жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
дёҖгҖҒз®Җд»Ӣ
е°ұеә”з”ЁжқҘиҜҙпјҢmapе·Із»ҸжҳҜSTLж ҮеҮҶеә“зҡ„жҲҗе‘ҳпјҢиҖҢhash_mapжҡӮж—¶иҝҳжңӘиҝӣе…Ҙж ҮеҮҶеә“пјҢжҳҜжү©еұ•extдёӯзҡ„дёҖдёӘеҠҹиғҪпјҢдҪҶд№ҹжҳҜйқһ常常用并且йқһеёёйҮҚиҰҒзҡ„еә“гҖӮ
дәҢгҖҒз®ҖеҚ•еҜ№жҜ”
йҰ–е…ҲпјҢиҰҒиҜҙзҡ„жҳҜиҝҷдёӨз§Қж•°жҚ®з»“жһ„зҡ„йғҪжҸҗдҫӣдәҶKEY-VALUEзҡ„еӯҳеӮЁе’ҢжҹҘжүҫзҡ„еҠҹиғҪгҖӮдҪҶжҳҜе®һзҺ°жҳҜдёҚдёҖж ·зҡ„пјҢmapжҳҜз”Ёзҡ„зәўй»‘ж ‘пјҢжҹҘиҜўж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰдёәlog(n)гҖӮиҖҢhash_mapжҳҜз”Ёзҡ„е“ҲеёҢиЎЁпјҢжҹҘиҜўж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰзҗҶи®әдёҠеҸҜд»ҘжҳҜеёёж•°пјҢдҪҶжҳҜж¶ҲиҖ—еҶ…еӯҳеӨ§пјҢжҳҜдёҖз§Қд»ҘеӯҳеӮЁжҚўж—¶й—ҙзҡ„ж–№жі•гҖӮ
ж ‘жҹҘжүҫпјҢеңЁжҖ»жҹҘжүҫж•ҲзҺҮдёҠжҜ”дёҚдёҠhashиЎЁпјҢдҪҶжҳҜе®ғеҫҲзЁіе®ҡпјҢе®ғзҡ„з®—жі•еӨҚжқӮеәҰдёҚдјҡеҮәзҺ°жіўеҠЁгҖӮеңЁдёҖж¬ЎжҹҘжүҫдёӯпјҢдҪ еҸҜд»Ҙж–ӯе®ҡе®ғжңҖеқҸзҡ„жғ…еҶөдёӢе…¶еӨҚжқӮеәҰдёҚдјҡи¶…иҝҮO(log2N)гҖӮиҖҢhashиЎЁе°ұдёҚдёҖж ·пјҢжҳҜO(1)пјҢиҝҳжҳҜO(N)пјҢжҲ–иҖ…еңЁе…¶д№Ӣй—ҙпјҢдҪ 并дёҚиғҪжҠҠжҸЎгҖӮ
дёүгҖҒhash_mapзҡ„дҪҝз”Ё
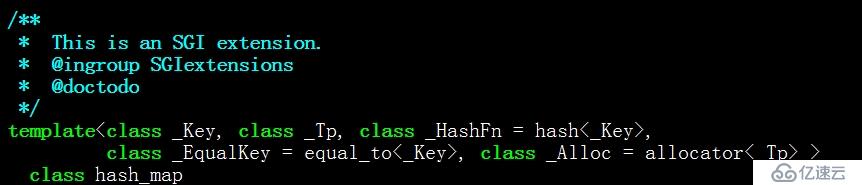
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢеҰӮжһңе®ҡд№үе®Ңж•ҙзҡ„hash_mapпјҢйңҖиҰҒжҸҗдҫӣ<keyзұ»еһӢпјҢvalueзұ»еһӢпјҢе“ҲеёҢеҮҪж•°пјҢkeyзӣёзӯүеҲӨж–ӯеҮҪж•°пјҢvalueзұ»еһӢеҶ…еӯҳеҲҶй…ҚеҷЁ>зӯү5дёӘжЁЎжқҝеҸӮж•°пјҢз”ұдәҺеҗҺдёүдёӘйғҪжңүй»ҳи®ӨеҖјпјҢжүҖд»ҘдёҖиҲ¬жҲ‘们еҸӘйңҖиҰҒжҸҗдҫӣеүҚдёӨдёӘгҖӮ
1> е®ҡд№ү__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int> myHashMapдёҚдјҡеҮәй”ҷпјҢ然иҖҢдёҖж—ҰеҜ№myHashMapиҝӣиЎҢж“ҚдҪңпјҢе°ұдјҡеҮәзҺ°зј–иҜ‘й”ҷиҜҜвҖңinstantiated from hereвҖқпјҢиҝҷжҳҜеӣ дёәgnuзүҲжң¬зҡ„hash_mapеҸӘе®һзҺ°дәҶжңүйҷҗзҡ„еҮ дёӘhashжЁЎжқҝеҮҪж•°пјҲи§Ғ第дёүдёӘжЁЎжқҝеҸӮж•°пјҢиҝҷдәӣеҮҪж•°еңЁhash_fun.hдёӯпјүпјҢиҖҢиҝҷдәӣеҮҪж•°йҮҢеҢ…жӢ¬hash<const char*>пјҢдҪҶжҳҜдёҚеҢ…жӢ¬hash<std::string>зҡ„е®һдҫӢеҢ–гҖӮи§ЈеҶіеҠһжі•жҳҜе®ҡд№үе“ҲеёҢиЎЁеүҚиҮӘе·ұзү№еҢ–дёҖдёӘе®һдҫӢпјҢиҝҷж ·зј–иҜ‘еҷЁе°ұзҹҘйҒ“и°ғз”ЁиҝҷдёӘеҮҪж•°дәҶгҖӮ
namespace __gnu_cxx
{
template <>
struct hash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string &s) const
{ return __stl_hash_string(s.c_str()); }
};
}2> 第еӣӣдёӘеҸӮж•°keyзӣёзӯүеҲӨж–ӯеҮҪж•°зҡ„ж„Ҹд№ү
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int> myHashMap;
char name1[10] = "zhu";
char name2[10] = "zhu";
myHashMap[name1] = 1;
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int>::iterator it = myHashMap.find(name2);
if (it == myHashMap.end())
cout << "not find" << endl;
return 0;
}дҪ дјҡеҸ‘зҺ°пјҢиҷҪ然name1е’Ңname2йғҪжҳҜzhuпјҢдҪҶжҳҜжҸ’е…ҘдәҶname1пјҢз”Ёname2еҺ»жҹҘжүҫж—¶пјҢиҝҳжҳҜжҹҘж— з»“жһңгҖӮиҝҷжҳҜж¶үеҸҠеҲ°з¬¬еӣӣдёӘжЁЎжқҝеҸӮж•°пјҢеҲӨж–ӯkeyзӣёзӯүпјҢй»ҳи®Өзҡ„жҳҜstd::equal_toпјҢиҖҢиҝҷдёӘеҮҪж•°зҡ„е®ҡд№үжҳҜз”Ёoperator==жқҘиҝӣиЎҢеҲӨж–ӯзҡ„пјҢжҢҮй’Ҳзҡ„зӣёзӯүеҪ“然е°ұжҳҜең°еқҖдёҖж ·дәҶпјҢиҖҢname1е’Ңname2зҡ„ең°еқҖжҳҫ然дёҚеҗҢгҖӮи§ЈеҶіеҠһжі•жҳҜз”ЁиҮӘе·ұжҢҮе®ҡзҡ„еҮҪж•°жЁЎжқҝжӣҝд»Јй»ҳи®Өзҡ„гҖӮ
