您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇“C#中的流怎么使用和分类”文章的知识点大部分人都不太理解,所以小编给大家总结了以下内容,内容详细,步骤清晰,具有一定的借鉴价值,希望大家阅读完这篇文章能有所收获,下面我们一起来看看这篇“C#中的流怎么使用和分类”文章吧。
使用流把文件读取到字节数组:
//FileMode.Create, FileMode.Append //FileAccess.Write, FileAccess.ReadWrite //FileMode和FileAccess搭配使用,如果第二个参数FileMode.Appden写追加,第三个参数FileAccess.Read只读,会抛异常 Stream source = new FileStream(@"1.jpg",FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read) byte[] buffer = new byte[source.Length]; int bytesRead = source.Read(buffer, i, (int)source.Length);
Int32类型的最大值,以及Byte, KB, MB, GB转换:
Int32.MaxValue = 2147483647 Byte
2147483647/1024 = 2097152 KB(1 KB = 1024 Byte)
2097152/1024 = 2048 MB(1 M = 1024 KB)
2048/1024 = 2 G(1G = 1024M)
使用流把字节数组写到文件:
Stream target = new FileStream(@"2.jpg", FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write); Stream source = new FileStream(@"1.jpg",FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read) byte[] buffer = new byte[source.Length]; int bytesRead = source.Read(buffer, i, (int)source.Length); target.Write(buffer, 0, buffer.Length); source.Dispose(); target.Dispose();
使用流对大文件进行分批读取和写入:
int BufferSize = 10240; // 10KB
Stream source = new FileStream(@"D:\a.mp3", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
Stream target = new FileStream(@"D:\b.mp3", FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
byte[] buffer = new byte[BufferSize];
int byteRead;
do{
byteRead = source.Read(buffer, 0, BufferSize);
target.Write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
} while(byteRead > 0);
target.Dispose();
source.Dispose();在Stream抽象类下包含:
→FileStream→IsolatedStoreageFileStream
→MemoryStream
→NetworkStream
CanRead()
Read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int count)
CanWrite()
Write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int count)
WriteByte(Byte value)
CanSeek()
Seek(long offset, SeekOrigion)
Position流的指针位置
Close()
Dispose()
Flush()将缓存设备写入存储设备
CanTimeout()
ReadTimeout()
WriteTimeout()
Length
SetLength(long value)
实现了Decorator模式,包含对Stream抽象基类的引用,同时继承自Stream抽象基类。
System.IO.Compression下的DeflateStream和GZipStream用于压缩和解压缩
System.Security.Cryptography下的CryptoStream用于加密和解密
System.Net.Security下的AuthenticatedStream用于安全性
System.IO下的BufferedStream用户缓存
不是流类型,而是协助开发者处理流包含的数据,并且不需要将流读取到Byte[]字节数组中。但流的包装器类包含了对流的引用。
继承自TextReader。
将流中的数据读取为字符。
FileStream fs = new FileStream("a.txt", FileMode.Open, FileAcess.Read);
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(fs, Encoding.GetEncoding("GB2312"));
//或者
//StreamReader reader = new StreamReader("a.txt"); //默认采用UTF-8编码方式继承自TextWriter。
将字符写入到流中。
string text =
@"aa
bb
cc";
StringReader reader = new StringReader(text);
int c = reader.Read();
Console.Write((char)c);
char[] buffer = new char[8];
reader.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
Console.Write(String.Join("",buffer));
string line = reader.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine(line);
string rest = reader.ReadToEnd();
Console.Write();
reader.Dispose();也继承自TextReader和TextWriter,但是用来处理字符串。
BinaryWriter用于向流中以二进制方式写入基元类型,比如int, float, char, string等.BinaryReader用于从流中读取基元类型。注意,这2个类并不是继承TextReader和TextWriter。
namespace ConsoleApplication29
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Product p = new Product("product.bin")
{
Id = 1,
Name = "GOOD",
Price = 500F
};
p.Save();
Product newP = new Product("product.bin");
newP.Load();
Console.WriteLine(newP);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
private string filePath;
public Product(string filePath)
{
this.filePath = filePath;
}
public void Save()
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.filePath, FileMode.Create,FileAccess.Write);
BinaryWriter writer = new BinaryWriter(fs);
writer.Write(this.Id);
writer.Write(this.Name);
writer.Write(this.Price);
writer.Dispose();
}
public void Load()
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.filePath, FileMode.Open,FileAccess.Read);
BinaryReader reader = new BinaryReader(fs);
this.Id = reader.ReadInt32();
this.Name = reader.ReadString();
this.Price = reader.ReadDouble();
reader.Dispose();
}
public override string ToString()
{
return String.Format("Id:{0},Name:{1},Price:{2}", this.Id, this.Name, this.Price);
}
}
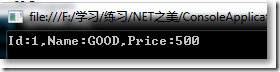
}结果:
编码方式:
定义了字节如何转换成人类可读的字符或者文本,可以看作是字节和字符的对应关系表。在读取文件采用的编码方式要和创建文件采用的编码方式保持一致。
在System.IO命名空间下。
File
FileStream fs = File.Create("a.txt");
Open(string path, FileMode mode)
OpenRead()
OpenWrite()
ReadAllText()
ReadAllByte()
WriteBllBytes()
WriteAllLines()
Copy(string sourceFileName, string destFileName)
FileInfo
Path
Directory
DirectoryInfo
以上就是关于“C#中的流怎么使用和分类”这篇文章的内容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小编分享的内容对大家有帮助,若想了解更多相关的知识内容,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。