您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
SpringCloud中@FeignClient()注解的使用方式是怎样的,很多新手对此不是很清楚,为了帮助大家解决这个难题,下面小编将为大家详细讲解,有这方面需求的人可以来学习下,希望你能有所收获。
由于SpringCloud采用分布式微服务架构,难免在各个子模块下存在模块方法互相调用的情况。比如service-admin服务要调用service-card 服务的方法。
@FeignClient()注解就是为了解决这个问题的。
@FeignClient()注解的源码要求它必须在Interface接口上使用。( FeignClient注解被@Target(ElementType.TYPE)修饰,表示FeignClient注解的作用目标在接口上)
@RequestLine与其它请求不同,只需要简单写请求方式和路径就能达到请求其它服务的目的。
@FeignClient(value = "feign-server",configuration = FeignConfig.class) //需要一个配置文件
public interface TestService {
@RequestLine("POST /feign/test") //对应请求方式和路径
String feign(@RequestBody UserDO userDO);
}@EnableFeignClients
@SpringBootConfiguration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
public Contract contract(){
return new feign.Contract.Default();
}
}value: 服务名
name: 指定FeignClient的名称,如果项目使用了Ribbon,name属性会作为微服务的名称,用于服务发现
url: url一般用于调试,可以手动指定@FeignClient调用的地址
decode404:当发生http 404错误时,如果该字段位true,会调用decoder进行解码,否则抛出FeignException
configuration: Feign配置类,可以自定义Feign的Encoder、Decoder、LogLevel、Contract
fallback: 定义容错的处理类,当调用远程接口失败或超时时,会调用对应接口的容错逻辑,fallback指定的类必须实现@FeignClient标记的接口
fallbackFactory: 工厂类,用于生成fallback类示例,通过这个属性我们可以实现每个接口通用的容错逻辑,减少重复的代码
path: 定义当前FeignClient的统一前缀
此外还要求服务的启动类要有@EnableFeignClients 注解才能使Fegin生效。
SpringCloud搭建各种微服务之后,服务间通常存在相互调用的需求,SpringCloud提供了@FeignClient 注解非常优雅的解决了这个问题
首先,保证几个服务都在一个Eureka中注册成功形成服务场。
如下,我一共有三个服务注册在服务场中。COMPUTE-SERVICE ; FEIGN-CONSUMER ; TEST-DEMO;
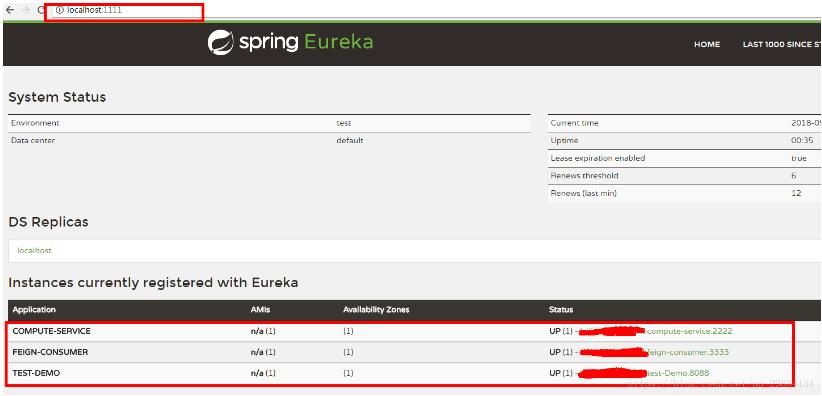
服务中调用其他两个服务的两个接口
分别为get带参和post不带参两个接口如下这个是COMPUTE-SERVICE中的get带参方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/add" ,method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Integer add(@RequestParam Integer a, @RequestParam Integer b) {
ServiceInstance instance = client.getLocalServiceInstance();
Integer r = a + b;
logger.info("/add, host:" + instance.getHost() + ", service_id:" + instance.getServiceId() + ", result:" + r);
return r;
}如果要在FEIGN-CONSUMER 服务中调用这个方法的话,需要在 FEIGN-CONSUMER 中新建一个接口类专门调用某一工程中的系列接口
@FeignClient("compute-service")
public interface ComputeClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/add")
Integer add(@RequestParam(value = "a") Integer a, @RequestParam(value = "b") Integer b);
}其中,@FeignClient注解中标识出准备调用的是当前服务场中的哪个服务,这个服务名在目标服务中的配置中取
spring.application.name
接下来,在@RequestMapping中设置目标接口的接口类型、接口地址等属性。然后在下面定义接口参数以及返回参数
Controller层调用方法的时候
将上面接口注入进来,就可以直接用了
@Autowired
ComputeClient computeClient;
@RequestMapping(value = "/add", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Integer add() {
return computeClient.add(10, 20);
}当然,post方法同理:
这是目标接口:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/test",method = RequestMethod.POST)
String test1(){
return "hello,test1()";
}
}这是在本项目定义的接口文件:
@FeignClient("test-Demo")
public interface TestDemo {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = "/demo/test")
String test();
} @RestController
public class ConsumerController {
@Autowired
TestDemo testDemo;
@Autowired
ComputeClient computeClient;
@RequestMapping(value = "/add", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Integer add() {
return computeClient.add(10, 20);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test() {
return testDemo.test();
}
}最终调用结果如下:
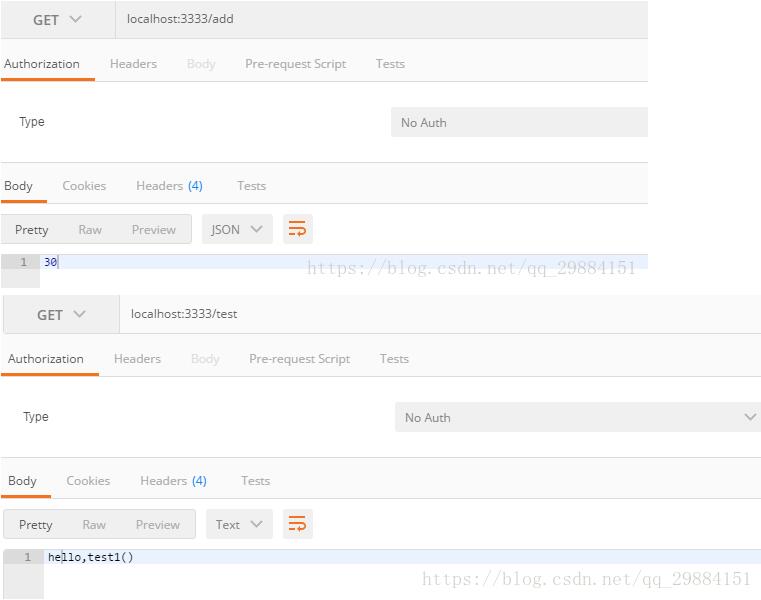
OK 服务间接口调用就是这样了!
看完上述内容是否对您有帮助呢?如果还想对相关知识有进一步的了解或阅读更多相关文章,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢您对亿速云的支持。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。