您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
密码登录
登录注册
点击 登录注册 即表示同意《亿速云用户服务条款》

如果n越大,则递归计算比较慢
//#include <stdio.h>
//#include <stdlib.h>
//
//int FibNoRecursion(int n) //斐波那契非递归
//{
// int a=0;
// int b=1;
// int c=a+b;
//
// if(n==0)
// return 0;
// if(n==1)
// return b;
// if(n==2)
// return a+b;
// for(int i=3;i<=n;i++)
// {
// a=b;
// b=c;
// c=a+b;
// }
// return c;
//}
//void test()
//{
// int n=0;
// printf("Please input n: ");
// scanf("%d",&n);
// int ret=FibNoRecursion(n);
// printf("Fibonacci(%d) = %d\n",n,ret);
//}
//int main()
//{
// test();
// system("pause");
// return 0;
//}
//数组实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int FibNoRecursion(int n) //斐波那契非递归
{
int fib_arr[100]={0}; //数组元素全部初始化为0
fib_arr[0]=1;
fib_arr[1]=1;
int count=0;
while(count<n-1)
{
fib_arr[count+2]=fib_arr[count+1]+fib_arr[count];
count++;
}
return fib_arr[n-1];
}
void test()
{
int n=0;
printf( "Please input n: ");
scanf( "%d",&n);
int ret=FibNoRecursion(n);
printf( "Fibonacci(%d) = %d\n",n,ret);
}
int main()
{
test();
system( "pause");
return 0;
}结果:
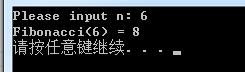

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void test()
{
char* str="abcdefghi123" ;
int count=0;
while(*str)
{
count++;
str++;
}
printf( "%d\n",count);
}
int main()
{
test();
system( "pause");
return 0;
}结果:
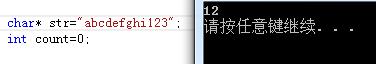

//不用临时变量,即可以用递归来求
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Strlen(char * str)
{
if(*str =='\0')
return 0;
if(*str )
{
str++;
return Strlen(str )+1;
}
}
void test()
{
char* str="0abc123def" ;
int ret=Strlen(str);
printf( "strlen=%d\n",ret);
}
int main()
{
test();
system( "pause");
return 0;
}结果:
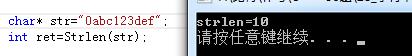

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 8
void test()
{
int arr[N ]={23,88,12,8,37,99,25,0};
for(int i=0;i<N-1;i++)
{
int j=i+1;
for(j;j<N ;j++)
{
if(arr[i]>arr[j])
{
int tmp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=tmp;
}
}
}
//输出
for(int m=0;m<N;m++)
{
printf( "%d ",arr[m]);
}
printf( "\n");
}
int main()
{
test();
system( "pause");
return 0;
}结果:
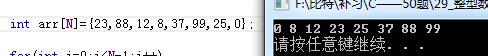


#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void test()
{
int a=15;
int count=0;
while(a)
{
if(a & 1) //按位与
count++;
a=a>>1;
}
printf( "%d\n",count);
}
int main()
{
test();
system( "pause");
return 0;
}结果:

免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。