您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章主要介绍了GraphQL如何创建的相关知识,内容详细易懂,操作简单快捷,具有一定借鉴价值,相信大家阅读完这篇GraphQL如何创建文章都会有所收获,下面我们一起来看看吧。
因为目前做的项目查询提供的接口都使用GraphQL替代典型的REST API,所以有必要去对它进行了解和源码的阅读。一种用于API的查询语言,让你的请求数据不多不少。前端按需获取,后端动态返回(不需要的数据不会返回甚至不会查库),对比起典型的REST API将更加灵活,后端代码提供可选能力。如果增加新的字段应用不想处理这部分数据可以不用区分版本。
后端确定哪些接口行为是被允许的,前端按需获取数据,让你的请求数据不多不少。
最好使用Spring Initializr去创建一个新的项目,不会产生一些冲突。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.graphql-java.tutorial</groupId> <artifactId>book-details</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>book-details</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.graphql-java/graphql-java --> <dependency> <groupId>com.graphql-java</groupId> <artifactId>graphql-java</artifactId> <version>11.0</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.graphql-java/graphql-java-spring-boot-starter-webmvc --> <dependency> <groupId>com.graphql-java</groupId> <artifactId>graphql-java-spring-boot-starter-webmvc</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.guava/guava --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>26.0-jre</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> <repositories> <repository> <id>central</id> <name>aliyun maven</name> <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url> <layout>default</layout> <!-- 是否开启发布版构件下载 --> <releases> <enabled>true</enabled> </releases> <!-- 是否开启快照版构件下载 --> <snapshots> <enabled>false</enabled> </snapshots> </repository> </repositories> </project>
在src/main/resources中创建schema.graphqls文件:
type Query {
bookById(id: ID): Book
}
type Book {
id: ID
name: String
pageCount: Int
author: Author
}
type Author {
id: ID
firstName: String
lastName: String
}可以看到定义了一个bookById查询,用于根据id查询书籍,书籍中包含id、name、pageCount、author属性,其中author是一个复合类型所以定义了type Author。
上面显示的用于描述schema的特定于域的语言称为schema定义语言或SDL。更多细节可以在这里找到。
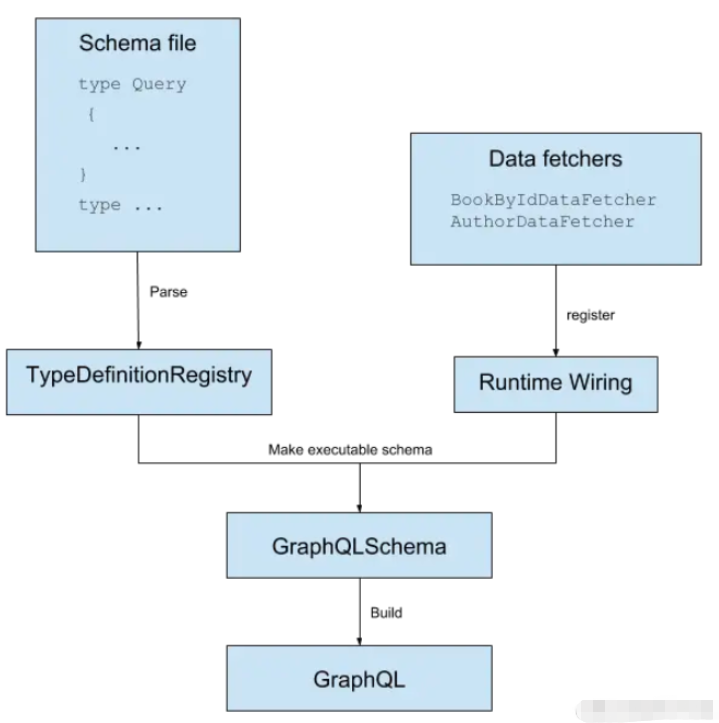
一旦我们有了这个文件,我们需要通过读取文件并解析它并且添加代码来为它获取数据使它“栩栩如生”。
package com.graphqljava.tutorial.bookdetails;
import com.google.common.base.Charsets;
import com.google.common.io.Resources;
import graphql.GraphQL;
import graphql.schema.GraphQLSchema;
import graphql.schema.idl.RuntimeWiring;
import graphql.schema.idl.SchemaGenerator;
import graphql.schema.idl.SchemaParser;
import graphql.schema.idl.TypeDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import static graphql.schema.idl.TypeRuntimeWiring.newTypeWiring;
@Component
public class GraphQLProvider {
private GraphQL graphQL;
/**
* 注入GraphQL实例,GraphQL Java Spring适配器将使用GraphQL实例使我们的schema可用,通过Http-使用默认的"/graphql"url路径
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public GraphQL graphQL() {
return graphQL;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() throws IOException {
//使用Resources读取graphqls文件
URL url = Resources.getResource("schema.graphqls");
//拿到graphqls文件内容
String sdl = Resources.toString(url, Charsets.UTF_8);
GraphQLSchema graphQLSchema = buildSchema(sdl);
this.graphQL = GraphQL.newGraphQL(graphQLSchema).build();
}
@Autowired
GraphQLDataFetchers graphQLDataFetchers;
/**
* 创建GraphQLSchema实例:解析schema并关联fetcher
*
* @param sdl
* @return
*/
private GraphQLSchema buildSchema(String sdl) {
