您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
这篇“Android Room数据库加密的示例分析”除了程序员外大部分人都不太理解,今天小编为了让大家更加理解“Android Room数据库加密的示例分析”,给大家总结了以下内容,具有一定借鉴价值,内容详细步骤清晰,细节处理妥当,希望大家通过这篇文章有所收获,下面让我们一起来看看具体内容吧。
Android平台自带的SQLite有一个致命的缺陷:不支持加密。这就导致存储在SQLite中的数据可以被任何人用任何文本编辑器查看到。如果是普通的数据还好,但是当涉及到一些账号密码,或者聊天内容的时候,我们的应用就会面临严重的安全漏洞隐患。
1、在数据存储之前进行加密,在加载数据之后再进行解密,这种方法大概是最容易想的到,而且也不能说这种方式不好,就是有些比较繁琐。 如果项目有特殊需求的话,可能还需要对数据库的表明,列明也进行加密。
2、对数据库整个文件进行加密,好处就是就是无需在插入之前对数据加密,也无需在查询数据之后再解密。比较出名的第三方库就是SQLCipher,它采用的方式就是对数据库文件进行加密,只需在打开数据库的时候输入密码,之后的操作更正常操作没有区别。
前面说了,加密的方式一比较繁琐的地方是需要在存储数据之前加密,在检索数据之后解密,那么是否有一种方式在Room操作数据库的过程中,自动对数据加密解密,答案是有的。
Dao编译之后的代码是这样的:
@Override
public long saveCache(final CacheTest cache) {
__db.assertNotSuspendingTransaction();
__db.beginTransaction();
try {
//核心代码,绑定数据
long _result = __insertionAdapterOfCacheTest.insertAndReturnId(cache);
__db.setTransactionSuccessful();
return _result;
} finally {
__db.endTransaction();
}
}__insertionAdapterOfCacheTest 是在CacheDaoTest_Impl 的构造方法里面创建的一个匿名内部类,这个匿名内部类实现了bind 方法
public CacheDaoTest_Impl(RoomDatabase __db) {
this.__db = __db;
this.__insertionAdapterOfCacheTest = new EntityInsertionAdapter<CacheTest>(__db) {
@Override
public String createQuery() {
return "INSERT OR REPLACE INTO `table_cache` (`key`,`name`) VALUES (?,?)";
}
@Override
public void bind(SupportSQLiteStatement stmt, CacheTest value) {
if (value.getKey() == null) {
stmt.bindNull(1);
} else {
stmt.bindString(1, value.getKey());
}
if (value.getName() == null) {
stmt.bindNull(2);
} else {
stmt.bindString(2, value.getName());
}
}
};
}关于SQLiteStatement 不清楚的同学可以百度一下,简单说他就代表一句sql语句,bind 方法就是绑定sql语句所需要的参数,现在的问题是我们可否自定义一个SupportSQLiteStatement ,然后在bind的时候加密参数呢。
我们看一下SupportSQLiteStatement 的创建过程。
public SupportSQLiteStatement acquire() {
assertNotMainThread();
return getStmt(mLock.compareAndSet(false, true));
}
private SupportSQLiteStatement getStmt(boolean canUseCached) {
final SupportSQLiteStatement stmt;
//代码有删减
stmt = createNewStatement();
return stmt;
}
kotlin
private SupportSQLiteStatement createNewStatement() {
String query = createQuery();
return mDatabase.compileStatement(query);
}可以看到SupportSQLiteStatement 最终来自RoomDataBase的compileStatement 方法,这就给我们hook 提供了接口,我们只要自定义一个SupportSQLiteStatement 类来代理原来的SupportSQLiteStatement 就可以了。
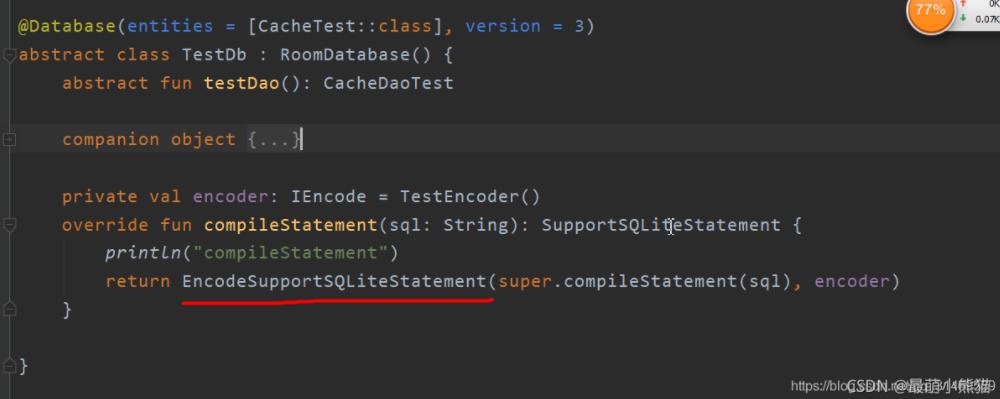
encoder 就是用来加密数据的。
加密数据之后剩余的就是解密数据了,解密数据我们需要在哪里Hook呢?
