您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章给大家介绍java对象作为key值的实例分析,内容非常详细,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考借鉴,希望对大家能有所帮助。
下面在---- 手写redis @ Cacheable注解支持过期时间设置 的基础之上进行扩展。
@ Cacheable(key = “'leader'+#p0 +#p1 +#p2” )一般用法,#p0表示方法的第一个参数,#p1表示第二个参数,以此类推。
目前方法的第一个参数为Java的对象,但是原注解只支持Java的的基本数据类型。
1.在原注解中加入新的参数,
objectIndexArray表示哪几个角标参数(从0开始)为java对象,objectFieldArray表示对应位置该对象的字段值作为key
2.如何获取参数的对象以及该字段的值
使用的java的反射,拼接get方法获取该字段值。
修改java注解@ExtCacheable,本文中使用@NewCacheable
package com.huajie.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface NewCacheable {
String key() default "";
int[] objectIndexArray();
String[] objectFieldArray();
int expireTime() default 1800;//30分钟
}SpringAop切面NewCacheableAspect
获取AOP整体流程没有任何变化
主要是关键值获取的方式,发生了变化

使用Java的反射技术
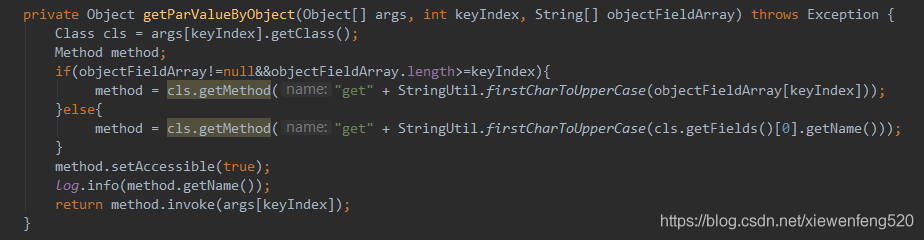
完整代码如下:
package com.huajie.aspect;
import com.huajie.annotation.NewCacheable;
import com.huajie.utils.RedisUtil;
import com.huajie.utils.StringUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* redis缓存处理 不适用与内部方法调用(this.)或者private
*/
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class NewCacheableAspect {
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisUtil;
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.huajie.annotation.NewCacheable)")
public void annotationPointcut() {
}
@Around("annotationPointcut()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 获得当前访问的class
Class<?> className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass();
// 获得访问的方法名
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
// 得到方法的参数的类型
Class<?>[] argClass = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getParameterTypes();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String key = "";
int expireTime = 3600;
try {
// 得到访问的方法对象
Method method = className.getMethod(methodName, argClass);
method.setAccessible(true);
// 判断是否存在@ExtCacheable注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(NewCacheable.class)) {
NewCacheable annotation = method.getAnnotation(NewCacheable.class);
key = getRedisKey(args, annotation);
expireTime = getExpireTime(annotation);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("redis缓存注解参数异常", e);
}
log.info(key);
boolean hasKey = redisUtil.hasKey(key);
if (hasKey) {
return redisUtil.get(key);
} else {
Object res = joinPoint.proceed();
redisUtil.set(key, res);
redisUtil.expire(key, expireTime);
return res;
}
}
private int getExpireTime(NewCacheable annotation) {
return annotation.expireTime();
}
private String getRedisKey(Object[] args, NewCacheable annotation) throws Exception{
String primalKey = annotation.key();
// 获取#p0...集合
List<String> keyList = getKeyParsList(primalKey);
for (String keyName : keyList) {
int keyIndex = Integer.parseInt(keyName.toLowerCase().replace("#p", ""));
Object parValue = getParValue(annotation, keyIndex, args);
primalKey = primalKey.replace(keyName, String.valueOf(parValue));
}
return primalKey.replace("+", "").replace("'", "");
}
private Object getParValue(NewCacheable annotation, int keyIndex, Object[] args) throws Exception{
int[] objectIndexArray = annotation.objectIndexArray();
String[] objectFieldArray = annotation.objectFieldArray();
if (existsObject(keyIndex, objectIndexArray)) {
return getParValueByObject(args, keyIndex, objectFieldArray);
} else {
return args[keyIndex];
}
}
private Object getParValueByObject(Object[] args, int keyIndex, String[] objectFieldArray) throws Exception {
Class cls = args[keyIndex].getClass();
Method method;
if(objectFieldArray!=null&&objectFieldArray.length>=keyIndex){
method = cls.getMethod("get" + StringUtil.firstCharToUpperCase(objectFieldArray[keyIndex]));
}else{
method = cls.getMethod("get" + StringUtil.firstCharToUpperCase(cls.getFields()[0].getName()));
}
method.setAccessible(true);
log.info(method.getName());
return method.invoke(args[keyIndex]);
}
private boolean existsObject(int keyIndex, int[] objectIndexArray) {
if (objectIndexArray == null || objectIndexArray.length <= 0) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < objectIndexArray.length; i++) {
if (keyIndex == objectIndexArray[i]) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 获取key中#p0中的参数名称
private static List<String> getKeyParsList(String key) {
List<String> ListPar = new ArrayList<String>();
if (key.indexOf("#") >= 0) {
int plusIndex = key.substring(key.indexOf("#")).indexOf("+");
int indexNext = 0;
String parName = "";
int indexPre = key.indexOf("#");
if (plusIndex > 0) {
indexNext = key.indexOf("#") + key.substring(key.indexOf("#")).indexOf("+");
parName = key.substring(indexPre, indexNext);
} else {
parName = key.substring(indexPre);
}
ListPar.add(parName.trim());
key = key.substring(indexNext + 1);
if (key.indexOf("#") >= 0) {
ListPar.addAll(getKeyParsList(key));
}
}
return ListPar;
}
}业务模块使用方法controller
@RequestMapping("queryQuotaTreeData")
@ResponseBody
public List<TreeNode> getTreeData() {
QuotaManage quotaManage = new QuotaManage();
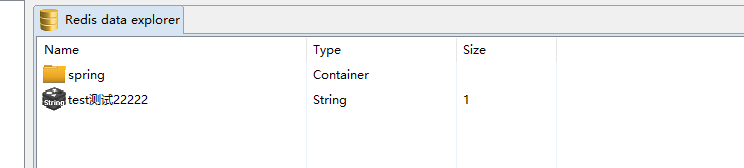
quotaManage.setQuotaName("测试22222");
List<TreeNode> list = this.quotaManageService.queryQuotaTreeData(quotaManage);
return list;
}实现层objectIndexArray中的{0}表示第0个参数,objectFieldArray中的“quotaName”表示对应对象中的字段名称
@Override
@NewCacheable(key="test+#p0",objectIndexArray = {0},objectFieldArray = {"quotaName"})
public List<TreeNode> queryQuotaTreeData(QuotaManage quotaManage) {
List<TreeNode> returnNodesList = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
List<TreeNode> nodeList = this.mapper.queryQuotaTreeData();
returnNodesList = treeUtils.getParentList(nodeList);
log.info(nodeList.size()+"");
return returnNodesList;
}控制台截图拼接的get方法名称和获取的字段值

Redis的截图
关于java对象作为key值的实例分析就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。