жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
C++ OpenCVеҰӮдҪ•иҝӣиЎҢеӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘпјҢзӣёдҝЎеҫҲеӨҡжІЎжңүз»ҸйӘҢзҡ„дәәеҜ№жӯӨжқҹжүӢж— зӯ–пјҢдёәжӯӨжң¬ж–ҮжҖ»з»“дәҶй—®йўҳеҮәзҺ°зҡ„еҺҹеӣ е’Ңи§ЈеҶіж–№жі•пјҢйҖҡиҝҮиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« еёҢжңӣдҪ иғҪи§ЈеҶіиҝҷдёӘй—®йўҳгҖӮ
дёӢйқўе°ҶдҪҝз”ЁOpenCV C++ иҝӣиЎҢеӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘгҖӮзӣ®еүҚдҪҝз”ЁOpenCVеҜ№дёӨе№…еӣҫеғҸиҝӣиЎҢжӢјжҺҘеӨ§иҮҙеҸҜд»ҘеҲҶдёәдёӨзұ»гҖӮ
дёҖгҖҒдҪҝз”ЁOpenCVеҶ…зҪ®API Stitcher иҝӣиЎҢжӢјжҺҘгҖӮ
дәҢгҖҒдҪҝз”Ёзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢз®—жі•еҢ№й…ҚдёӨе№…еӣҫдёӯзӣёдјјзҡ„зӮ№гҖҒи®Ўз®—еҸҳжҚўзҹ©йҳөгҖҒжңҖеҗҺеҜ№е…¶иҝӣиЎҢйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚўе°ұеҸҜд»ҘдәҶгҖӮ
imageA

imageB

еҺҹеӣҫеҰӮеӣҫжүҖзӨәгҖӮжң¬жЎҲдҫӢзҡ„йңҖжұӮжҳҜе°ҶдёҠиҝ°дёӨе№…еӣҫзүҮжӢјжҺҘжҲҗдёҖе№…еӣҫеғҸгҖӮйҰ–е…ҲдҪҝз”ЁOpenCVжҸҗдҫӣзҡ„StitcherиҝӣиЎҢжӢјжҺҘгҖӮе…ідәҺStitcherзҡ„е…·дҪ“еҺҹзҗҶиҜ·еӨ§е®¶иҮӘиЎҢжҹҘжүҫзӣёе…іиө„ж–ҷгҖӮ
bool OpenCV_Stitching(Mat imageA, Mat imageB)
{
vector<Mat>images;
images.push_back(imageA);
images.push_back(imageB);
Ptr<Stitcher>stitcher = Stitcher::create();
Mat result;
Stitcher::Status status = stitcher->stitch(images, result);// дҪҝз”ЁstitchеҮҪж•°иҝӣиЎҢжӢјжҺҘ
if (status != Stitcher::OK) return false;
imshow("OpenCVеӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘ", result);
return true;
}
иҝҷе°ұжҳҜдҪҝз”ЁOpenCV еҶ…зҪ®StitcherжӢјжҺҘеҮәжқҘзҡ„ж•ҲжһңгҖӮ
дҪҝз”Ёж–№жі•дәҢиҝӣиЎҢеӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘгҖӮзӣ®еүҚзҪ‘дёҠж•ҷзЁӢеӨ§иҮҙжөҒзЁӢеҪ’дёәпјҡ
1гҖҒдҪҝз”Ёзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢз®—еӯҗжҸҗеҸ–дёӨе№…еӣҫеғҸзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№пјҢ然еҗҺиҝӣиЎҢзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ°еӯҗеҢ№й…ҚгҖӮжҲ‘иҝҷйҮҢдҪҝз”Ёзҡ„жҳҜSURFз®—еӯҗгҖӮеҪ“然SIFTзӯүе…¶д»–зү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢз®—еӯҗд№ҹеҸҜд»ҘгҖӮ
//еҲӣе»әSURFзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢеҷЁ int Hessian = 800; Ptr<SURF>detector = SURF::create(Hessian); //иҝӣиЎҢеӣҫеғҸзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢгҖҒзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ° vector<KeyPoint>keypointA, keypointB; Mat descriptorA, descriptorB; detector->detectAndCompute(imageA, Mat(), keypointA, descriptorA); detector->detectAndCompute(imageB, Mat(), keypointB, descriptorB); //дҪҝз”ЁFLANNз®—жі•иҝӣиЎҢзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ°еӯҗзҡ„еҢ№й…Қ FlannBasedMatcher matcher; vector<DMatch>matches; matcher.match(descriptorA, descriptorB, matches);

еҰӮеӣҫдёәдҪҝз”ЁFLANNз®—жі•иҝӣиЎҢзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ°еӯҗеҢ№й…Қзҡ„з»“жһңгҖӮжҲ‘们йңҖиҰҒжҠҠйӮЈдәӣеҢ№й…ҚзЁӢеәҰй«ҳзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№зӯӣйҖүеҮәжқҘз”Ёд»ҘдёӢйқўи®Ўз®—дёӨе№…еӣҫеғҸзҡ„еҚ•еә”жҖ§зҹ©йҳөгҖӮ
2гҖҒзӯӣйҖүеҮәеҢ№й…ҚзЁӢеәҰй«ҳзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№
