您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
1. Examples of Today's Popular Communication Tools
Instant Messaging(real-time communication)/Texting(Such as QQ, MSN)
Weblogs (blogs)(individual):easy to update and edit
Wikis: groups of people can edit and view together.
Podcasting: an audio-based medium that originally enabled people to record audio and convert it for use.
Collaboration Tools(work together on shared documents)
P2P File Sharing: share files with each other.
Social Media: interactive websites where people create and share user-generated content with friends and family
TelePresence: provides real-time audio and video conferencing.
2. Networks Supporting the Way We Learn
Virtual cla***ooms
Collaborative learning spaces
On-demand video
Mobile learning
3. What is Computer Netwrok?
计算机网络就是指将分布在不同地点具有独立功能的多台计算机及其外部设备用通信线路链接起来,在网络管理设备或管理软件的协调管理下,实现资源共享,信息处理的系统。
4. Components of the Network
Devices: end devices & intermediary devices
Media: copper cable & fiber optic cable & radio
Services: protocols
4.1 End Devices (originate data flow) (host)
Computers (work stations, laptops, file servers, web servers)
Network printers
VoIP phones
Security cameras
Mobile handheld devices (such as wireless barcode scanners, PDAs)
4.2 Intermediary Devices (ensure data flows across the network)
Network Access Devices (Hubs, switches, and wireless access points)
Internetworking Devices (routers)
Communication Servers and Modems
Security Devices (firewalls)
Processes running on the intermediary network devices perform these functions:
Regenerate and re-transmit data signals
Maintain information about what pathways exist through the network and internetwork
Notify other devices of errors and communication failures
Direct data along alternate pathways when there is a link failure
Classify and direct messages according to QoS priorities
Permit or deny the flow of data, based on security settings
4.3 Network Media
Metallic wires within cables (copper cable)
Glass or plastic fibers (fiber optic cable)
Wireless transmission (radio)
Criteria for choosing a network media are:
The distance the media can successfully carry a signal.
The environment in which the media is to be installed.
The amount of data and the speed at which it must be transmitted.
The cost of the media and installation
5. The Interaction of Protocols
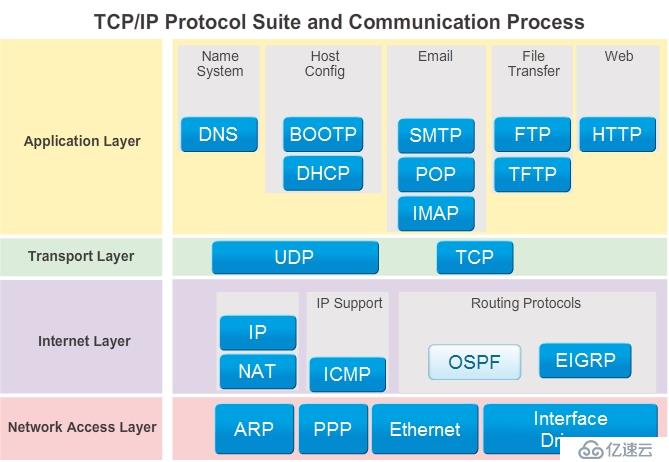
5.1 Networking protocol suites describe processes such as:
The format or structure of the message
The method by which networking devices share information about pathways with other networks
How and when error and system messages are passed between devices
The setup and termination of data transfer sessions
5.2 Technology Independent Protocols
(1) Networking protocols describe the functions that occur during network communications.
(2) Protocols generally do not describe how to accomplish a particular function.
5.3 The Benefits of Using a Layered Model
Assists in protocol design, because protocols that operate at a specific layer have defined information that they act upon and a defined interface to the layers above and below.
Fosters competition because products from different vendors can work together.
Prevents technology or capability changes in one layer from affecting other layers above and below.
Provides a common language to describe networking functions and capabilities.
5.4 Protocol and Reference Models
There are two basic types of networking models: protocol models and reference models.
Protocol model (TCP/IP): provides a model that closely matches the structure of a particular protocol suite.
