您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
密码登录
登录注册
点击 登录注册 即表示同意《亿速云用户服务条款》
本篇内容主要讲解“详解Python人工智能混合高斯模型运动目标检测”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“详解Python人工智能混合高斯模型运动目标检测”吧!
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 高斯算法
class gaussian:
def __init__(self):
self.mean = np.zeros((1, 3))
self.covariance = 0
self.weight = 0;
self.Next = None
self.Previous = None
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.pixel_s = None
self.pixel_r = None
self.no_of_components = 0
self.Next = None
class Node1:
def __init__(self):
self.gauss = None
self.no_of_comp = 0
self.Next = None
covariance0 = 11.0
def Create_gaussian(info1, info2, info3):
ptr = gaussian()
if (ptr is not None):
ptr.mean[1, 1] = info1
ptr.mean[1, 2] = info2
ptr.mean[1, 3] = info3
ptr.covariance = covariance0
ptr.weight = 0.002
ptr.Next = None
ptr.Previous = None
return ptr
def Create_Node(info1, info2, info3):
N_ptr = Node()
if (N_ptr is not None):
N_ptr.Next = None
N_ptr.no_of_components = 1
N_ptr.pixel_s = N_ptr.pixel_r = Create_gaussian(info1, info2, info3)
return N_ptr
List_node = []
def Insert_End_Node(n):
List_node.append(n)
List_gaussian = []
def Insert_End_gaussian(n):
List_gaussian.append(n)
def Delete_gaussian(n):
List_gaussian.remove(n);
class Process:
def __init__(self, alpha, firstFrame):
self.alpha = alpha
self.background = firstFrame
def get_value(self, frame):
self.background = frame * self.alpha + self.background * (1 - self.alpha)
return cv2.absdiff(self.background.astype(np.uint8), frame)
def denoise(frame):
frame = cv2.medianBlur(frame, 5)
frame = cv2.GaussianBlur(frame, (5, 5), 0)
return frame
capture = cv2.VideoCapture('1.mp4')
ret, orig_frame = capture.read( )
if ret is True:
value1 = Process(0.1, denoise(orig_frame))
run = True
else:
run = False
while (run):
ret, frame = capture.read()
value = False;
if ret is True:
cv2.imshow('input', denoise(frame))
grayscale = value1.get_value(denoise(frame))
ret, mask = cv2.threshold(grayscale, 15, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
cv2.imshow('mask', mask)
key = cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF
else:
break
if key == 27:
break
if value == True:
orig_frame = cv2.resize(orig_frame, (340, 260), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