我们知道数据库检索返回的数据一般都是通过Cursor 传递给用户,这里我们就可以通过代理数据库返回的这个Cursor 进而实现解密数据。
@Database(entities = [CacheTest::class], version = 3)
abstract class TestDb : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun testDao(): CacheDaoTest
companion object {
val MIGRATION_2_1: Migration = object : Migration(2, 1) {
override fun migrate(database: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
}
}
val MIGRATION_2_3: Migration = object : Migration(2, 3) {
override fun migrate(database: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
}
}
val MIGRATION_3_4: Migration = object : Migration(3,4) {
override fun migrate(database: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
}
}
val MIGRATION_2_4: Migration = object : Migration(2, 4) {
override fun migrate(database: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
}
}
}
private val encoder: IEncode = TestEncoder()
override fun query(query: SupportSQLiteQuery): Cursor {
var cusrosr = super.query(query)
println("开始查询1")
return DencodeCursor(cusrosr, encoder)
}
override fun query(query: String, args: Array<out Any>?): Cursor {
var cusrosr = super.query(query, args)
println("开始查询2")
return DencodeCursor(cusrosr, encoder)
}
override fun query(query: SupportSQLiteQuery, signal: CancellationSignal?): Cursor {
println("开始查询3")
return DencodeCursor(super.query(query, signal), encoder)
}
}我们这里重写了RoomDatabase 的是query 方法,代理了原先的Cursor 。
class DencodeCursor(val delete: Cursor, val encoder: IEncode) : Cursor {
//代码有删减
override fun getString(columnIndex: Int): String {
return encoder.decodeString(delete.getString(columnIndex))
}
}如上,最终加密解密的都被hook在了Room框架中间。但是这种有两个个缺陷
加密解密的过程中不可以改变数据的类型,也就是整型在加密之后还必须是整型,整型在解密之后也必须是整型。同时有些字段可能不需要加密也不需要解密,例如自增长的整型的primary key。其实这种方式也比较好解决,可以规定key 为整数型,其余的数据一律是字符串。这样所有的树数字类型的数据都不需要参与加密解密的过程。
sql 与的参数必须是动态绑定的,而不是在sql语句中静态指定。
@Query("select * from table_cache where `key`=:primaryKey")
fun getCache(primaryKey: String): LiveData<CacheTest>@Query("select * from table_cache where `key`= '123' ")
fun getCache(): LiveData<CacheTest>SQLCipher 仿照官方的架构自己重写了一套代码,官方提供的各种数据库相关的类在SQLCipher 里面也是存在的而且名字都一样除了包名不同。
SQLCipher 与Room的结合方式同上面的情形是类似,也是通过代理的方式实现。由于Room需要的类跟SQLCipher 提供的类包名不一致,所以这里需要对SQLCipher 提供的类进行一下代理然后传递给Room架构使用就可以了。
fun init(context: Context) {
val mDataBase1 = Room.databaseBuilder(
context.applicationContext,
TestDb::class.java,
"user_login_info_db"
).openHelperFactory(SafeHelperFactory("".toByteArray()))
.build()
}这里主要需要自定义一个SupportSQLiteOpenHelper.Factory也就是SafeHelperFactory 这个SafeHelperFactory 完全是仿照Room架构默认的Factory 也就是FrameworkSQLiteOpenHelperFactory 实现。主要是用户创建一个用于打开数据库的SQLiteOpenHelper,主要的区别是自定义的Facttory 需要一个用于加密与解密的密码。
我们首先需要定义一个自己的OpenHelperFactory
public class SafeHelperFactory implements SupportSQLiteOpenHelper.Factory {
public static final String POST_KEY_SQL_MIGRATE = "PRAGMA cipher_migrate;";
public static final String POST_KEY_SQL_V3 = "PRAGMA cipher_compatibility = 3;";
final private byte[] passphrase;
final private Options options;
public SafeHelperFactory(byte[] passphrase, Options options) {
this.passphrase = passphrase;
this.options = options;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public SupportSQLiteOpenHelper create(
SupportSQLiteOpenHelper.Configuration configuration) {
return(create(configuration.context, configuration.name,
configuration.callback));
}
public SupportSQLiteOpenHelper create(Context context, String name,
SupportSQLiteOpenHelper.Callback callback) {
//创建一个Helper
return(new Helper(context, name, callback, passphrase, options));
}
private void clearPassphrase(char[] passphrase) {
for (int i = 0; i < passphrase.length; i++) {
passphrase[i] = (byte) 0;
}
}SafeHelperFactory 的create创建了一个Helper,这个Helper实现了Room框架的SupportSQLiteOpenHelper ,实际这个Helper 是个代理类被代理的类为OpenHelper ,OpenHelper 用于操作SQLCipher 提供的数据库类。
class Helper implements SupportSQLiteOpenHelper {
private final OpenHelper delegate;
private final byte[] passphrase;
private final boolean clearPassphrase;
Helper(Context context, String name, Callback callback, byte[] passphrase,
SafeHelperFactory.Options options) {
SQLiteDatabase.loadLibs(context);
clearPassphrase=options.clearPassphrase;
delegate=createDelegate(context, name, callback, options);
this.passphrase=passphrase;
}
private OpenHelper createDelegate(Context context, String name,
final Callback callback, SafeHelperFactory.Options options) {
final Database[] dbRef = new Database[1];
return(new OpenHelper(context, name, dbRef, callback, options));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
