您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
密码登录
登录注册
点击 登录注册 即表示同意《亿速云用户服务条款》
C语言中怎么实现一个K-means算法,针对这个问题,这篇文章详细介绍了相对应的分析和解答,希望可以帮助更多想解决这个问题的小伙伴找到更简单易行的方法。
K-means算法是很典型的基于距离的聚类算法,采用距离作为相似性的评价指标,即认为两个对象的距离越近,其相似度就越大。该算法认为簇是由距离靠近的对象组成的,因此把得到紧凑且独立的簇作为最终目标。
算法过程如下:
1)从N个样本随机选取K个样本作为质心
2)对剩余的每个样本测量其到每个质心的距离,并把它归到最近的质心的类
3)重新计算已经得到的各个类的质心
4)迭代2~3步直至新的质心与原质心相等或小于指定阈值,算法结束
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<math.h>
#define DIMENSIOM 2 //目前只是处理2维的数据
#define MAX_ROUND_TIME 100 //最大的聚类次数
typedef struct Item{
int dimension_1; //用于存放第一维的数据
int dimension_2; //用于存放第二维的数据
int clusterID; //用于存放该item的cluster center是谁
}Item;
Item* data;
typedef struct ClusterCenter{
double dimension_1;
double dimension_2;
int clusterID;
}ClusterCenter;
ClusterCenter* cluster_center_new;
int isContinue;
int* cluster_center; //记录center
double* distanceFromCenter; //记录一个“点”到所有center的距离
int data_size;
char filename[200];
int cluster_count;
void initial();
void readDataFromFile();
void initial_cluster();
void calculateDistance_ToOneCenter(int itemID, int centerID, int count);
void calculateDistance_ToAllCenter(int itemID);
void partition_forOneItem(int itemID);
void partition_forAllItem_OneCluster(int round);
void calculate_clusterCenter(int round);
void K_means();
void writeClusterDataToFile(int round);
void writeClusterCenterToFile(int round);
void compareNew_OldClusterCenter(double* new_X_Y);
void test_1();
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if( argc != 4 )
{
printf("This application need other parameter to run:"
"\n\t\tthe first is the size of data set,"
"\n\t\tthe second is the file name that contain data"
"\n\t\tthe third indicate the cluster_count"
"\n");
exit(0);
}
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
data_size = atoi(argv[1]);
strcat(filename, argv[2]);
cluster_count = atoi(argv[3]);
initial();
readDataFromFile();
initial_cluster();
//test_1();
//partition_forAllItem_OneCluster();
//calculate_clusterCenter();
K_means();
return 0;
}
/*
* 对涉及到的二维动态数组根据main函数中传入的参数分配空间
* */
void initial(){
data = (Item*)malloc(sizeof(struct Item) * (data_size + 1));
if( !data )
{
printf("malloc error:data!");
exit(0);
}
cluster_center = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (cluster_count + 1));
if( !cluster_center )
{
printf("malloc error:cluster_center!\n");
exit(0);
}
distanceFromCenter = (double*)malloc(sizeof(double) * (cluster_count + 1));
if( !distanceFromCenter )
{
printf("malloc error: distanceFromCenter!\n");
exit(0);
}
cluster_center_new = (ClusterCenter*)malloc(sizeof(struct ClusterCenter) * (cluster_count + 1));
if( !cluster_center_new )
{
printf("malloc cluster center new error!\n");
exit(0);
}
}
/*
* 从文件中读入x和y数据
* */
void readDataFromFile(){
FILE* fread;
if( NULL == (fread = fopen(filename, "r")))
{
printf("open file(%s) error!\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
int row;
for( row = 1; row <= data_size; row++ )
{
if( 2 != fscanf(fread, "%d %d ", &data[row].dimension_1, &data[row].dimension_2))
{
printf("fscanf error: %d\n", row);
}
data[row].clusterID = 0;
}
}
/*
* 根据从主函数中传入的@cluster_count(聚类的个数)来随机的选择@cluster_count个
* 初始的聚类的起点
* */
void initial_cluster(){
//辅助产生不重复的数
int* auxiliary;
int i;
auxiliary = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (data_size + 1));
if( !auxiliary )
{
printf("malloc error: auxiliary");
exit(0);
}
for( i = 1; i <= data_size; i++ )
{
auxiliary[i] = i;
}
//产生初始化的cluster_count个聚类
int length = data_size;
int random;
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