orig_frame = cv2.cvtColor(orig_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
orig_image_row = len(orig_frame)
orig_image_col = orig_frame[0]
bin_frame = np.zeros((orig_image_row, orig_image_col))
value = []
for i in range(0, orig_image_row):
for j in range(0, orig_image_col):
N_ptr = Create_Node(orig_frame[i][0], orig_frame[i][1], orig_frame[i][2])
if N_ptr is not None:
N_ptr.pixel_s.weight = 1.0
Insert_End_Node(N_ptr)
else:
print("error")
exit(0)
nL = orig_image_row
nC = orig_image_col
dell = np.array((1, 3));
mal_dist = 0.0;
temp_cov = 0.0;
alpha = 0.002;
cT = 0.05;
cf = 0.1;
cfbar = 1.0 - cf;
alpha_bar = 1.0 - alpha;
prune = -alpha * cT;
cthr = 0.00001;
var = 0.0
muG = 0.0;
muR = 0.0;
muB = 0.0;
dR = 0.0;
dB = 0.0;
dG = 0.0;
rval = 0.0;
gval = 0.0;
bval = 0.0;
while (1):
duration3 = 0.0;
count = 0;
count1 = 0;
List_node1 = List_node;
counter = 0;
duration = cv2.getTickCount( );
for i in range(0, nL):
r_ptr = orig_frame[i]
b_ptr = bin_frame[i]
for j in range(0, nC):
sum = 0.0;
sum1 = 0.0;
close = False;
background = 0;
rval = r_ptr[0][0];
gval = r_ptr[0][0];
bval = r_ptr[0][0];
start = List_node1[counter].pixel_s;
rear = List_node1[counter].pixel_r;
ptr = start;
temp_ptr = None;
if (List_node1[counter].no_of_component > 4):
Delete_gaussian(rear);
List_node1[counter].no_of_component = List_node1[counter].no_of_component - 1;
for k in range(0, List_node1[counter].no_of_component):
weight = List_node1[counter].weight;
mult = alpha / weight;
weight = weight * alpha_bar + prune;
if (close == False):
muR = ptr.mean[0];
muG = ptr.mean[1];
muB = ptr.mean[2];
dR = rval - muR;
dG = gval - muG;
dB = bval - muB;
var = ptr.covariance;
mal_dist = (dR * dR + dG * dG + dB * dB);
if ((sum < cfbar) and (mal_dist < 16.0 * var * var)):
background = 255;
if (mal_dist < (9.0 * var * var)):
weight = weight + alpha;
if mult < 20.0 * alpha:
mult = mult;
else:
mult = 20.0 * alpha;
close = True;
ptr.mean[0] = muR + mult * dR;
ptr.mean[1] = muG + mult * dG;
ptr.mean[2] = muB + mult * dB;
temp_cov = var + mult * (mal_dist - var);
if temp_cov < 5.0:
ptr.covariance = 5.0
else:
if (temp_cov > 20.0):
ptr.covariance = 20.0
else:
ptr.covariance = temp_cov;
temp_ptr = ptr;
if (weight < -prune):
ptr = Delete_gaussian(ptr);
weight = 0;
List_node1[counter].no_of_component = List_node1[counter].no_of_component - 1;
