您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
密码登录
登录注册
点击 登录注册 即表示同意《亿速云用户服务条款》
小编给大家分享一下Spring注解如何实现applicationContext.xml效果,相信大部分人都还不怎么了解,因此分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大有收获,下面让我们一起去了解一下吧!
随着越来越多地使用Springboot敏捷开发,更多地使用注解配置Spring,而不是Spring的applicationContext.xml文件。
Configuration注解: Spring解析为配置类,相当于spring配置文件
Bean注解:容器注册Bean组件,默认id为方法名
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
}等同于beans.xml文件
<beans> <bean id="myService" class="com.acme.services.MyServiceImpl"/> </beans>
1)applicationContext.xml文件-包扫描
@ComponentScans(value = {@ComponentScan(value = "com.self",excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
})
})
@Configuration
public class RootConfig {
//测试Bean
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person("张励",22,"工程师");
}
}2)导入properties文件
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfProperty {
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person();
}
}赋值
public class Person {
@Value("${person.name}")//配置文件属性
private String name;
}3)数据源
@EnableTransactionManagement//开启基于注解的事务管理功能
@ComponentScan("com.self.ds")
@Configuration
public class TxConfig {
//数据源
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() throws Exception{
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser("root");
dataSource.setPassword("000111");
dataSource.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/self");
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() throws Exception{
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource());
return jdbcTemplate;
}
//事务管理器
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() throws Exception{
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource());
}
}单元测试
public class IOCTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
@Test
public void test02() {
Object bean1 = applicationContext.getBean("person");
Object bean2 = applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println( bean1 == bean2);
}
@Test
public void test01() {
Object bean = applicationContext.getBean("person01");
System.out.println("结果: " + bean);
}
@Test
public void test() {
String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for(String beanDef:beanDefinitionNames) {
System.out.println("输出: " + beanDef);
}
}
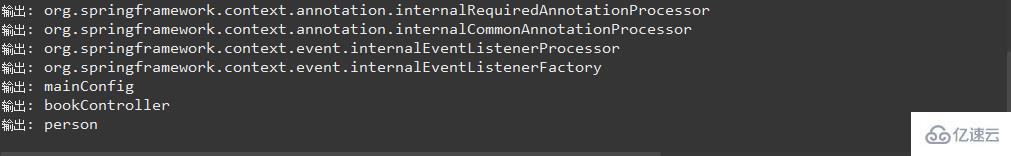
}执行结果
以上是“Spring注解如何实现applicationContext.xml效果”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。