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <ext/hash_map>
#include <backward/hash_fun.h>
using namespace std;
template <class _Tp>
struct my_equal_to : public binary_function<_Tp, _Tp, bool>
{
bool operator()(const _Tp& __x, const _Tp& __y) const
{ return strcmp(__x, __y) == 0; }
};
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int, __gnu_cxx::hash<const char*>, my_equal_to<const char*> > myHashMap;
char name1[10] = "zhu";
char name2[10] = "zhu";
myHashMap[name1] = 1;
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<const char *, int, __gnu_cxx::hash<const char*>, my_equal_to<const char*> >::iterator it = myHashMap.find(name2);
if (it == myHashMap.end())
cout << "not find" << endl;
else
cout << it->second << endl;
return 0;
}з”ЁеҲҡеҲҡзү№еҢ–зҡ„hash_map<string, int>е°ұжҳҜеҸҜд»ҘжүҫеҲ°зҡ„пјҢеӣ дёәstringйҮҚиҪҪдәҶoperator==ж“ҚдҪңз¬ҰгҖӮ
зј–иҜ‘дҪҝз”Ё-Wno-deprecatedйҖүйЎ№пјҢдёҚ然дјҡжңүbackward_warning.hеӨҙж–Ү件йҮҢзҡ„е‘ҠиӯҰгҖӮ
еӣӣгҖҒиӮӨжө…зҡ„еҜ№жҜ”жөӢиҜ•(map,зі»з»ҹhashеҮҪж•°зҡ„hash_mapеҸҠиҮӘеҶҷhashеҮҪж•°зҡ„hash_map)
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ cat /tmp/name.txt | wc -l 25848136 #д»ҺзҺ°жңүзҡ„жёёжҲҸж•°жҚ®еә“йҮҢжӢүдәҶ561916дёӘи§’иүІеҗҚ(йҮҢйқўжң¬жқҘе°ұжңүйҮҚеӨҚзҡ„)пјҢ然еҗҺйҮҚеӨҚиҝҪеҠ дәҶеҮ ж¬ЎпјҢеҸҳжҲҗдәҶ #2584дёҮиЎҢзҡ„ж•°жҚ®
1.зі»з»ҹhashеҮҪж•°зҡ„hash_mapе®һзҺ°
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
//зү№еҢ–hashеҮҪж•°зҡ„stringзүҲжң¬
namespace __gnu_cxx
{
template <>
struct hash<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string &s) const
{ return __stl_hash_string(s.c_str()); }
};
}
//и®Ўз®—еҪ“еүҚж—¶й—ҙ
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime(&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int> fileMap;
string temp; //еӯҳж”ҫжҜҸиЎҢзҡ„дёҙж—¶еӯ—з¬ҰдёІ
int i = 0; //з»ҹи®ЎжҖ»дёӘж•°
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime(); //д»ҺиҝҷйҮҢејҖе§Ӣи®Ўж—¶
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime(); //и®Ўж—¶з»“жқҹ
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#зј–иҜ‘ [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ -Wno-deprecated 3.cpp -o hashMap
2.иҮӘеҶҷhashеҮҪж•°зҡ„hash_map
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
struct strHash{
size_t operator()(const string& str) const
{
unsigned long __h = 0;
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < str.size() ; i ++)
__h = 107*__h + str[i];
return size_t(__h);
}
};
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime(&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<string, int, strHash> fileMap;