random = rand()%length + 1;
//printf("%d \n", auxiliary[random]);
//data[auxiliary[random]].clusterID = auxiliary[random];
cluster_center[i] = auxiliary[random];
auxiliary[random] = auxiliary[length--];
}
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
cluster_center_new[i].dimension_1 = data[cluster_center[i]].dimension_1;
cluster_center_new[i].dimension_2 = data[cluster_center[i]].dimension_2;
cluster_center_new[i].clusterID = i;
data[cluster_center[i]].clusterID = i;
}
}
/*
* 计算一个点(还没有划分到cluster center的点)到一个cluster center的distance
* @itemID: 不属于任何cluster中的点
* @centerID: center的ID
* @count: 表明在计算的是itemID到第几个@center的distance,并且指明了结果放在distanceFromCenter的第几号元素
* */
void calculateDistance_ToOneCenter(int itemID,int centerID){
distanceFromCenter[centerID] = sqrt( (data[itemID].dimension_1-cluster_center_new[centerID].dimension_1)*(double)(data[itemID].dimension_1-cluster_center_new[centerID].dimension_1) + (double)(data[itemID].dimension_2-cluster_center_new[centerID].dimension_2) * (data[itemID].dimension_2-cluster_center_new[centerID].dimension_2) );
}
/*
* 计算一个点(还没有划分到cluster center的点)到每个cluster center的distance
* */
void calculateDistance_ToAllCenter(int itemID){
int i;
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
calculateDistance_ToOneCenter(itemID, i);
}
}
void test_1()
{
calculateDistance_ToAllCenter(3);
int i;
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
printf("%f ", distanceFromCenter[i]);
}
}
/*
* 在得到任一的点(不属于任一cluster的)到每一个cluster center的distance之后,决定它属于哪一个cluster center,即取距离最小的
* 函数功能:得到一个item所属的cluster center
* */
void partition_forOneItem(int itemID){
//操作对象是 distanceFromCenter和cluster_center
int i;
int min_index = 1;
double min_value = distanceFromCenter[1];
for( i = 2; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
if( distanceFromCenter[i] < min_value )
{
min_value = distanceFromCenter[i];
min_index = i;
}
}
data[itemID].clusterID = cluster_center_new[min_index].clusterID;
}
/*
* 得到所有的item所属于的cluster center , 在一轮的聚类中
* */
void partition_forAllItem_OneCluster(int round){ //changed!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
int i;
for( i = 1; i <= data_size; i++ )
{
if( data[i].clusterID != 0 )
continue;
else
{
calculateDistance_ToAllCenter(i); //计算i到所有center的distance
partition_forOneItem(i); //根据distance对i进行partition
}
}
//把聚类得到的数据写入到文件中
writeClusterDataToFile(round);
}
/*
* 将聚类得到的数据写入到文件中,每一个类写入一个文件中
* @round: 表明在进行第几轮的cluster,该参数的另一个作用是指定了文件名字中的第一个项.
* */
void writeClusterDataToFile(int round){
int i;
char filename[200];
FILE** file;
file = (FILE**)malloc(sizeof(FILE*) * (cluster_count + 1));
if( !file )
{
printf("malloc file error!\n");
exit(0);
}
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
sprintf(filename, ".//ClusterProcess//round%d_cluster%d.data", round, i);
if( NULL == (file[i] = fopen(filename, "w")))
{
printf("file open(%s) error!", filename);
exit(0);
}
}
for( i = 1; i <= data_size; i++ )
{
//sprintf(filename, ".//ClusterProcess//round%d_cluster%d.data", round, data[i].clusterID);
fprintf(file[data[i].clusterID], "%d\t%d\n", data[i].dimension_1, data[i].dimension_2);
}
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
//sprintf(filename, ".//ClusterProcess//round%d_cluster%d.data", round, i);
fclose(file[i]);
}
}
/*
* 重新计算新的cluster center
* */
void calculate_clusterCenter(int round){ //changed!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
int i;
double* new_X_Y; /*
用来计算和保存新的cluster center的值,同样的,0号元素不用。1,2号元素分别用来
存放第一个聚类的所有的项的x和y的累加和。3,4号元素分别用来存放第二个聚类的所有
的项的x和y的累加和......
