您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
小编给大家分享一下JPA怎么通过Specification实现复杂查询,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后都有所收获,下面让我们一起去探讨吧!
JPA中继承BaseRepo之后,可以使用最基本的增删改查,如果想实现复杂查询,则需要借助Specification来完成这个功能:
public void findAll(ConstructPlanPageReqEntity constructPlanPageReqEntity) {
Integer pageNum = page.getPageNum();
Integer pageSize = page.getPageSize();
String costType = constructPlanPageReqEntity.getCostType();
String name = constructPlanPageReqEntity.getName();
String planMoneyStart = constructPlanPageReqEntity.getPlanMoneyStart();
String planMoneyEnd = constructPlanPageReqEntity.getPlanMoneyEnd();
String singMoneyEnd = constructPlanPageReqEntity.getSingMoneyEnd();
String signMoneyStart = constructPlanPageReqEntity.getSignMoneyStart();
long projectId = Long.parseLong(constructPlanPageReqEntity.getProjectId());
String status = constructPlanPageReqEntity.getStatus();
//分页
pageNum=pageNum-1;
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(pageNum, pageSize);
//多条件匹配查询
Specification specification= new Specification<ContractPlanBean>() {
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<ContractPlanBean> root, CriteriaQuery<?> criteriaQuery, CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder) {
ArrayList<Predicate> list = new ArrayList<>();
Path<String> costType1 = root.get("costType");
Path<String> name1 = root.get("name");
Path<Long> projectId1 = root.get("projectId");
Path<Object> status1 = root.get("status");
if (projectId>0){
list.add(criteriaBuilder.equal(projectId1,projectId));
}
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(status)){
list.add(criteriaBuilder.equal(status1,status));
}
//条件查询
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(costType)){
list.add(criteriaBuilder.equal(costType1,costType));
}
//模糊查询
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(name)){
list.add(criteriaBuilder.like(name1,"%"+name+"%"));
}
//范围查询
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(planMoneyStart)&&StringUtil.isNotEmpty(planMoneyEnd)){
try {
list.add(criteriaBuilder.between(root.get("planMoney"),NumberUtil.strToDouble(planMoneyStart),NumberUtil.strToDouble(planMoneyEnd)));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ApiException("规划金额查询失败");
}
}
//排序
criteriaQuery.orderBy(criteriaBuilder.asc(root.get("name")));
Predicate[] array = new Predicate[list.size()];
return criteriaBuilder.and(list.toArray(array));
}
};
}以上代码实现了多条件查询,其中需要重写toPredicate方法,具体参数:
用root.get()获取bean中的数据库对应字段
用criteriaBuilder来组建条件查询语句
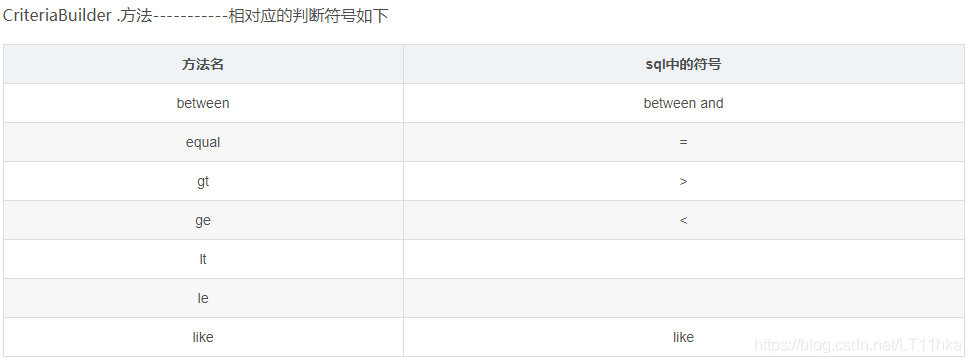
上图是criteriaBuilder各种sql符号的方法名,根据需求组建不同的sql语句
criteriaBuilder.and(list.toArray(array))这句是最后定义各个sql查询条件的关系,这里用的and
至此,复杂sql语句就拼接完成,本人对Specification的使用未进行深入研究,个人觉得相对filter Strem的复杂查询来说Specification更繁琐,因此更倾向于通过Strem的复杂查询,这回就不多说了,下次就介绍下如何使用Stream进行复杂查询
public Page<ServiceItem> findAll(Map<String, String[]> params, ServiceItemConsumeStatus serviceItemConsumeStatus,ServiceItemStatus serviceItemStatus, Pageable pageable) {
return dao.findAll(spec(serviceItemConsumeStatus, serviceItemStatus, params), pageable);
}
private Specification<ServiceItem> spec(final ServiceItemConsumeStatus serviceItemConsumeStatus,
final ServiceItemStatus serviceItemStatus, Map<String, String[]> params) {
Collection<SearchFilter> filters = SearchFilter.parse(params).values();
final Specification<ServiceItem> fsp = SearchFilter.spec(filters, ServiceItem.class);
Specification<ServiceItem> sp = new Specification<ServiceItem>() {
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<ServiceItem> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) {
Predicate pred = fsp.toPredicate(root, query, cb);
if (ServiceItemConsumeStatus.可消费.equals(serviceItemConsumeStatus)) {
pred = cb.and(pred, cb.gt(root.get("countLeft").as(int.class), 0));
} else if (ServiceItemConsumeStatus.消费完毕.equals(serviceItemConsumeStatus)) {
pred = cb.and(pred, cb.le(root.get("countLeft").as(int.class), 0));
}
if (serviceItemStatus != null) {
pred = cb.and(pred, cb.equal(root.get("status"), serviceItemStatus));
}
return pred;
}
};
return sp;
}看完了这篇文章,相信你对“JPA怎么通过Specification实现复杂查询”有了一定的了解,如果想了解更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。