else:
sum += weight;
ptr.weight = weight;
ptr = ptr.Next;
if (close == False):
ptr = gaussian( );
ptr.weight = alpha;
ptr.mean[0] = rval;
ptr.mean[1] = gval;
ptr.mean[2] = bval;
ptr.covariance = covariance0;
ptr.Next = None;
ptr.Previous = None;
Insert_End_gaussian(ptr);
List_gaussian.append(ptr);
temp_ptr = ptr;
List_node1[counter].no_of_components = List_node1[counter].no_of_components + 1;
ptr = start;
while (ptr != None):
ptr.weight = ptr.weight / sum;
ptr = ptr.Next;
while (temp_ptr != None and temp_ptr.Previous != None):
if (temp_ptr.weight <= temp_ptr.Previous.weight):
break;
else:
next = temp_ptr.Next;
previous = temp_ptr.Previous;
if (start == previous):
start = temp_ptr;
previous.Next = next;
temp_ptr.Previous = previous.Previous;
temp_ptr.Next = previous;
if (previous.Previous != None):
previous.Previous.Next = temp_ptr;
if (next != None):
next.Previous = previous;
else:
rear = previous;
previous.Previous = temp_ptr;
temp_ptr = temp_ptr.Previous;
List_node1[counter].pixel_s = start;
List_node1[counter].pixel_r = rear;
counter = counter + 1;
capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()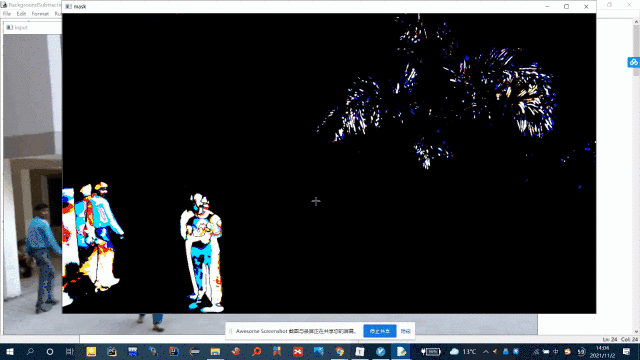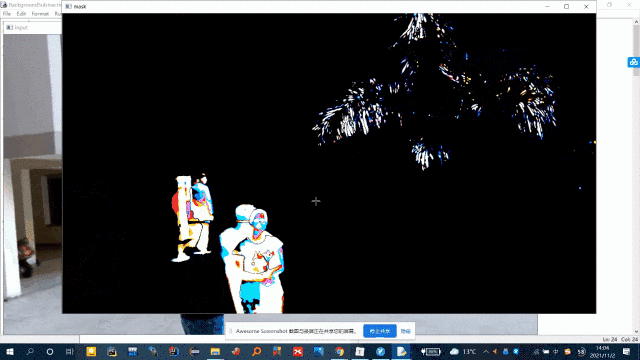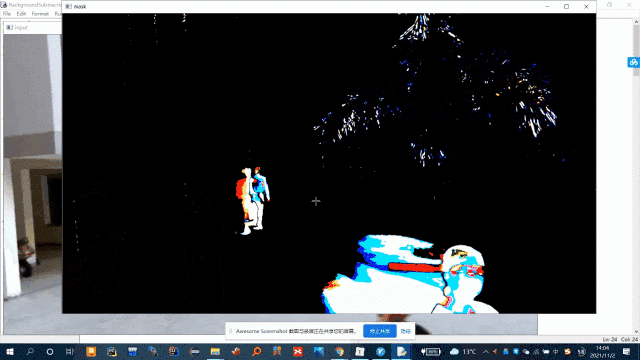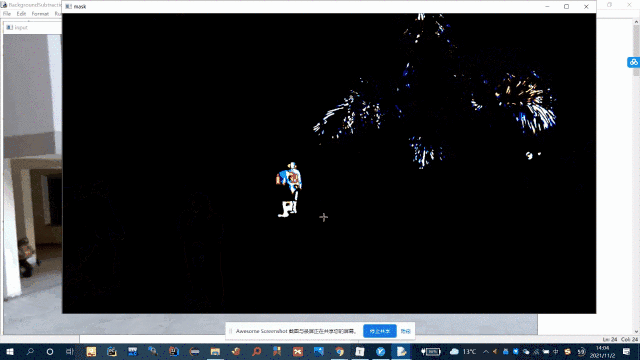
背景减法 (BS) 是一种常用且广泛使用的技术,用于通过使用静态相机生成前景蒙版(即,包含属于场景中运动物体的像素的二值图像)。
顾名思义,BS 计算前景蒙版,在当前帧和背景模型之间执行减法运算,其中包含场景的静态部分,或者更一般地说,根据观察到的场景的特征,可以将所有内容视为背景。
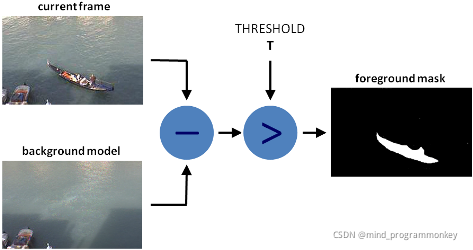
背景建模包括两个主要步骤:
后台初始化;
背景更新。
在第一步中,计算背景的初始模型,而在第二步中,更新该模型以适应场景中可能的变化。
import cv2
#构造VideoCapture对象
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('1.mp4')
# 创建一个背景分割器
# createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()函数里,可以指定detectShadows的值
# detectShadows=True,表示检测阴影,反之不检测阴影。默认是true
fgbg = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG2()
while True :
ret, frame = cap.read() # 读取视频
fgmask = fgbg.apply(frame) # 背景分割
cv2.imshow('frame', fgmask) # 显示分割结果
if cv2.waitKey(100) & 0xff == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()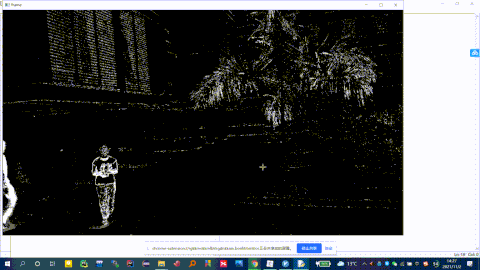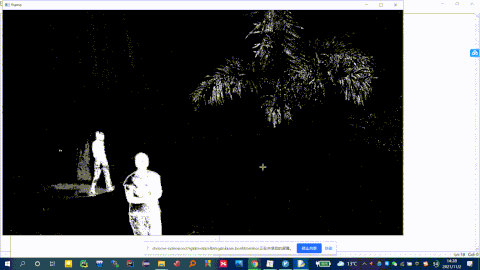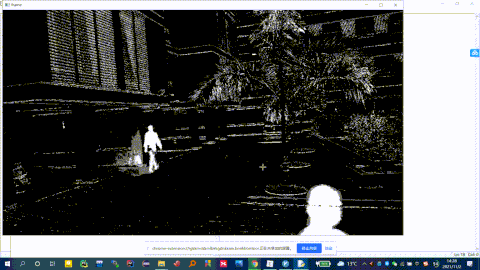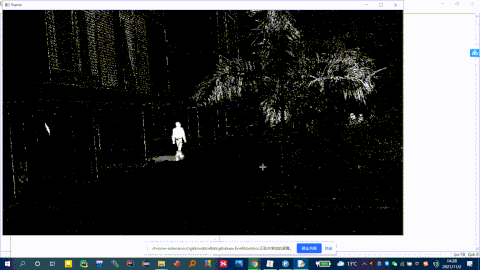
到此,相信大家对“详解Python人工智能混合高斯模型运动目标检测”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。