您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇文章主要介绍了SpringBoot动态定时任务如何实现的相关知识,内容详细易懂,操作简单快捷,具有一定借鉴价值,相信大家阅读完这篇SpringBoot动态定时任务如何实现文章都会有所收获,下面我们一起来看看吧。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.TaskScheduler;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskScheduler;
@Configuration
public class SchedulingConfig {
@Bean
public TaskScheduler taskScheduler() {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
// 定时任务执行线程池核心线程数
taskScheduler.setPoolSize(6);
taskScheduler.setRemoveOnCancelPolicy(true);
taskScheduler.setThreadNamePrefix("TaskSchedulerThreadPool-");
return taskScheduler;
}
}ScheduledFuture是ScheduledExecutorService定时任务线程池的执行结果。
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
public final class ScheduledTask {
volatile ScheduledFuture<?> future;
/**
* 取消定时任务
*/
public void cancel() {
ScheduledFuture<?> future = this.future;
if (future != null) {
future.cancel(true);
}
}
}被定时任务线程池调用,用来执行指定bean里面的方法。
import com.ying.demo.utils.springContextUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Objects;
public class SchedulingRunnable implements Runnable {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SchedulingRunnable.class);
private String beanName;
private String methodName;
private String params;
public SchedulingRunnable(String beanName, String methodName) {
this(beanName, methodName, null);
}
public SchedulingRunnable(String beanName, String methodName, String params) {
this.beanName = beanName;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.params = params;
}
@Override
public void run() {
logger.info("定时任务开始执行 - bean:{},方法:{},参数:{}", beanName, methodName, params);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Object target = springContextUtils.getBean(beanName);
Method method = null;
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(params)) {
method = target.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(methodName, String.class);
} else {
method = target.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(methodName);
}
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(params)) {
method.invoke(target, params);
} else {
method.invoke(target);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.error(String.format("定时任务执行异常 - bean:%s,方法:%s,参数:%s ", beanName, methodName, params), ex);
}
long times = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("定时任务执行结束 - bean:{},方法:{},参数:{},耗时:{} 毫秒", beanName, methodName, params, times);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
SchedulingRunnable that = (SchedulingRunnable) o;
if (params == null) {
return beanName.equals(that.beanName) &&
methodName.equals(that.methodName) &&
that.params == null;
}
return beanName.equals(that.beanName) &&
methodName.equals(that.methodName) &&
params.equals(that.params);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (params == null) {
return Objects.hash(beanName, methodName);
}
return Objects.hash(beanName, methodName, params);
}
}用来增加、删除定时任务
@Component
public class CronTaskRegistrar implements DisposableBean {
private final Map<Runnable, ScheduledTask> scheduledTasks = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
@Autowired
private TaskScheduler taskScheduler;
public TaskScheduler getScheduler() {
return this.taskScheduler;
}
public void addCronTask(Runnable task, String cronExpression) {
addCronTask(new CronTask(task, cronExpression));
}
public void addCronTask(CronTask cronTask) {
if (cronTask != null) {
Runnable task = cronTask.getRunnable();
if (this.scheduledTasks.containsKey(task)) {
removeCronTask(task);
}
this.scheduledTasks.put(task, scheduleCronTask(cronTask));
}
}
public void removeCronTask(Runnable task) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = this.scheduledTasks.remove(task);
if (scheduledTask != null)
scheduledTask.cancel();
}
public ScheduledTask scheduleCronTask(CronTask cronTask) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask();
scheduledTask.future = this.taskScheduler.schedule(cronTask.getRunnable(), cronTask.getTrigger());
return scheduledTask;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