double Max = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
//float distance вҖ“>д»ЈиЎЁиҝҷдёҖеҜ№еҢ№й…Қзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰпјҲжң¬иҙЁжҳҜеҗ‘йҮҸпјүзҡ„欧ж°Ҹи·қзҰ»пјҢж•°еҖји¶Ҡе°Ҹд№ҹе°ұиҜҙжҳҺдёӨдёӘзү№еҫҒзӮ№и¶ҠзӣёеғҸгҖӮ
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis > Max)
{
Max = dis;
}
}
//зӯӣйҖүеҮәеҢ№й…ҚзЁӢеәҰй«ҳзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№
vector<DMatch>goodmatches;
vector<Point2f>goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis < 0.15*Max)
{
//int queryIdx вҖ“>жҳҜжөӢиҜ•еӣҫеғҸзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰпјҲdescriptorпјүзҡ„дёӢж ҮпјҢеҗҢж—¶д№ҹжҳҜжҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰеҜ№еә”зү№еҫҒзӮ№пјҲkeypoint)зҡ„дёӢж ҮгҖӮ
goodkeypointA.push_back(keypointA[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//int trainIdx вҖ“> жҳҜж ·жң¬еӣҫеғҸзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬Ұзҡ„дёӢж ҮпјҢеҗҢж ·д№ҹжҳҜзӣёеә”зҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№зҡ„дёӢж ҮгҖӮ
goodkeypointB.push_back(keypointB[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
goodmatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
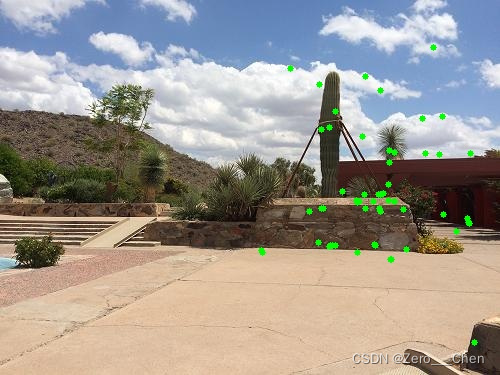
}еҰӮеӣҫдёәimageAзӯӣйҖүеҮәжқҘзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№гҖӮ
еҰӮеӣҫдёәimageBзӯӣйҖүеҮәжқҘзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№гҖӮ

д»ҺдёҠеӣҫеҸҜд»ҘзңӢеҮәпјҢжҲ‘们已з»ҸзӯӣйҖүеҮәimageAпјҢimageBе…ұжңүзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№йғЁеҲҶгҖӮжҺҘдёӢжқҘпјҢжҲ‘们йңҖиҰҒдҪҝз”ЁиҝҷдёӨдёӘзӮ№йӣҶи®Ўз®—дёӨе№…еӣҫзҡ„еҚ•еә”жҖ§зҹ©йҳөгҖӮ
и®Ўз®—еҚ•еә”жҖ§еҸҳжҚўзҹ©йҳө
//иҺ·еҸ–еӣҫеғҸAеҲ°еӣҫеғҸBзҡ„жҠ•еҪұжҳ е°„зҹ©йҳөпјҢе°әеҜёдёә3*3 Mat H = findHomography(goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB, RANSAC); Mat M = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0, 0, imageA.cols, 0, 1.0, 0, 0, 0, 1.0); Mat Homo = M * H;
ж №жҚ®и®Ўз®—еҮәжқҘзҡ„еҚ•еә”жҖ§зҹ©йҳөеҜ№imageAиҝӣиЎҢйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚў
//иҝӣиЎҢйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚў
Mat DstImg;
warpPerspective(imageA, DstImg, Homo, Size(imageB.cols + imageA.cols, imageB.rows));
imshow("йҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚў", DstImg);
еҰӮеӣҫжүҖзӨәдёәimageAиҝӣиЎҢйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚўеҫ—еҲ°зҡ„з»“жһңгҖӮ
ж №жҚ®дёҠиҝ°ж“ҚдҪңпјҢжҲ‘们已з»Ҹеҫ—еҲ°дәҶз»ҸйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚўзҡ„imageAпјҢжҺҘдёӢжқҘеҸӘйңҖе°ҶimageAдёҺimageBжӢјжҺҘиө·жқҘе°ұеҸҜд»ҘдәҶгҖӮ
imageB.copyTo(DstImg(Rect(imageA.cols, 0, imageB.cols, imageB.rows)));
imshow("еӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘ", DstImg);bool Image_Stitching(Mat imageA, Mat imageB, bool draw)
{
//еҲӣе»әSURFзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢеҷЁ
int Hessian = 800;
Ptr<SURF>detector = SURF::create(Hessian);
