жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
иҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« дё»иҰҒд»Ӣз»ҚC++дёӯеҜ№иұЎжҺ’еәҸзҡ„зӨәдҫӢеҲҶжһҗпјҢж–Үдёӯд»Ӣз»Қзҡ„йқһеёёиҜҰз»ҶпјҢе…·жңүдёҖе®ҡзҡ„еҸӮиҖғд»·еҖјпјҢж„ҹе…ҙи¶Јзҡ„е°Ҹдјҷдјҙ们дёҖе®ҡиҰҒзңӢе®ҢпјҒ
еңЁжҺ’еәҸдёӯиҝӣиЎҢдәӨжҚўзҡ„еүҚжҸҗдё»иҰҒжҳҜиҝӣиЎҢеҜ№иұЎй—ҙзҡ„ жҜ”иҫғгҖҒ
иҖҢеёёи§Ғзҡ„жҺ’еәҸжҳҜеҜ№дёҖдёӘж•°з»„жҺ’еәҸ,然еҗҺеҜ№жҜҸдёӘж•°з»„еҶ…е®№иҝӣиЎҢжҜ”иҫғдёҺдәӨжҚўгҖҒ
еҰӮжһңжҳҜеҜ№дёҖдёӘclassиҝӣиЎҢжҺ’еәҸ,еҲҷйңҖиҰҒиҝӣиЎҢе…ій”®еӯ—жҲҗе‘ҳиҝӣиЎҢжҜ”иҫғ,йңҖиҰҒйҮҚеҶҷдёӢйқўеҮ дёӘж“ҚдҪңз¬Ұ:
bool operator == (const class& t); // иҝ”еӣһtureеҲҷиЎЁзӨәзӣёзӯү
bool operator != (const class& t); // е’Ң==зӣёзӯүж“ҚдҪңз¬Ұиҝ”еӣһеҖјзӣёеҸҚ
bool operator <(const class& t); // иҝ”еӣһtrueеҲҷеҪ“еүҚеҜ№иұЎе°ҸдәҺtеҜ№иұЎ
bool operator > (const class& t);
bool operator <=(const class& t);
bool operator >=(const class& t);
жҜ”еҰӮе°ҶеӯҰз”ҹжҲҗз»©еҚ•жҢүж•°еӯҰжҲҗз»©з”ұй«ҳеҲ°дҪҺжҺ’еәҸпјҢеҰӮжһңж•°еӯҰжҲҗз»©зӣёеҗҢзҡ„еӯҰз”ҹеҶҚжҢүиӢұиҜӯжҲҗз»©зҡ„й«ҳдҪҺзӯүзә§жҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
д»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢжүҖзӨә:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student {
int number; // еӯҰеҸ·
int mathScore; // ж•°еӯҰжҲҗз»©
int enScore; // иӢұиҜӯжҲҗз»©
public:
Student() {
}
Student(int number, int mathScore, int enScore) {
this->number = number;
this->mathScore = mathScore;
this->enScore = enScore;
}
void printString() {
cout<<"number:"<<number <<" mathScore:" << mathScore <<" enScore:"<< enScore << endl;
}
bool operator == (const Student& t) {
return mathScore == t.mathScore && enScore == t.enScore;
}
// дёҚзӯүдәҺеҲҷи°ғз”Ё==ж“ҚдҪңз¬ҰпјҢеҸ–еҸҚеҚіеҸҜ
bool operator != (const Student& t) {
return !(*this == t);
}
bool operator <(const Student& t) {
return mathScore < t.mathScore || (mathScore == t.mathScore && enScore < t.enScore);
}
bool operator > (const Student& t) {
return mathScore > t.mathScore || (mathScore == t.mathScore && enScore > t.enScore);
}
bool operator <=(const Student& t) {
return !(*this > t);
}
bool operator >=(const Student& t) {
return !(*this < t);
}
};жөӢиҜ•д»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢжүҖзӨә(дҪҝз”ЁдёҠз« жҲ‘们еҶҷзҡ„еҶ’жіЎжҺ’еәҸ):
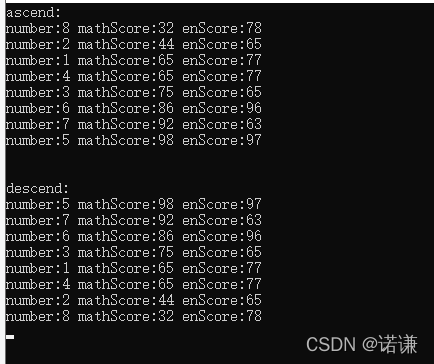
Student arr[8] = {
Student(1,65,77),
Student(2,44,65),
Student(3,75,65),
Student(4,65,77),
Student(5,98,97),
Student(6,86,96),
Student(7,92,63),
Student(8,32,78)
};
bubbleSort(arr, 8); // дҪҝз”ЁеҶ’жіЎжҺ’еәҸ еҚҮеәҸ
cout<<"ascend: "<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
arr[i].printString();
}
cout<<endl;
bubbleSort(arr, 8, false); // дҪҝз”ЁеҶ’жіЎжҺ’еәҸ йҷҚеәҸ
cout<<endl<<"descend: "<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
arr[i].printString();
}иҝҗиЎҢжү“еҚ°:
д»ҘдёҠжҳҜвҖңC++дёӯеҜ№иұЎжҺ’еәҸзҡ„зӨәдҫӢеҲҶжһҗвҖқиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« зҡ„жүҖжңүеҶ…е®№пјҢж„ҹи°ўеҗ„дҪҚзҡ„йҳ…иҜ»пјҒеёҢжңӣеҲҶдә«зҡ„еҶ…е®№еҜ№еӨ§е®¶жңүеё®еҠ©пјҢжӣҙеӨҡзӣёе…ізҹҘиҜҶпјҢж¬ўиҝҺе…іжіЁдәҝйҖҹдә‘иЎҢдёҡиө„и®Ҝйў‘йҒ“пјҒ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