synchronized public String getDatabaseName() {
return delegate.getDatabaseName();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN)
synchronized public void setWriteAheadLoggingEnabled(boolean enabled) {
delegate.setWriteAheadLoggingEnabled(enabled);
}
@Override
synchronized public SupportSQLiteDatabase getWritableDatabase() {
SupportSQLiteDatabase result;
try {
result = delegate.getWritableSupportDatabase(passphrase);
}
catch (SQLiteException e) {
if (passphrase != null) {
boolean isCleared = true;
for (byte b : passphrase) {
isCleared = isCleared && (b == (byte) 0);
}
if (isCleared) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The passphrase appears to be cleared. This happens by" +
"default the first time you use the factory to open a database, so we can remove the" +
"cleartext passphrase from memory. If you close the database yourself, please use a" +
"fresh SafeHelperFactory to reopen it. If something else (e.g., Room) closed the" +
"database, and you cannot control that, use SafeHelperFactory.Options to opt out of" +
"the automatic password clearing step. See the project README for more information.");
}
}
throw e;
}
if (clearPassphrase && passphrase != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < passphrase.length; i++) {
passphrase[i] = (byte) 0;
}
}
return(result);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* NOTE: this implementation delegates to getWritableDatabase(), to ensure
* that we only need the passphrase once
*/
@Override
public SupportSQLiteDatabase getReadableDatabase() {
return(getWritableDatabase());
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
synchronized public void close() {
delegate.close();
}
static class OpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private final Database[] dbRef;
private volatile Callback callback;
private volatile boolean migrated;
}真正操作数据库的类OpenHelper,OpenHelper 继承的SQLiteOpenHelper 是net.sqlcipher.database 包下的
static class OpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private final Database[] dbRef;
private volatile Callback callback;
private volatile boolean migrated;
OpenHelper(Context context, String name, final Database[] dbRef, final Callback callback,
final SafeHelperFactory.Options options) {
super(context, name, null, callback.version, new SQLiteDatabaseHook() {
@Override
public void preKey(SQLiteDatabase database) {
if (options!=null && options.preKeySql!=null) {
database.rawExecSQL(options.preKeySql);
}
}
@Override
public void postKey(SQLiteDatabase database) {
if (options!=null && options.postKeySql!=null) {
database.rawExecSQL(options.postKeySql);
}
}
}, new DatabaseErrorHandler() {
@Override
public void onCorruption(SQLiteDatabase dbObj) {
Database db = dbRef[0];
if (db != null) {
callback.onCorruption(db);
}
}
});
this.dbRef = dbRef;
this.callback=callback;
}
synchronized SupportSQLiteDatabase getWritableSupportDatabase(byte[] passphrase) {
migrated = false;
SQLiteDatabase db=super.getWritableDatabase(passphrase);
if (migrated) {
close();
return getWritableSupportDatabase(passphrase);
}
return getWrappedDb(db);
}
synchronized Database getWrappedDb(SQLiteDatabase db) {
Database wrappedDb = dbRef[0];
if (wrappedDb == null) {
wrappedDb = new Database(db);
dbRef[0] = wrappedDb;
}
return(dbRef[0]);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) {
callback.onCreate(getWrappedDb(sqLiteDatabase));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
migrated = true;
callback.onUpgrade(getWrappedDb(sqLiteDatabase), oldVersion, newVersion);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void onConfigure(SQLiteDatabase db) {
callback.onConfigure(getWrappedDb(db));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void onDowngrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
migrated = true;
callback.onDowngrade(getWrappedDb(db), oldVersion, newVersion);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void onOpen(SQLiteDatabase db) {
if (!migrated) {
// from Google: "if we've migrated, we'll re-open the db so we should not call the callback."
callback.onOpen(getWrappedDb(db));
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public synchronized void close() {
super.close();
dbRef[0] = null;
}
}这里的OpenHelper 完全是仿照Room 框架下的OpenHelper 实现的。
Android是一种基于Linux内核的自由及开放源代码的操作系统,主要使用于移动设备,如智能手机和平板电脑,由美国Google公司和开放手机联盟领导及开发。
感谢你的阅读,希望你对“Android Room数据库加密的示例分析”这一关键问题有了一定的理解,具体使用情况还需要大家自己动手实验使用过才能领会,快去试试吧,如果想阅读更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。