您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章主要介绍了C#中对象状态模式怎么实现的相关知识,内容详细易懂,操作简单快捷,具有一定借鉴价值,相信大家阅读完这篇C#中对象状态模式怎么实现文章都会有所收获,下面我们一起来看看吧。
首先用一个枚举,表示教程进行的不同程度
enum TutorialState
{
GetGold,
GetIron,
KillEnemy,
LevelUp
}无需多言,封装收集到的资源数、击杀敌人数量、角色等级和一些升级接口等
class Player
{
private int ironNum;
private int goldNum;
private int enemyKilled;
private int level;
public int IronNum => ironNum;
public int GoldNum => goldNum;
public int EnemyKilled => enemyKilled;
public int Level => level;
public void CollectIron(int num)
{
ironNum += num;
}
public void CollectGold(int num)
{
goldNum += num;
}
public void KillEnemy()
{
enemyKilled++;
}
public void LevelUp()
{
level++;
}
}定义一个教程类,包括
显示帮助文字以协助玩家通过当前教程步骤
判断玩家是否已经完成当前教程步骤,若是,切换到下一个步骤直到完成教程
class GameTutorial
{
private TutorialState currentState;
private Player player;
public GameTutorial(Player player)
{
this.player = player;
}
public void ShowHelpDescription()
{
switch (currentState)
{
case TutorialState.GetGold:
Console.WriteLine("Please follow instruction to get gold");
break;
case TutorialState.GetIron:
Console.WriteLine("Please follow instruction to get Iron");
break;
case TutorialState.KillEnemy:
Console.WriteLine("Please follow instruction to kill enemy");
break;
case TutorialState.LevelUp:
Console.WriteLine("Please follow instruction to Up your level");
break;
default:
throw new Exception("Not Support");
}
}
public void ValidateState()
{
switch (currentState)
{
case TutorialState.GetGold:
{
if (player.GoldNum > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Congratulations, you finished Gold Collect Phase");
currentState = TutorialState.GetIron;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("You need to collect gold");
}
break;
}
case TutorialState.GetIron:
{
if (player.IronNum > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Congratulations, you finished Iron Collect Phase");
currentState = TutorialState.KillEnemy;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("You need to collect Iron");
}
break;
}
case TutorialState.KillEnemy:
{
if (player.EnemyKilled > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Congratulations, you finished Enemy Kill Phase");
currentState = TutorialState.LevelUp;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("You need to kill enemy");
}
break;
}
case TutorialState.LevelUp:
{
if (player.Level > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Congratulations, you finished the whole tutorial");
currentState = TutorialState.LevelUp;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("You need to level up");
}
break;
}
default:
throw new Exception("Not Support");
}
}
}static void Main(string[] args)
{
Player player = new Player();
GameTutorial tutorial = new GameTutorial(player);
tutorial.ShowHelpDescription();
tutorial.ValidateState();
//收集黄金
player.CollectGold(1);
tutorial.ValidateState();
tutorial.ShowHelpDescription();
//收集木头
player.CollectIron(1);
tutorial.ValidateState();
tutorial.ShowHelpDescription();
//杀敌
player.KillEnemy();
tutorial.ValidateState();
tutorial.ShowHelpDescription();
//升级
player.LevelUp();
tutorial.ValidateState();
}运行结果
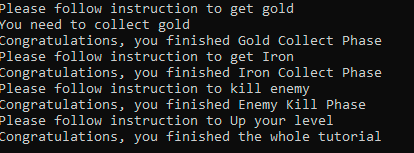
看起来一切都好。。编写的代码既能够根据当前步骤显示不同的提示,还可以成功的根据玩家的进度切换到下一个步骤。
于是,我自信满满的申请了code review,按照我的想法,这段代码通过code review应该是板上钉钉的事情,谁知,老大看到代码,差点没背过气去。。。稍微平复了一下心情之后,他给了我几个灵魂拷问。
GameTutorial需要知道各个步骤的满足条件和提示,它是不是知道的太多了?这符合迪米特法则吗?
如果我们游戏之后新增一个教程步骤,指导玩家升级武器,是不是GameTutorial需要修改?能有办法规避这种新增的改动吗?
如果我们要修改现在的教程步骤之间的顺序关系,GameTutorial是不是又不能避免要被动刀?能有办法尽量减少这种修改的工作量吗?
Switch case 在现有的情况下已经如此长,如果我们再加入新的步骤,这个方法会变成又臭又长的裹脚布吗?