Reference model (OSI/RM): provides a common reference for maintaining consistency within all types of network protocols and services.
5.5 Protocol Data Units and Encapsulation
As application data is passed down the protocol stack on its way to be transmitted across the network media, various protocols add information to it at each level. This is commonly known as the encapsulation process.
Data - The general term for the PDU used at the Application layer
Segment - Transport Layer PDU
Packet - Internetwork Layer PDU
Frame - Network Access Layer PDU
Bits - A PDU used when physically transmitting data over the medium
5.6 The TCP/IP Model
Application: Represents data to the user plus encoding and dialog control
Transport: Supports communication between diverse devices across diverse networks.
Internet: Determines the best path through the network.
Network Access: Controls the hardware devices and media that make up the network.
5.7 The OSI Model
Application the means for end-to-end connectivity between individuals in the human network using data networks
Presentation common representation of the data transferred and to manage data exchange
Session this layer create and maintain dialog between source and destination applications.
Transport defines serves to segment, transfer, and reassemble the data for individual communications between the end devices.
Network Provides services to exchange the individual pieces of data over the network between identified end devices.
Data Link describe methods for exchanging data frames between devices over a common media
Physical describe the mechanical, electrical, functional, and produral means to activate maintain and de-activate physical connections for bit transmission to and from a network device.
5.8 Addressing in the Network
| Upper layers | Encoded Application Data |
| Transport Layer | Destination & Source Process Number(Ports) |
| Network Layer | Destination & Source Logical Network Addr |
| Data Link Layer | Destination and Source Physical Address |
| Physical Layer | Timing & Synchronization Bits |
6. Providing Network Security
There are two types of network security concerns that must be addressed to prevent serious consequences: network infrastructure security and content security.
Securing a network infrastructure includes the physical securing of devices that provide network connectivity and preventing unauthorized access to the management software that resides on them.
Content security refers to protecting the information contained within the packets being transmitted over the network and the information stored on network attached devices.
6.1 Security measures taken in a network should:
Prevent unauthorized disclosure or theft of information
Prevent unauthorized modification of information
Prevent Denial of Service(DoS)
6.2 Network Security:
Viruses, worms, and Trojan horses
Spyware and adware
Zero-day attacks (zero-hour attacks)
Hacker attacks
Denial of service attacks (DoS)
Data interception and theft
Identity theft
6.3 Means to achieve these goals include:
Ensuring confidentiality: Only the intended recipients can access and read the data
Maintaining integrity: The assurance that the information has not been altered during transmission.
Ensuring availability: The assurance of timely and reliable access to data
7. What is data? What is a data network? What is a converged network?
Data is the pieces of information, such as files, audio, phone calls and video shared across the network.
A data network consists of:
Devices that communicate with each other
A means of connecting these devices together—a medium that can transport messages from one device to another
The digital messages or units of information that will travel from one device to another
Rules or agreements to govern how the messages are sent, directed, and received
Converged networks:
One network now carries multiple types of messages and information. Separate networks are no longer required to support voice, video, and data traffic.
Network Architectures:
Cisco Borderless Networks architecture
The Cisco Borderless Network Architecture is a network solution that allows organizations and individuals to connect securely, reliably, and seamlessly to the corporate network in a BYOD environment.
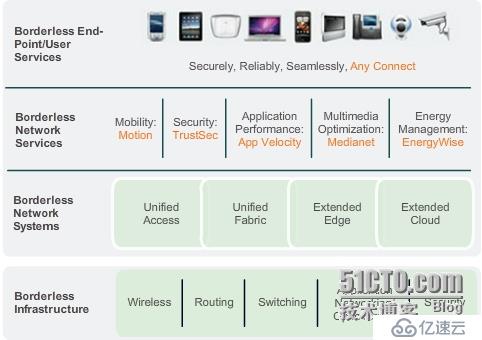
Collaboration architecture (meet expanding collaboration needs)
Tele-Presence
Collaboration Applications
Customer Collaboration
Unified Communications
Data center and virtualization architecture
Cisco Unified Computing: Modular Stateless Computing Elements
Cisco Unified Fabric: Highly Scalable, Secure Network Traffic
Cisco Unified Management: Automated Resource Management (Physical and Virtual)
Communicating the Messages
Segmenting messages has two primary benefits. Multiplexing & reliability
(1) Multiplexing: The process used to interleave the pieces of separate conversations together on the network
(2) Segmentation can increase the reliability of network communications.
