжҒҜ з”ЁдәҺserviceеұӮжіЁи§Ј . <br/>
* @author lcma
* @param joinPoint еҲҮзӮ№
* @return ж–№жі•жҸҸиҝ°
* @throws Exception
* @since JDK 1.7
*/
private String getServiceMthodDescription(JoinPoint joinPoint)
throws Exception {
String targetName = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object[] arguments = joinPoint.getArgs();
Class targetClass = Class.forName(targetName);
Method[] methods = targetClass.getMethods();
String description = "";
for(Method method : methods) {
if(method.getName().equals(methodName)) {
Class[] clazzs = method.getParameterTypes();
if(clazzs.length == arguments.length) {
description = method.getAnnotation(SystemServiceLog.class).description();
break;
}
}
}
return description;
}
/**
* getServiceMthodTableType:иҺ·еҸ–жіЁи§ЈдёӯеҜ№ж–№жі•зҡ„ж•°жҚ®иЎЁзұ»еһӢ з”ЁдәҺserviceеұӮжіЁи§Ј . <br/>
* @author lcma
* @param joinPoint
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @since JDK 1.7
*/
private nt getServiceMthodTableType(JoinPoint joinPoint)
throws Exception {
String targetName = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object[] arguments = joinPoint.getArgs();
Class targetClass = Class.forName(targetName);
Method[] methods = targetClass.getMethods();
int tableType = 0;
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.getName().equals(methodName)) {
Class[] clazzs = method.getParameterTypes();
if (clazzs.length == arguments.length) {
tableType = method.getAnnotation(SystemServiceLog.class).tableType();
break;
}
}
}
return tableType;
}
/**
* getServiceMthodParams:иҺ·еҸ–jsonж јејҸзҡ„еҸӮж•°. <br/>
* @author lcma
* @param joinPoint
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @since JDK 1.7
*/
private String getServiceMthodParams(JoinPoint joinPoint)
throws Exception {
Object[] arguments = joinPoint.getArgs();
String params = JacksonUtil.toJSon(arguments);
return params;
}
}йңҖиҰҒжіЁж„Ҹзҡ„жҳҜпјҢе®ҡд№үеҲҮзӮ№зҡ„ж—¶еҖҷпјҢ@PointcutйҮҢйқўжҳҜиҮӘе®ҡд№үжіЁи§Јзҡ„и·Ҝеҫ„