string temp;
int i = 0;
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime();
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime();
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#зј–иҜ‘ [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ -Wno-deprecated 4.cpp -o strhashMap
3.STLзҡ„map
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void curTime()
{
time_t aTime = time(NULL);
struct tm * curtime = localtime (&aTime);
char ctemp[20];
strftime(ctemp, 20, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" , curtime);
cout<<ctemp<<endl;
}
int main()
{
map<string, int> fileMap;
string temp;
int i = 0;
ifstream in;
in.open("/tmp/name.txt", ifstream::in);
if (!in)
{
cout << "open file failed" << endl;
return 1;
}
curTime();
while (in >> temp)
{
if (fileMap.find(temp) == fileMap.end())
{
++i;
fileMap[temp] = i;
}
}
curTime();
cout << i << endl;
in.close();
return 0;
}#зј–иҜ‘ [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ g++ 2.cpp -o map
4.жү§иЎҢжҹҘзңӢз»“жһң
[zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./hashMap #7з§’ 2015-11-06 16:25:41 2015-11-06 16:25:48 459256 [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./strhashMap #8з§’пјҢе’ҢдёҠйқўзҡ„зӣёе·®ж— еҮ 2015-11-06 16:25:50 2015-11-06 16:25:58 459256 [zhuhuifeng@localhost ~]$ ./map #26з§’ 2015-11-06 16:26:02 2015-11-06 16:26:28 459256
дә”гҖҒжҖ»з»“
иҝҷдёӘжөӢиҜ•д»…д»…жҳҜдёӘдәәеЁұд№җпјҢ并没жңүд»Җд№Ҳе®һйҷ…д»·еҖјгҖӮжңҖеҗҺе°ұжҳҜдёҖеҸҘиҜқпјҢhash_mapжҳҜеҹәдәҺhash_tableе®һзҺ°зҡ„пјҢиҖҢhash_tableжҳҜжҠҠд»ҘеҸҢеҲғеү‘пјҢз”Ёзҡ„еҘҪж•ҲзҺҮеҫҲй«ҳO(1)пјҢз”Ёзҡ„дёҚеҘҪеҘ”зқҖO(N)е°ұеҺ»дәҶгҖӮ
е…ӯгҖҒжіЁж„Ҹhash_mapжӯ»еҫӘзҺҜ
иҝҷдёӘй—®йўҳз®ҖеҚ•иҜҙжқҘпјҢе°ұжҳҜgnuзҡ„е®һзҺ°жҳҜпјҢеҶ…йғЁжңүдёӘ_M_CurжҢҮй’ҲжҢҮзӨәеҪ“еүҚдҪҚзҪ®AпјҢжҜҸж¬Ўи®Ўз®—operator++пјҢйғҪз”ЁеҪ“еүҚдҪҚзҪ®зҡ„keyи°ғз”ЁhashеҮҪж•°и®Ўз®—дёӢдёҖдёӘдҪҚзҪ®BпјҢеҰӮжһңkeyдј е…Ҙhash_mapд»ҘеҗҺпјҢеҸҲеңЁеӨ–йғЁе°Ҷе…¶еҶ…е®№з ҙеқҸпјҢеҜјиҮҙhashеҮҪж•°и®Ўз®—еҗҺзҡ„BдҪҚзҪ®еңЁAдҪҚзҪ®д№ӢеүҚпјҢйӮЈд№Ҳд»ҺBеҲ°иҫҫAд»ҘеҗҺпјҢеҸҲдјҡи·іеӣһBпјҢеҪўжҲҗB-AеҢәй—ҙзҡ„жӯ»еҫӘзҺҜгҖӮ
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <ext/hash_map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
__gnu_cxx::hash_map<char *, int> hashMap;
char name[10] = "zhu";
hashMap.insert(pair<char *, int>(name, 1));
strncpy(name, "wang", 10); //еңЁеӨ–йғЁж”№еҸҳдәҶе·Із»Ҹдј е…Ҙhash_mapдёӯзҡ„keyпјҢеҜјиҮҙжӯ»еҫӘзҺҜ
for (__gnu_cxx::hash_map<char *, int>::iterator it = hashMap.begin(); it != hashMap.end(); ++it)
{
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
}
return 0;
}е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