жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
иҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« дё»иҰҒд»Ӣз»ҚдәҶPythonеҰӮдҪ•е®һзҺ°зәҝжҖ§еӣһеҪ’е’Ңжү№йҮҸжўҜеәҰдёӢйҷҚжі•пјҢе…·жңүдёҖе®ҡеҖҹйүҙд»·еҖјпјҢж„ҹе…ҙи¶Јзҡ„жңӢеҸӢеҸҜд»ҘеҸӮиҖғдёӢпјҢеёҢжңӣеӨ§е®¶йҳ…иҜ»е®ҢиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« д№ӢеҗҺеӨ§жңү收иҺ·пјҢдёӢйқўи®©е°Ҹзј–еёҰзқҖеӨ§е®¶дёҖиө·дәҶи§ЈдёҖдёӢгҖӮ
зӨәдҫӢ
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
class dataMinning:
datasets = []
labelsets = []
addressD = '' #Data folder
addressL = '' #Label folder
npDatasets = np.zeros(1)
npLabelsets = np.zeros(1)
cost = []
numIterations = 0
alpha = 0
theta = np.ones(2)
#pCols = 0
#dRows = 0
def __init__(self,addressD,addressL,theta,numIterations,alpha,datasets=None):
if datasets is None:
self.datasets = []
else:
self.datasets = datasets
self.addressD = addressD
self.addressL = addressL
self.theta = theta
self.numIterations = numIterations
self.alpha = alpha
def readFrom(self):
fd = open(self.addressD,'r')
for line in fd:
tmp = line[:-1].split()
self.datasets.append([int(i) for i in tmp])
fd.close()
self.npDatasets = np.array(self.datasets)
fl = open(self.addressL,'r')
for line in fl:
tmp = line[:-1].split()
self.labelsets.append([int(i) for i in tmp])
fl.close()
tm = []
for item in self.labelsets:
tm = tm + item
self.npLabelsets = np.array(tm)
def genData(self,numPoints,bias,variance):
self.genx = np.zeros(shape = (numPoints,2))
self.geny = np.zeros(shape = numPoints)
for i in range(0,numPoints):
self.genx[i][0] = 1
self.genx[i][1] = i
self.geny[i] = (i + bias) + random.uniform(0,1) * variance
def gradientDescent(self):
xTrans = self.genx.transpose() #
i = 0
while i < self.numIterations:
hypothesis = np.dot(self.genx,self.theta)
loss = hypothesis - self.geny
#record the cost
self.cost.append(np.sum(loss ** 2))
#calculate the gradient
gradient = np.dot(xTrans,loss)
#updata, gradientDescent
self.theta = self.theta - self.alpha * gradient
i = i + 1
def show(self):
print 'yes'
if __name__ == "__main__":
c = dataMinning('c:\\city.txt','c:\\st.txt',np.ones(2),100000,0.000005)
c.genData(100,25,10)
c.gradientDescent()
cx = range(len(c.cost))
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(cx,c.cost)
plt.ylim(0,25000)
plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(c.genx[:,1],c.geny,'b.')
x = np.arange(0,100,0.1)
y = x * c.theta[1] + c.theta[0]
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.margins(0.2)
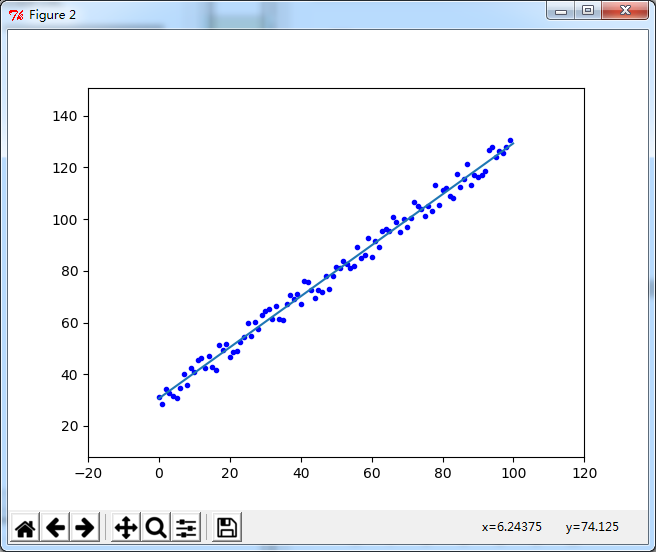
plt.show()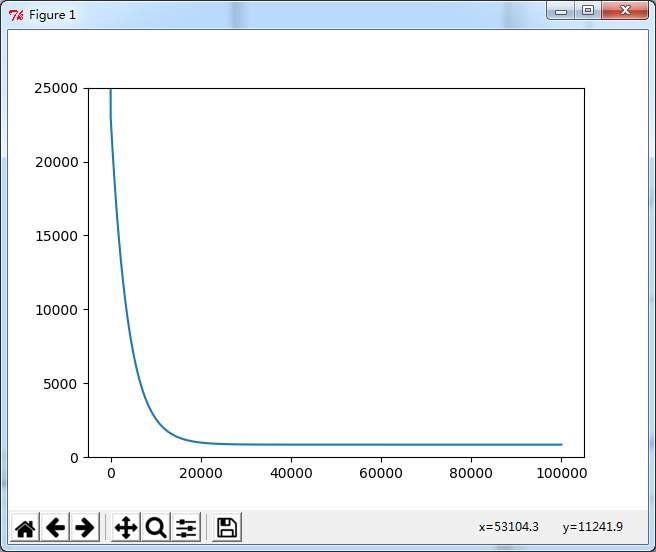
еӣҫ1. иҝӯд»ЈиҝҮзЁӢдёӯзҡ„иҜҜе·®cost
ж„ҹи°ўдҪ иғҪеӨҹи®Өзңҹйҳ…иҜ»е®ҢиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« пјҢеёҢжңӣе°Ҹзј–еҲҶдә«зҡ„вҖңPythonеҰӮдҪ•е®һзҺ°зәҝжҖ§еӣһеҪ’е’Ңжү№йҮҸжўҜеәҰдёӢйҷҚжі•вҖқиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« еҜ№еӨ§е®¶жңүеё®еҠ©пјҢеҗҢж—¶д№ҹеёҢжңӣеӨ§е®¶еӨҡеӨҡж”ҜжҢҒдәҝйҖҹдә‘пјҢе…іжіЁдәҝйҖҹдә‘иЎҢдёҡиө„и®Ҝйў‘йҒ“пјҢжӣҙеӨҡзӣёе…ізҹҘиҜҶзӯүзқҖдҪ жқҘеӯҰд№ !
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