жҜҸдёӘеҲҮйқўдј йҖ’зҡ„ж•°жҚ®зҡ„йғҪдёҚдёҖж ·пјҢжңҖз»ҲеҶіе®ҡпјҢиҺ·еҸ–еҲҮйқўзҡ„жүҖжңүеҸӮж•°пјҢиҪ¬жҲҗjsonеӯ—з¬ҰдёІпјҢдҝқеӯҳеҲ°ж•°жҚ®еә“дёӯгҖӮ
еңЁserviceйңҖиҰҒи®°еҪ•ж—Ҙеҝ—зҡ„ең°ж–№иҝӣиЎҢжіЁи§ЈпјҢд»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢпјҡ
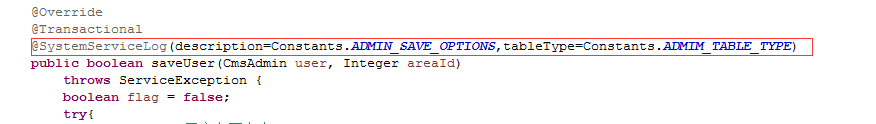
@SystemServiceLog(description=Constants.ADMIN_SAVE_OPTIONS,tableType=Constants.ADMIM_TABLE_TYPE)
д»Јз ҒеӣҫзүҮпјҡ
еңЁеёёйҮҸзұ»йҮҢйқўй…ҚзҪ®иҮӘе®ҡд№үжіЁи§Јзҡ„еҸӮж•°еҶ…е®№:
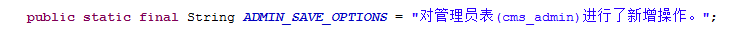
жҠҠеҲҮйқўзұ»жүҖеңЁзҡ„еҢ…и·Ҝеҫ„ж·»еҠ еҲ°SpringжіЁи§ЈиҮӘеҠЁжү«жҸҸи·Ҝеҫ„дёӢпјҢ并且еҗҜеҠЁеҜ№@AspectJжіЁи§Јзҡ„ж”ҜжҢҒпјҢд»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢпјҡ
<!-- еҗҜеҠЁеҜ№@AspectJжіЁи§Јзҡ„ж”ҜжҢҒ --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true" /> <!-- иҮӘеҠЁжү«жҸҸеҢ…и·Ҝеҫ„ --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.iflytek.zhbs.common.aoplog" /> <context:component-scan base-package="com.iflytek.zhbs.service" />
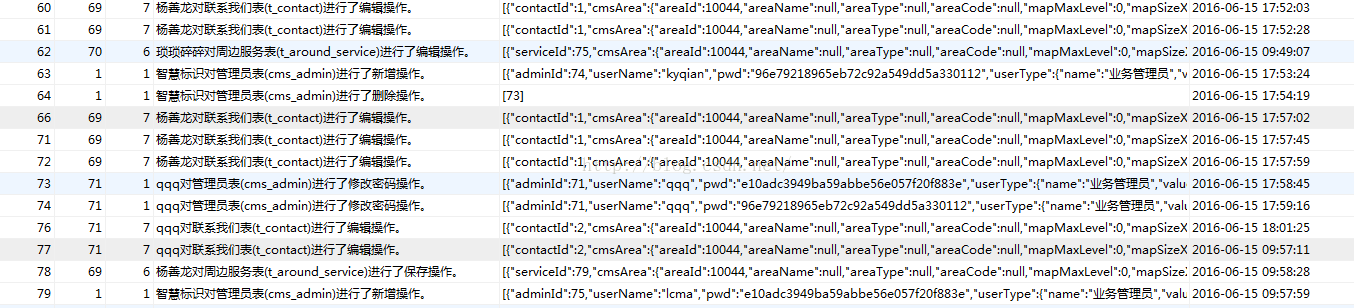
жңҖеҗҺж•°жҚ®еә“и®°еҪ•ж•°жҚ®зҡ„ж•ҲжһңеҰӮеӣҫпјҡ
OKпјҢеҠҹиғҪе·Із»Ҹе®һзҺ°пјҢеҲқж¬ЎеҶҷеҚҡе®ўпјҢеҶҷзҡ„дёҚеҘҪзҡ„ең°ж–№иҜ·и°…и§ЈгҖӮ
springдёӯжңүж—¶еҖҷдёҖдёӘзұ»дёҠйқўж Үи®°еҫҲеӨҡжіЁи§ЈгҖӮ
е®һйҷ…дёҠJavaжіЁи§ЈеҸҜд»ҘиҝӣиЎҢ继жүҝ(д№ҹе°ұжҳҜжҠҠеӨҡдёӘжіЁи§ЈеҗҲ并жҲҗ1дёӘ)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/person")еҸҜд»ҘеҗҲ并дёәдёҖдёӘ
@PathRestController("/user")е®һзҺ°жҳҜпјҡ
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@RestController
@RequestMapping
public @interface PathRestController {
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
}д»ҘдёҠжҳҜвҖңSpring AOPеҰӮдҪ•е®һзҺ°еӨҚжқӮзҡ„ж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•ж“ҚдҪңвҖқиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« зҡ„жүҖжңүеҶ…е®№пјҢж„ҹи°ўеҗ„дҪҚзҡ„йҳ…иҜ»пјҒзӣёдҝЎеӨ§е®¶йғҪжңүдәҶдёҖе®ҡзҡ„дәҶи§ЈпјҢеёҢжңӣеҲҶдә«зҡ„еҶ…е®№еҜ№еӨ§е®¶жңүжүҖеё®еҠ©пјҢеҰӮжһңиҝҳжғіеӯҰд№ жӣҙеӨҡзҹҘиҜҶпјҢж¬ўиҝҺе…іжіЁдәҝйҖҹдә‘иЎҢдёҡиө„и®Ҝйў‘йҒ“пјҒ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