您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章给大家介绍Java Spring AOP该怎么理解,内容非常详细,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考借鉴,希望对大家能有所帮助。
面向切面编程,利用 AOP 可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
即不改变源代码而添加新功能,可插拔的.
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
有接口:jdk动态代理,即创建接口实现类代理对象
无接口:CGLIB动态代理,即创建子类代理对象
jdk动态代理的实现

创建接口
package com.vector.spring5;
public interface UserDao {
public int add(int a,int b);
public String update(String id);
}接口实现类
接口实现类的方法,属于源代码,用aop思想增添新功能时这里不能动!
package com.vector.spring5;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
@Override
public String update(String id) {
return id;
}
}使用JDK动态代理对象,增添新功能
package com.vector.spring5;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class JDKProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建接口实现类代理对象
Class[] interfaces = {UserDao.class};
UserDaoImpl userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
UserDao dao= (UserDao) Proxy.newProxyInstance(JDKProxy.class.getClassLoader(),interfaces,new UserDaoProxy(userDao));
int result = dao.add(1,2);
System.out.println("result: "+result);
}
}
//创建代理对象
class UserDaoProxy implements InvocationHandler{
//有参构造传递增强对象
private Object obj;
public UserDaoProxy(){};
public UserDaoProxy(Object obj){
this.obj=obj;
}
//增强的逻辑
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//方法之前
System.out.println("方法之前执行: "+method.getName()+":传递的参数: "+ Arrays.toString(args));
//被增强的方法执行
//可以根据method.getName()判断选择增强
Object res = method.invoke(obj,args);
//方法之后
System.out.println("方法之后执行: "+obj);
return res;
}
}
jdk代理图像解析
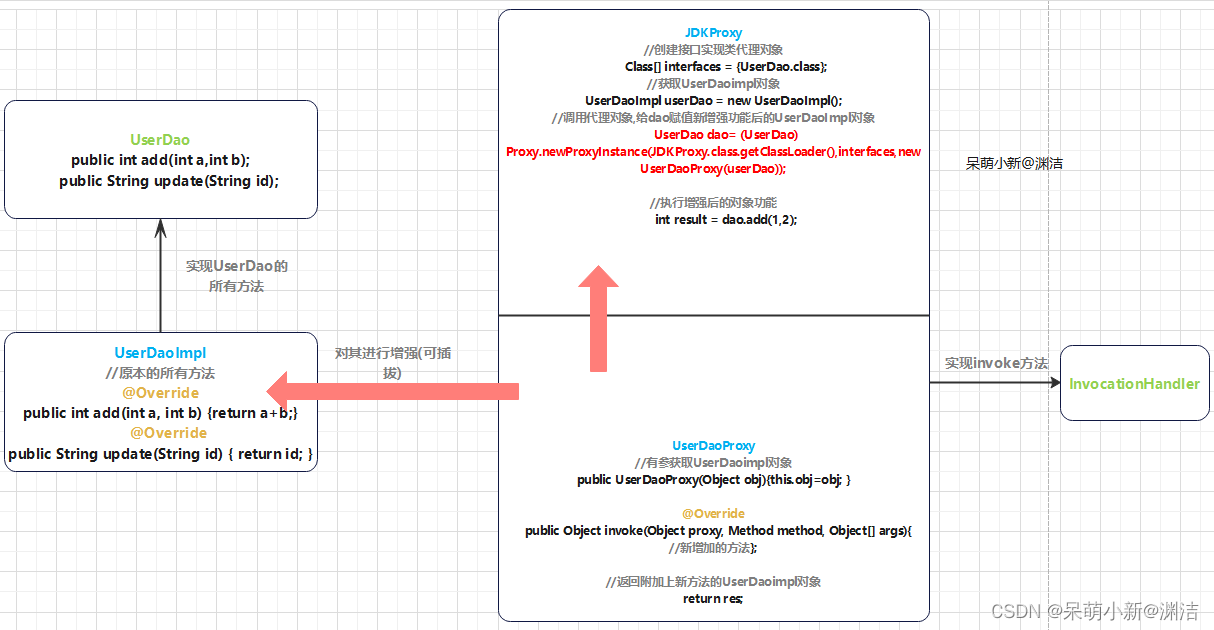
类里可以被增强的方法,称为连接点.
类中实际被增强的方法,成为切入点.
(1)实际被增强的方法中的逻辑部分称为通知(增强).
(2)通知包含:前置通知,后置通知,环绕通知,异常通知,最终通知
把增强应用到切入点的过程称为切面
(1)AspectJ 不是 Spring 组成部分,独立 AOP 框架,一般把 AspectJ 和 Spirng 框架一起使用,进行 AOP 操作
maven准备
<dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.8.RC1</version> </dependency>
实现组合crud和日志功能结合
applicationContext.xml
<context:component-scan base-package="com.vector"/> <aop:config> <!-- 切入点: expression:表达式 execution(要执行的位置!* * * * *)--> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.vector.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <!-- 执行环绕增加!--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:config>
log.java
package com.vector.log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Component("log")
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
//method: 要执行的目标对象的方法
//args: 参数
//target: 目标对象
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"被执行了");
}
}userService.java
package com.vector.service;
public interface UserService {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void query();
}userServiceImpl.java
package com.vector.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("增加了一个用户");
}
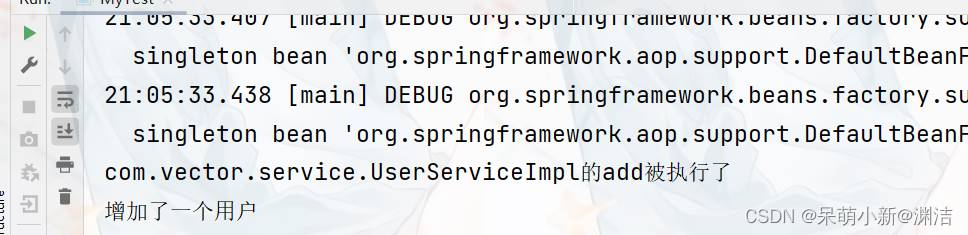
}MyTest.java
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//动态代理的是接口
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
}
}
DiyPoint.java
package com.vector.diy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("diyPointCut")
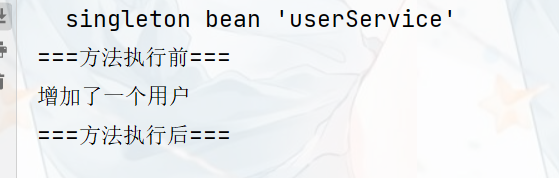
public class DiyPointCut {
public void before(){
System.out.println("===方法执行前===");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("===方法执行后===");
}
}UserServiceImpl.java
package com.vector.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("增加了一个用户");
}
}applicationContext.xml
<aop:config> <!-- 自定义切面,ref要引用的类--> <aop:aspect ref="diyPointCut"> <!-- 切入点--> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.vector.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <!-- 通知--> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
MyTest.java
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//动态代理的是接口
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
}
}
UserServiceImpl.java
package com.vector.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("增加了一个用户");
}
}AnnotationPointCut.java
package com.vector;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//标注这个类是一个切面
@Aspect
@Component("annotationPointCut")
//开启aop注解驱动
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AnnotationPointCut {
@Before("execution(* com.vector.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("===方法执行前===");
}
@After("execution(* com.vector.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("===方法执行后===");
}
}MyTest.java
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//动态代理的是接口
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
}
}
关于Java Spring AOP该怎么理解就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。