for (ScheduledTask task : this.scheduledTasks.values()) {
task.cancel();
}
this.scheduledTasks.clear();
}
}@Slf4j
@Component("taskDemo")
public class Task1 {
public void taskByParams(String params) {
log.info("taskByParams执行时间:{}", new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
log.info("taskByParams执行有参示例任务:{}",params);
}
public void taskNoParams() {
log.info("taskByParams执行时间:{}", new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
log.info("taskNoParams执行无参示例任务");
}
public void test(String params) {
log.info("test执行时间:{}", new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
log.info("test执行有参示例任务:{}",params);
}
}CREATE TABLE `schedule_setting` ( `job_id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '任务ID', `bean_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'bean名称', `method_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '方法名称', `method_params` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '方法参数', `cron_expression` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'cron表达式', `remark` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '备注', `job_status` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '状态(1正常 0暂停)', `create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间', `update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改时间', PRIMARY KEY (`job_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
@Data
public class ScheduleSetting extends Model<ScheduleSetting> {
/**
* 任务ID
*/
@Id
private Integer jobId;
/**
* bean名称
*/
private String beanName;
/**
* 方法名称
*/
private String methodName;
/**
* 方法参数
*/
private String methodParams;
/**
* cron表达式
*/
private String cronExpression;
/**
* 状态(1正常 0暂停)
*/
private Integer jobStatus;
/**
* 备注
*/
private String remark;
/**
* 创建时间
*/
private Date createTime;
/**
* 更新时间
*/
private Date updateTime;
}spring boot项目启动完成后,加载数据库里状态为正常的定时任务
@Service
public class SysJobRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SysJobRunner.class);
@Autowired
private CronTaskRegistrar cronTaskRegistrar;
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
// 初始加载数据库里状态为正常的定时任务
ScheduleSetting existedSysJob = new ScheduleSetting();
List<ScheduleSetting> jobList = existedSysJob.selectList(new QueryWrapper<ScheduleSetting>().eq("job_status", 1));
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(jobList)) {
for (ScheduleSetting job : jobList) {
SchedulingRunnable task = new SchedulingRunnable(job.getBeanName(), job.getMethodName(), job.getMethodParams());
cronTaskRegistrar.addCronTask(task, job.getCronExpression());
}
logger.info("定时任务已加载完毕...");
}
}
}用来从spring容器里获取bean
@Component
public class SpringContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)
throws BeansException {
SpringContextUtils.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public static Object getBean(String name) {
return applicationContext.getBean(name);
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) {
return applicationContext.getBean(requiredType);
}
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) {
return applicationContext.getBean(name, requiredType);
}
public static boolean containsBean(String name) {
return applicationContext.containsBean(name);
}
public static boolean isSingleton(String name) {
return applicationContext.isSingleton(name);
}
public static Class<? extends Object> getType(String name) {
return applicationContext.getType(name);
}
}@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private CronTaskRegistrar cronTaskRegistrar;
/**
* 添加定时任务
*
* @param sysJob
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("add")
public boolean add(@RequestBody ScheduleSetting sysJob) {
sysJob.setCreateTime(new Date());
sysJob.setUpdateTime(new Date());
boolean insert = sysJob.insert();
if (!insert) {
return false;
}else {
if (sysJob.getJobStatus().equals(1)) {// 添加成功,并且状态是1,直接放入任务器
SchedulingRunnable task = new SchedulingRunnable(sysJob.getBeanName(), sysJob.getMethodName(), sysJob.getMethodParams());
cronTaskRegistrar.addCronTask(task, sysJob.getCronExpression());
}
}
return insert;
}
/**
* 修改定时任务
*
* @param sysJob
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("update")