*/
new_X_Y = (double*)malloc(sizeof(double) * (2 * cluster_count + 1));
if( !new_X_Y )
{
printf("malloc error: new_X_Y!\n");
exit(0);
}
//初始化为0
for( i = 1; i <= 2*cluster_count; i++ )
new_X_Y[i] = 0.0;
//用来统计属于各个cluster的item的个数
int* counter;
counter = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (cluster_count + 1));
if( !counter )
{
printf("malloc error: counter\n");
exit(0);
}
//初始化为0
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
counter[i] = 0;
for( i = 1; i <= data_size; i++ )
{
new_X_Y[data[i].clusterID * 2 - 1] += data[i].dimension_1;
new_X_Y[data[i].clusterID * 2] += data[i].dimension_2;
counter[data[i].clusterID]++;
}
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
new_X_Y[2 * i - 1] = new_X_Y[2 * i - 1] / (double)(counter[i]);
new_X_Y[2 * i] = new_X_Y[2 * i] / (double)(counter[i]);
}
//要将cluster center的值保存在文件中,后续作图
writeClusterCenterToFile(round);
/*
* 在这里比较一下新的和旧的cluster center值的差别。如果是相等的,则停止K-means算法。
* */
compareNew_OldClusterCenter(new_X_Y);
//将新的cluster center的值放入cluster_center_new
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
cluster_center_new[i].dimension_1 = new_X_Y[2 * i - 1];
cluster_center_new[i].dimension_2 = new_X_Y[2 * i];
cluster_center_new[i].clusterID = i;
}
free(new_X_Y);
free(counter);
//在重新计算了新的cluster center之后,意味着我们要重新来为每一个Item进行聚类,所以data中用于表示聚类ID的clusterID
//要都重新置为0。
for( i = 1; i <= data_size; i++ )
{
data[i].clusterID = 0;
}
}
/*
* 将得到的新的cluster_count个cluster center的值保存在文件中。以便于观察聚类的过程。
* */
void writeClusterCenterToFile(int round){
FILE* file;
int i;
char filename[200];
sprintf(filename, ".//ClusterProcess//round%d_clusterCenter.data", round);
if( NULL == (file = fopen(filename, "w")))
{
printf("open file(%s) error!\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
fprintf(file, "%f\t%f\n", cluster_center_new[i].dimension_1, cluster_center_new[i].dimension_2);
}
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
fclose(file);
}
}
/*
* 比较新旧的cluster center的差异
* */
void compareNew_OldClusterCenter(double* new_X_Y){
int i;
isContinue = 0; //等于0表示的是不要继续
for( i = 1; i <= cluster_count; i++ )
{
if( new_X_Y[2 * i - 1] != cluster_center_new[i].dimension_1 || new_X_Y[2 * i] != cluster_center_new[i].dimension_2)
{
isContinue = 1; //要继续
break;
}
}
}
/************************************************************************************************
* K-means算法 *
***********************************************************************************************/
void K_means(){
int times_cluster;
for( times_cluster = 1; times_cluster <= MAX_ROUND_TIME; times_cluster++ )
{
printf("\n times : %d \n", times_cluster);
partition_forAllItem_OneCluster(times_cluster);
calculate_clusterCenter(times_cluster);
if( 0 == isContinue )
{
break;
//printf("\n\nthe application can stop!\n\n");
}
}
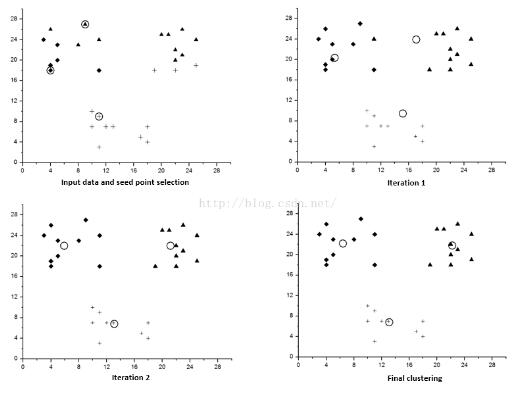
} 
关于C语言中怎么实现一个K-means算法问题的解答就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,如果你还有很多疑惑没有解开,可以关注亿速云行业资讯频道了解更多相关知识。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。