//иҝӣиЎҢеӣҫеғҸзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢгҖҒзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ°
vector<KeyPoint>keypointA, keypointB;
Mat descriptorA, descriptorB;
detector->detectAndCompute(imageA, Mat(), keypointA, descriptorA);
detector->detectAndCompute(imageB, Mat(), keypointB, descriptorB);
//дҪҝз”ЁFLANNз®—жі•иҝӣиЎҢзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ°еӯҗзҡ„еҢ№й…Қ
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch>matches;
matcher.match(descriptorA, descriptorB, matches);
double Max = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
//float distance вҖ“>д»ЈиЎЁиҝҷдёҖеҜ№еҢ№й…Қзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰпјҲжң¬иҙЁжҳҜеҗ‘йҮҸпјүзҡ„欧ж°Ҹи·қзҰ»пјҢж•°еҖји¶Ҡе°Ҹд№ҹе°ұиҜҙжҳҺдёӨдёӘзү№еҫҒзӮ№и¶ҠзӣёеғҸгҖӮ
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis > Max)
{
Max = dis;
}
}
//зӯӣйҖүеҮәеҢ№й…ҚзЁӢеәҰй«ҳзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№
vector<DMatch>goodmatches;
vector<Point2f>goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis < 0.15*Max)
{
//int queryIdx вҖ“>жҳҜжөӢиҜ•еӣҫеғҸзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰпјҲdescriptorпјүзҡ„дёӢж ҮпјҢеҗҢж—¶д№ҹжҳҜжҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰеҜ№еә”зү№еҫҒзӮ№пјҲkeypoint)зҡ„дёӢж ҮгҖӮ
goodkeypointA.push_back(keypointA[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//int trainIdx вҖ“> жҳҜж ·жң¬еӣҫеғҸзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬Ұзҡ„дёӢж ҮпјҢеҗҢж ·д№ҹжҳҜзӣёеә”зҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№зҡ„дёӢж ҮгҖӮ
goodkeypointB.push_back(keypointB[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
goodmatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
if (draw)
{
Mat result;
drawMatches(imageA, keypointA, imageB, keypointB, goodmatches, result);
imshow("зү№еҫҒеҢ№й…Қ", result);
Mat temp_A = imageA.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < goodkeypointA.size(); i++)
{
circle(temp_A, goodkeypointA[i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
imshow("goodkeypointA", temp_A);
Mat temp_B = imageB.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < goodkeypointB.size(); i++)
{
circle(temp_B, goodkeypointB[i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
imshow("goodkeypointB", temp_B);
}
//findHomographyи®Ўз®—еҚ•еә”жҖ§зҹ©йҳөиҮіе°‘йңҖиҰҒ4дёӘзӮ№
/*
и®Ўз®—еӨҡдёӘдәҢз»ҙзӮ№еҜ№д№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„жңҖдјҳеҚ•жҳ е°„еҸҳжҚўзҹ©йҳөHпјҲ3x3пјүпјҢдҪҝз”ЁMSEжҲ–RANSACж–№жі•пјҢжүҫеҲ°дёӨе№ійқўд№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„еҸҳжҚўзҹ©йҳө
*/
if (goodkeypointA.size() < 4 || goodkeypointB.size() < 4) return false;
//иҺ·еҸ–еӣҫеғҸAеҲ°еӣҫеғҸBзҡ„жҠ•еҪұжҳ е°„зҹ©йҳөпјҢе°әеҜёдёә3*3
Mat H = findHomography(goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB, RANSAC);
Mat M = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0, 0, imageA.cols, 0, 1.0, 0, 0, 0, 1.0);
Mat Homo = M * H;
//иҝӣиЎҢйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚў
