您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
本篇内容主要讲解“什么是React原理”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“什么是React原理”吧!
1.setState() 说明
1.1 更新数据
1.2 推荐语法
1.3 第二个参数
2.JSX 语法的转化过程
3.组件更新机制
4.组件性能优化
4.1 减轻 state
4.2 避免不必要的重新渲染
setState() 是异步更新数据
可以多次调用 setState() ,只会触发一次重新渲染
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
class Opp extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 1,
}
handleClick = () => {
// 异步更新数据
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
})
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
})
console.log(this.state.count) // 1
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>计数器:{this.state.count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Opp />, document.getElementById('root'))使用 setState((state,props)=>{}) 语法
state:表示最新的 state, props:表示最新的 props
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
class Opp extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 1,
}
handleClick = () => {
/* // 异步更新数据
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
})
console.log(this.state.count) //1
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
})
console.log(this.state.count) //1
*/
// 推荐语法
this.setState((state, props) => {
return {
count: state.count + 1,
}
})
this.setState((state, props) => {
console.log('第二次调用:', state) //2
return {
count: state.count + 1,
}
})
console.log(this.state.count) // 3
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>计数器:{this.state.count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Opp />, document.getElementById('root'))在状态更新(页面完成重新渲染)后立即执行某个操作
语法:setState(updater[,callback])
callback 是指回调函数 可加可不加
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
class Opp extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 1,
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState(
(state, props) => {
return {
count: state.count + 1,
}
},
// 状态更新后并且重新渲染后,立即执行
() => {
console.log('状态更新完成:', this.state.count) // 2
console.log(document.getElementById('title').innerText) // 计数器:2
document.title = '更新后的 count 为:' + this.state.count
}
)
console.log(this.state.count) //1
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2 id='title'>计数器:{this.state.count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Opp />, document.getElementById('root'))JSX 仅仅是 createElement() 方法的语法糖(简化语法)
JSX 语法被 @babel/preset-react 插件编译为 createElement() 方法
React元素:是一个对象,用来描述你希望在屏幕上看到的内容

import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
// JSX 语法的转化过程
// const element = <h2 className='greeting'>Hello JSX</h2>
const element = React.createElement(
'h2',
{
className: 'greeting',
},
'Hello JSX'
)
console.log(element)
ReactDOM.render(element, document.getElementById('root'))setState() 的两个作用:1.修改 state 2.更新组件(UI)
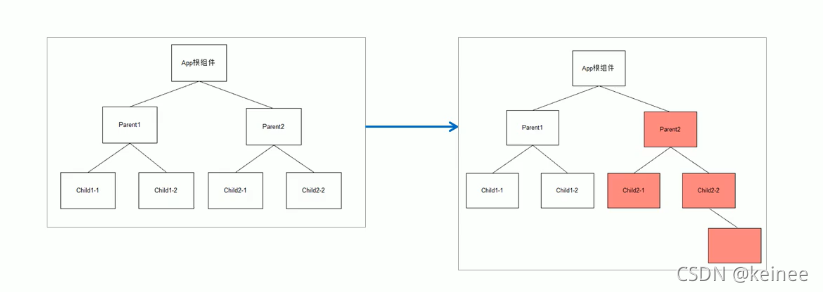
过程:父组件重新渲染是,也会重新渲染子组件,但只会渲染当前组件子树(当前组件及其所有子组件)
减轻 state :只存储跟组件渲染相关的数据(比如:count /列表数据/ loading 等)
注意:不用渲染的书籍不要放在 state 中(比如定时器 id 等)
需要在多个方法中用到的数据,应该放在 this 中
组件更新机制:父组件更新会引起子组件也被更新
问题:子组件没有变化时也会被重新渲染,造成不必要的重新渲染
解决方式:使用钩子函数shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps,nextState)
作用:通过返回值决定该组件是否重新渲染,返回 true 表示重新渲染, false 表示不重新渲染
触发时机:更新阶段的钩子函数,组件重新渲染前执行(shouldComponentUpdate -> render)
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
class Opp extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0,
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState((state) => {
return {
count: this.state.count + 1,
}
})
}
// 钩子函数
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// 返回 false,阻止组件重新渲染
// return false
// 最新的状态
console.log('最新的state', nextState)
// 更新前的状态
console.log(this.state)
// 返回 true,组件重新渲染
return true
}
render() {
console.log('组件更新了')
return (
<div>
<h2>计数器:{this.state.count}</h2>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Opp />, document.getElementById('root'))案例:随机数
通过 nextState
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
// 生成随机数
class Opp extends React.Component {
state = {
number: 0,
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState((state) => {
return {
number: Math.floor(Math.random() * 3),
}
})
}
// 两次生成的随机数可能相同,则没必要重新渲染
shouldComponentUpdate(nextState) {
console.log('最新状态:', nextState, '当前状态:', this.state)
return nextState.number !== this.state.number
/* if ( nextState.number !== this.state.number) {
return true
}
return false*/
}
render() {
console.log('render')
return (
<div>
<h2>随机数:{this.state.number}</h2>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>重新生成</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Opp />, document.getElementById('root'))通过 nextState
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
// 生成随机数
class Opp extends React.Component {
state = {
number: 0,
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState((state) => {
return {
number: Math.floor(Math.random() * 3),
}
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<NumberBox number={this.state.number} />
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>重新生成</button>
</div>
)
}
}
class NumberBox extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps) {
console.log('最新props:', nextProps, '当前props:', this.props)
return nextProps.number !== this.props.number
}
render() {
console.log('子组件render')
return <h2>随机数:{this.props.number}</h2>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Opp />, document.getElementById('root'))到此,相信大家对“什么是React原理”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。