public boolean update(@RequestBody ScheduleSetting sysJob) {
sysJob.setCreateTime(new Date());
sysJob.setUpdateTime(new Date());
// 查询修改前任务
ScheduleSetting existedSysJob = new ScheduleSetting();
existedSysJob = existedSysJob.selectOne(new QueryWrapper<ScheduleSetting>().eq("job_id", sysJob.getJobId()));
// 修改任务
boolean update = sysJob.update(new UpdateWrapper<ScheduleSetting>().eq("job_id", sysJob.getJobId()));
if (!update) {
return false;
} else {
// 修改成功,则先删除任务器中的任务,并重新添加
SchedulingRunnable task1 = new SchedulingRunnable(existedSysJob.getBeanName(), existedSysJob.getMethodName(), existedSysJob.getMethodParams());
cronTaskRegistrar.removeCronTask(task1);
if (sysJob.getJobStatus().equals(1)) {// 如果修改后的任务状态是1就加入任务器
SchedulingRunnable task = new SchedulingRunnable(sysJob.getBeanName(), sysJob.getMethodName(), sysJob.getMethodParams());
cronTaskRegistrar.addCronTask(task, sysJob.getCronExpression());
}
}
return update;
}
/**
* 删除任务
*
* @param jobId
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("del/{jobId}")
public boolean del(@PathVariable("jobId") Integer jobId) {
// 先查询要删除的任务信息
ScheduleSetting existedSysJob = new ScheduleSetting();
existedSysJob = existedSysJob.selectOne(new QueryWrapper<ScheduleSetting>().eq("job_id", jobId));
// 删除
boolean del = existedSysJob.delete(new QueryWrapper<ScheduleSetting>().eq("job_id", jobId));
if (!del)
return false;
else {// 删除成功时要清除定时任务器中的对应任务
SchedulingRunnable task = new SchedulingRunnable(existedSysJob.getBeanName(), existedSysJob.getMethodName(), existedSysJob.getMethodParams());
cronTaskRegistrar.removeCronTask(task);
}
return del;
}
// 停止/启动任务
@PostMapping("changesStatus/{jobId}/{stop}")
public boolean changesStatus(@PathVariable("jobId") Integer jobId, @PathVariable("stop") Integer stop) {
// 修改任务状态
ScheduleSetting scheduleSetting = new ScheduleSetting();
scheduleSetting.setJobStatus(stop);
boolean job_id = scheduleSetting.update(new UpdateWrapper<ScheduleSetting>().eq("job_id", jobId));
if (!job_id) {
return false;
}
// 查询修改后的任务信息
ScheduleSetting existedSysJob = new ScheduleSetting();
existedSysJob = existedSysJob.selectOne(new QueryWrapper<ScheduleSetting>().eq("job_id", jobId));
// 如果状态是1则添加任务
if (existedSysJob.getJobStatus().equals(1)) {
SchedulingRunnable task = new SchedulingRunnable(existedSysJob.getBeanName(), existedSysJob.getMethodName(), existedSysJob.getMethodParams());
cronTaskRegistrar.addCronTask(task, existedSysJob.getCronExpression());
} else {
// 否则清除任务
SchedulingRunnable task = new SchedulingRunnable(existedSysJob.getBeanName(), existedSysJob.getMethodName(), existedSysJob.getMethodParams());
cronTaskRegistrar.removeCronTask(task);
}
return true;
}
cron表达式语法:
[秒] [分] [小时] [日] [月] [周] [年]
注:[年]不是必须的域,可以省略[年],则一共6个域
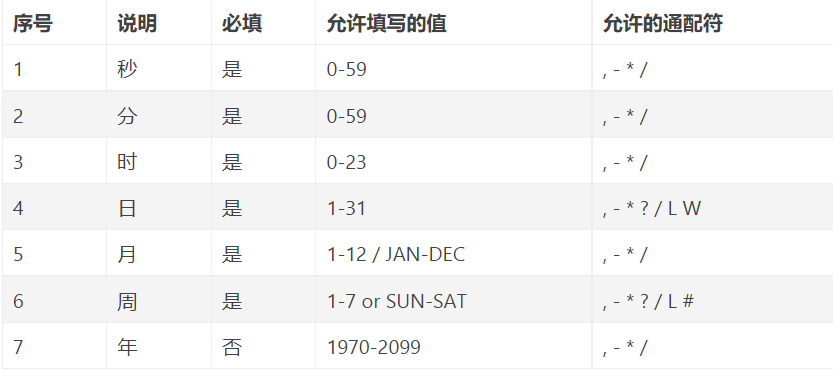
通配符说明:
* 表示所有值。 例如:在分的字段上设置 *,表示每一分钟都会触发。
? 表示不指定值。使用的场景为不需要关心当前设置这个字段的值。例如:要在每月的10号触发一个操作,但不关心是周几,所以需要周位置的那个字段设置为”?” 具体设置为 0 0 0 10 * ?
- 表示区间。例如 在小时上设置 “10-12”,表示 10,11,12点都会触发。
, 表示指定多个值,例如在周字段上设置 “MON,WED,FRI” 表示周一,周三和周五触发
/ 用于递增触发。如在秒上面设置”5/15” 表示从5秒开始,每增15秒触发(5,20,35,50)。 在日字段上设置’1/3’所示每月1号开始,每隔三天触发一次。
L 表示最后的意思。在日字段设置上,表示当月的最后一天(依据当前月份,如果是二月还会依据是否是润年[leap]), 在周字段上表示星期六,相当于”7”或”SAT”。如果在”L”前加上数字,则表示该数据的最后一个。例如在周字段上设置”6L”这样的格式,则表示“本月最后一个星期五”
W 表示离指定日期的最近那个工作日(周一至周五). 例如在日字段上置”15W”,表示离每月15号最近的那个工作日触发。如果15号正好是周六,则找最近的周五(14号)触发, 如果15号是周未,则找最近的下周一(16号)触发.如果15号正好在工作日(周一至周五),则就在该天触发。如果指定格式为 “1W”,它则表示每月1号往后最近的工作日触发。如果1号正是周六,则将在3号下周一触发。(注,”W”前只能设置具体的数字,不允许区间”-“)。
# 序号(表示每月的第几个周几),例如在周字段上设置”6#3”表示在每月的第三个周六.注意如果指定”#5”,正好第五周没有周六,则不会触发该配置(用在母亲节和父亲节再合适不过了) ;小提示:’L’和 ‘W’可以一组合使用。如果在日字段上设置”LW”,则表示在本月的最后一个工作日触发;周字段的设置,若使用英文字母是不区分大小写的,即MON与mon相同。
示例:
每隔5秒执行一次:*/5 * * * * ?
每隔1分钟执行一次:0 */1 * * * ?
每天23点执行一次:0 0 23 * * ?
每天凌晨1点执行一次:0 0 1 * * ?
每月1号凌晨1点执行一次:0 0 1 1 * ?
每月最后一天23点执行一次:0 0 23 L * ?
每周星期六凌晨1点实行一次:0 0 1 ? * L
在26分、29分、33分执行一次:0 26,29,33 * * * ?
每天的0点、13点、18点、21点都执行一次:0 0 0,13,18,21 * * ?
cron在线表达式生成器:http://tools.jb51.net/code/Quartz_Cron_create
关于“SpringBoot动态定时任务如何实现”这篇文章的内容就介绍到这里,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家对“SpringBoot动态定时任务如何实现”知识都有一定的了解,大家如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。