Mat DstImg;
warpPerspective(imageA, DstImg, Homo, Size(imageB.cols + imageA.cols, imageB.rows));
imshow("йҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚў", DstImg);
imageB.copyTo(DstImg(Rect(imageA.cols, 0, imageB.cols, imageB.rows)));
imshow("еӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘ", DstImg);
return true;
}
жңҖз»ҲжӢјжҺҘж•ҲжһңеҰӮеӣҫжүҖзӨәгҖӮ
#include<iostream>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
#include<opencv2/stitching.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
//1гҖҒдҪҝз”Ёзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢз®—жі•жүҫеҲ°дёӨеј еӣҫеғҸдёӯзӣёдјјзҡ„зӮ№пјҢи®Ўз®—еҸҳжҚўзҹ©йҳө
//2гҖҒе°ҶAйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚўеҗҺеҫ—еҲ°зҡ„еӣҫзүҮдёҺBжӢјжҺҘ
bool Image_Stitching(Mat imageA, Mat imageB, bool draw)
{
//еҲӣе»әSURFзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢеҷЁ
int Hessian = 800;
Ptr<SURF>detector = SURF::create(Hessian);
//иҝӣиЎҢеӣҫеғҸзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢгҖҒзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ°
vector<KeyPoint>keypointA, keypointB;
Mat descriptorA, descriptorB;
detector->detectAndCompute(imageA, Mat(), keypointA, descriptorA);
detector->detectAndCompute(imageB, Mat(), keypointB, descriptorB);
//дҪҝз”ЁFLANNз®—жі•иҝӣиЎҢзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ°еӯҗзҡ„еҢ№й…Қ
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch>matches;
matcher.match(descriptorA, descriptorB, matches);
double Max = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
//float distance вҖ“>д»ЈиЎЁиҝҷдёҖеҜ№еҢ№й…Қзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰпјҲжң¬иҙЁжҳҜеҗ‘йҮҸпјүзҡ„欧ж°Ҹи·қзҰ»пјҢж•°еҖји¶Ҡе°Ҹд№ҹе°ұиҜҙжҳҺдёӨдёӘзү№еҫҒзӮ№и¶ҠзӣёеғҸгҖӮ
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis > Max)
{
Max = dis;
}
}
//зӯӣйҖүеҮәеҢ№й…ҚзЁӢеәҰй«ҳзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№
vector<DMatch>goodmatches;
vector<Point2f>goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
double dis = matches[i].distance;
if (dis < 0.15*Max)
{
//int queryIdx вҖ“>жҳҜжөӢиҜ•еӣҫеғҸзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰпјҲdescriptorпјүзҡ„дёӢж ҮпјҢеҗҢж—¶д№ҹжҳҜжҸҸиҝ°з¬ҰеҜ№еә”зү№еҫҒзӮ№пјҲkeypoint)зҡ„дёӢж ҮгҖӮ
goodkeypointA.push_back(keypointA[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//int trainIdx вҖ“> жҳҜж ·жң¬еӣҫеғҸзҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№жҸҸиҝ°з¬Ұзҡ„дёӢж ҮпјҢеҗҢж ·д№ҹжҳҜзӣёеә”зҡ„зү№еҫҒзӮ№зҡ„дёӢж ҮгҖӮ
goodkeypointB.push_back(keypointB[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
goodmatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
if (draw)
{
Mat result;
drawMatches(imageA, keypointA, imageB, keypointB, goodmatches, result);
imshow("зү№еҫҒеҢ№й…Қ", result);
Mat temp_A = imageA.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < goodkeypointA.size(); i++)
{
circle(temp_A, goodkeypointA[i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