TypeDefinitionRegistry typeRegistry = new SchemaParser().parse(sdl);
RuntimeWiring runtimeWiring = buildWiring();
SchemaGenerator schemaGenerator = new SchemaGenerator();
return schemaGenerator.makeExecutableSchema(typeRegistry, runtimeWiring);
}
/**
* 根据层级去关联fetcher构建RuntimeWiring。最外层为Query可以提供bookById所需参数。第二层为Book-经过第一层获得的,可以为author提供所需参数。
*
* @return
*/
private RuntimeWiring buildWiring() {
return RuntimeWiring.newRuntimeWiring()
.type(newTypeWiring("Query")
.dataFetcher("bookById", graphQLDataFetchers.getBookByIdDataFetcher()))
.type(newTypeWiring("Book")
.dataFetcher("author", graphQLDataFetchers.getAuthorDataFetcher()))
.build();
}
}package com.graphqljava.tutorial.bookdetails;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap;
import graphql.schema.DataFetcher;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class GraphQLDataFetchers {
/**
* books静态数据
*/
private static List<Map<String, String>> books = Arrays.asList(
ImmutableMap.of("id", "book-1",
"name", "Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone",
"pageCount", "223",
"authorId", "author-1"),
ImmutableMap.of("id", "book-2",
"name", "Moby Dick",
"pageCount", "635",
"authorId", "author-2"),
ImmutableMap.of("id", "book-3",
"name", "Interview with the vampire",
"pageCount", "371",
"authorId", "author-3")
);
/**
* autors静态数据
*/
private static List<Map<String, String>> authors = Arrays.asList(
ImmutableMap.of("id", "author-1",
"firstName", "Joanne",
"lastName", "Rowling"),
ImmutableMap.of("id", "author-2",
"firstName", "Herman",
"lastName", "Melville"),
ImmutableMap.of("id", "author-3",
"firstName", "Anne",
"lastName", "Rice")
);
/**
* bookById的fetcher,这里只是简单的通过静态数据进行筛选,具体生产使用sql进行查询
*
* @return
*/
public DataFetcher getBookByIdDataFetcher() {
return dataFetchingEnvironment -> {
// 获得查询筛选参数
String bookId = dataFetchingEnvironment.getArgument("id");
return books
.stream()
.filter(book -> book.get("id").equals(bookId))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
};
}
/**
* 第二层author fetcher
*
* @return
*/
public DataFetcher getAuthorDataFetcher() {
return dataFetchingEnvironment -> {
//获得上级对象
Map<String, String> book = dataFetchingEnvironment.getSource();
//根据上级对象找到关联id(相当于外键)
String authorId = book.get("authorId");
return authors
.stream()
.filter(author -> author.get("id").equals(authorId))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
};
}
}对于GraphQL Java服务器来说,最重要的概念可能是DataFetcher:DataFetcher在执行查询时获取一个字段的数据。
GraphQL Java在执行查询时,会为查询中遇到的每个字段调用相应的DataFetcher。DataFetcher是函数接口,函数具有一个参数为DataFetchingEnvironment类型。
public interface DataFetcher<T> {
T get(DataFetchingEnvironment dataFetchingEnvironment) throws Exception;
}如上我们实现了两个DataFetchers。如上所述,如果你不指定一个,PropertyDataFetcher则是被默认使用。比如上面的例子中Book.id,Book.name,Book.pageCount,Author.id,Author.firstName和Author.lastName都有一个PropertyDataFetcher与之关联。
PropertyDataFetcher尝试以多种方式查找Java对象的属性。如果是java.util.Map,简单的通过key查找。这对我们来说非常好,因为book和author Maps的keys与schema中指定的字段相同。
关于“GraphQL如何创建”这篇文章的内容就介绍到这里,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家对“GraphQL如何创建”知识都有一定的了解,大家如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。