本来以为如此简单的一个功能,没想到还是有那么多弯弯道道,只怪自己还是太年轻啊!最后他悠悠的告诉我,去看看状态模式吧,想想这段代码可以怎么重构。
对象拥有内在状态,当内在状态改变时允许其改变行为,这个对象看起来像改变了其类
有点意思,看来我们可以把教程的不同步骤抽象成不同的状态,然后在各个状态内部实现切换状态和显示帮助文档的逻辑,这样做的好处是
符合迪米特法则,把各个步骤所对应的逻辑推迟到子类,教程类就不需要了解每个步骤的逻辑细节,同时隔离了教程类和状态类,确保状态类的修改不会影响教程类
符合开闭原则,如果新添加步骤,我们仅仅需要添加步骤子类并修改相邻的步骤切换逻辑,教程类无需任何改动
接着我们看看UML,
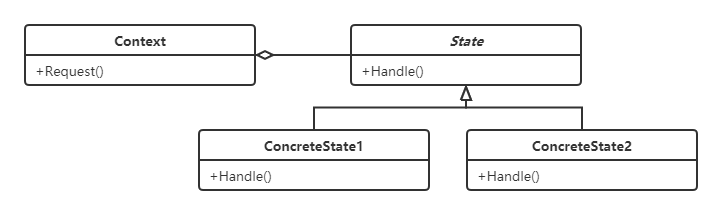
一目了然,在我们的例子里面,state就是教程子步骤,context就是教程类,内部包含教程子步骤并转发请求给教程子步骤,我们跟着来重构一下代码吧。
第一步我们需要删除之前的枚举,取而代之的是一个抽象类当作状态基类,即,各个教程步骤类的基类。注意,每个子状态要自己负责状态切换,所以我们需要教程类暴露接口以满足这个功能。
abstract class TutorialState
{
public abstract void ShowHelpDescription();
public abstract void Validate(GameTutorial tutorial);
}重构教程类体现在以下方面
添加内部状态表面当前处于哪个步骤,在构造函数中给予初始值
暴露接口以让子状态能修改当前状态以完成状态切换
因为需要子状态能访问玩家当前数据以判断是否能切换状态,需要新加接口以避免方法链
修改ShowHelpDescription和ValidateState的逻辑,直接转发方法调用至当前状态
class GameTutorial
{
private TutorialState currentState;
private Player player;
public int PlayerIronNum => player.IronNum;
public int PlayerLevel => player.Level;
public int PlayerGoldNum => player.GoldNum;
public int PlayerEnemyKilled => player.EnemyKilled;
public void SetState(TutorialState state)
{
currentState = state;
}
public GameTutorial(Player player)
{
this.player = player;
currentState = TutorialStateContext.GetGold;
}
public void ShowHelpDescription()
{
currentState.ShowHelpDescription();
}
public void ValidateState()
{
currentState.Validate(this);
}
}接着我们创建各个子状态代表不同的教程步骤
class TutorialSateGetGold : TutorialState
{
public override void ShowHelpDescription()
{
Console.WriteLine("Please follow instruction to get gold");
}
public override void Validate(GameTutorial tutorial)
{
if (tutorial.PlayerGoldNum > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Congratulations, you finished Gold Collect Phase");
tutorial.SetState(TutorialStateContext.GetIron);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("You need to collect gold");
}
}
}
class TutorialStateGetIron : TutorialState
{
public override void ShowHelpDescription()
{
Console.WriteLine("Please follow instruction to get Iron");
}
public override void Validate(GameTutorial tutorial)
{
if (tutorial.PlayerIronNum > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Congratulations, you finished Iron Collect Phase");
tutorial.SetState(TutorialStateContext.KillEnemy);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("You need to collect iron");
}
}
}
class TutorialStateKillEnemy : TutorialState
{
public override void ShowHelpDescription()
{
Console.WriteLine("Please follow instruction to kill enemy");
}
public override void Validate(GameTutorial tutorial)
{
if (tutorial.PlayerEnemyKilled > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Congratulations, you finished enemy kill Phase");
tutorial.SetState(TutorialStateContext.LevelUp);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("You need to collect kill enemy");
}
}
}
class TutorialStateLevelUp : TutorialState
{
public override void ShowHelpDescription()
{
Console.WriteLine("Please follow instruction to level up");
}
public override void Validate(GameTutorial tutorial)
{
if (tutorial.PlayerLevel > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Congratulations, you finished the whole tutorial");
}
}
}这是模式中没有提到的知识点,一般来说,为了避免大量的子状态对象被创建,我们会构造一个状态容器,以静态变量的方式初始化需要使用的子状态。
static class TutorialStateContext
{
public static TutorialState GetGold;
public static TutorialState GetIron;
public static TutorialState KillEnemy;
public static TutorialState LevelUp;
static TutorialStateContext()
{
GetGold = new TutorialSateGetGold();
GetIron = new TutorialStateGetIron();
KillEnemy = new TutorialStateKillEnemy();
LevelUp = new TutorialStateLevelUp();
}
}测试代码部分保持不变,直接运行,结果和原来一样,重构成功。
关于“C#中对象状态模式怎么实现”这篇文章的内容就介绍到这里,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家对“C#中对象状态模式怎么实现”知识都有一定的了解,大家如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。