Disadvantages:
The downside to using segmentation and multiplexing to transmit messages across a network is the level of complexity that is added to the process.
All networks have four basic elements in common (Sender, Receiver, and channel)
Rules
Medium
Messages
Devices
Connecting to the Internet:
Cable: a high bandwidth, always on , uses coaxial cable as a medium
DSL: a high bandwidth, always on, telephone cable, split into three channels:
One channel: voice telephone calls
Second channel: faster download channel
Third channel: for sending or uploading information.
Cellular: use a cell phone network to connect.
Satellite: for homes or offices don’t need DSL or cable. Not suited Heavily wooded areas
Dial-up Telephone: an inexpensive option that uses any phone line and a modem. Low BW
Many homes and small offices are more commonly being connected directly with fiber optic cables. This enables an Internet service provider to provide higher bandwidth speeds and support more services such as Internet, phone, and TV. Satellite
Connecting Businesses to the Internet:Higher bandwidth, dedicated bandwidth, managed service
Dedicated Leased Line: T1 (1.544MB/s) and T3 (44.7MB/s) E1 (2MB/s) E3 (34MB/s)
Metro Ethernet: providing bandwidth speeds of 10Mb/s to 10Gb/s
DSL: Business DSL is available in various formats. Symmetric Digital Subscriber Lines.(upload=download)
Satellite: provide a connection when a wired solution is not available. geographical location and service provider availability.
Appendx Protocol Suites and Industry Standards
ISOC: The Internet Society
Responsible for promoting open development, evolution, and Internet use throughout the world.
IAB: The Internet Architecture Board
Responsible for the overall management and development of Internet standards.
IEEE: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
A professional organization for those in the electrical engineering and electronics fields who are dedicated to advancing technological innovation and creating standards.
Standards are developed using a six stage lifecycle diagram
Offers online tools and resources for standards and developers.
802.1 Higher Layer LAN Protocols Working Group
802.3 Ethernet Working Group
802.11 Wireless LAN Working Group
802.15 Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) Working Group
802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group
802.18 Radio Regulatory TAG
802.19 Wireless Coexistence Working Group
802.21 Media Independent Handover Services Working Group
802.22 Wireless Regional Area Networks
802.24 Smart Grid TAG
IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force
Develop, update, and maintain Internet and TCP/IP technologies. Produce RFC documents.
Makes the Internet work better, using and engineering approach
RFC are official documents which are used to describe a standard or protocol that is related to the Internet.
These protocols are open standards ¬ vendor proprietary. The RFC process includes significant review and comment by the community.
Once an RFC is published, it means that the standard is completed
ISO: The International Organization for Standardization
ICANN: The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers
Coordinates IP address allocation, the management of domain names used by DNS, and the protocol identifiers or port numbers used by TCP and UDP protocols
IANA: The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
Overseeing and managing IP address allocation, domain name management, and protocol identifiers for ICANN.
TIA: The Telecommunications Industry Association
Responsible for developing communication standards in variety of areas including radio equipment, cellular towers, voice over IP (VoIP) devices, satellite communications.
Creates standards for worldwide cabling infrastructure
Develops standards/protocols affecting cloud computing
Develops standards for homeland security/emergency response teams.
ITU-T: The International Telecommunications Union-Telecommunication Standardization Sector
Video compression, IPTV, broadband communications, DSL Uses communications standards to predict famines and global climate changes Supports “bridge the digital divide” initiatives
Supports navigation and online maps via radio/satellite transmissions
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。