imshow("goodkeypointA", temp_A);
Mat temp_B = imageB.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < goodkeypointB.size(); i++)
{
circle(temp_B, goodkeypointB[i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
imshow("goodkeypointB", temp_B);
}
//findHomographyи®Ўз®—еҚ•еә”жҖ§зҹ©йҳөиҮіе°‘йңҖиҰҒ4дёӘзӮ№
/*
и®Ўз®—еӨҡдёӘдәҢз»ҙзӮ№еҜ№д№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„жңҖдјҳеҚ•жҳ е°„еҸҳжҚўзҹ©йҳөHпјҲ3x3пјүпјҢдҪҝз”ЁMSEжҲ–RANSACж–№жі•пјҢжүҫеҲ°дёӨе№ійқўд№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„еҸҳжҚўзҹ©йҳө
*/
if (goodkeypointA.size() < 4 || goodkeypointB.size() < 4) return false;
//иҺ·еҸ–еӣҫеғҸAеҲ°еӣҫеғҸBзҡ„жҠ•еҪұжҳ е°„зҹ©йҳөпјҢе°әеҜёдёә3*3
Mat H = findHomography(goodkeypointA, goodkeypointB, RANSAC);
Mat M = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1.0, 0, imageA.cols, 0, 1.0, 0, 0, 0, 1.0);
Mat Homo = M * H;
//иҝӣиЎҢйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚў
Mat DstImg;
warpPerspective(imageA, DstImg, Homo, Size(imageB.cols + imageA.cols, imageB.rows));
imshow("йҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚў", DstImg);
imageB.copyTo(DstImg(Rect(imageA.cols, 0, imageB.cols, imageB.rows)));
imshow("еӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘ", DstImg);
return true;
}
bool OpenCV_Stitching(Mat imageA, Mat imageB)
{
vector<Mat>images;
images.push_back(imageA);
images.push_back(imageB);
Ptr<Stitcher>stitcher = Stitcher::create();
Mat result;
Stitcher::Status status = stitcher->stitch(images, result);// дҪҝз”ЁstitchеҮҪж•°иҝӣиЎҢжӢјжҺҘ
if (status != Stitcher::OK) return false;
imshow("OpenCVеӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘ", result);
return true;
}
int main()
{
Mat imageA = imread("image1.jpg");
Mat imageB = imread("image2.jpg");
if (imageA.empty() || imageB.empty())
{
cout << "No Image!" << endl;
system("pause");
return -1;
}
if (!Image_Stitching(imageA, imageB, true))
{
cout << "can not stitching the image!" << endl;
}
if (!OpenCV_Stitching(imageA, imageB))
{
cout << "can not stitching the image!" << endl;
}
waitKey(0);
system("pause");
return 0;
}е°Ҹзј–дҪҝз”ЁOpenCV C++иҝӣиЎҢеӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘпјҢе…ій”®жӯҘйӘӨжңүд»ҘдёӢеҮ зӮ№гҖӮ
1гҖҒдҪҝз”Ёзү№еҫҒжЈҖжөӢз®—еӯҗжҸҗеҸ–дёӨе№…еӣҫеғҸзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№пјҢ然еҗҺиҝӣиЎҢзү№еҫҒжҸҸиҝ°еӯҗеҢ№й…ҚгҖӮ
2гҖҒзӯӣйҖүеҮәеҢ№й…ҚзЁӢеәҰй«ҳзҡ„е…ій”®зӮ№и®Ўз®—дёӨе№…еӣҫзҡ„еҚ•еә”жҖ§зҹ©йҳөгҖӮ
3гҖҒеҲ©з”Ёи®Ўз®—еҮәжқҘзҡ„еҚ•еә”жҖ§зҹ©йҳөеҜ№е…¶дёӯдёҖеј еӣҫзүҮиҝӣиЎҢйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚўгҖӮ
4гҖҒе°ҶйҖҸи§ҶеҸҳжҚўзҡ„еӣҫзүҮдёҺеҸҰдёҖеј еӣҫзүҮиҝӣиЎҢжӢјжҺҘгҖӮ
зңӢе®ҢдёҠиҝ°еҶ…е®№пјҢдҪ 们жҺҢжҸЎC++ OpenCVеҰӮдҪ•иҝӣиЎҢеӣҫеғҸе…ЁжҷҜжӢјжҺҘзҡ„ж–№жі•дәҶеҗ—пјҹеҰӮжһңиҝҳжғіеӯҰеҲ°жӣҙеӨҡжҠҖиғҪжҲ–жғідәҶи§ЈжӣҙеӨҡзӣёе…іеҶ…е®№пјҢж¬ўиҝҺе…іжіЁдәҝйҖҹдә‘иЎҢдёҡиө„и®Ҝйў‘йҒ“пјҢж„ҹи°ўеҗ„дҪҚзҡ„йҳ…иҜ»пјҒ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