您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
本篇内容主要讲解“spring Kafka中的@KafkaListener源码分析”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“spring Kafka中的@KafkaListener源码分析”吧!
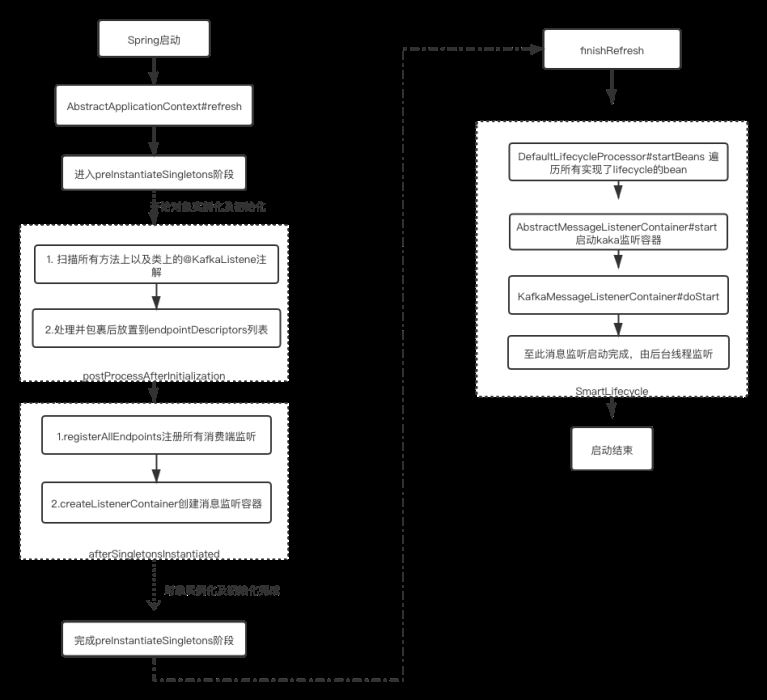
从spring启动开始处理@KafkaListener,到start消息监听整体流程图
KafkaListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, final String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(bean.getClass())) {
Class<?> targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean);
// 扫描@KafkaListener注解
Collection<KafkaListener> classLevelListeners = findListenerAnnotations(targetClass);
......
if (annotatedMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(bean.getClass());
this.logger.trace(() -> "No @KafkaListener annotations found on bean type: " + bean.getClass());
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
for (Map.Entry<Method, Set<KafkaListener>> entry : annotatedMethods.entrySet()) {
Method method = entry.getKey();
// 遍历扫描到的所有@KafkaListener注解并开始处理
for (KafkaListener listener : entry.getValue()) {
processKafkaListener(listener, method, bean, beanName);
}
}
this.logger.debug(() -> annotatedMethods.size() + " @KafkaListener methods processed on bean '"
+ beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods);
}
// 处理在类上的@KafkaListener注解
if (hasClassLevelListeners) {
processMultiMethodListeners(classLevelListeners, multiMethods, bean, beanName);
}
}
return bean;
}KafkaListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#processKafkaListener
protected void processKafkaListener(KafkaListener kafkaListener, Method method, Object bean, String beanName) {
Method methodToUse = checkProxy(method, bean);
MethodKafkaListenerEndpoint<K, V> endpoint = new MethodKafkaListenerEndpoint<>();
endpoint.setMethod(methodToUse);
processListener(endpoint, kafkaListener, bean, methodToUse, beanName);
}KafkaListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#processListener
将每个kafkaListener转变成MethodKafkaListenerEndpoint并注册到KafkaListenerEndpointRegistrar容器,方便后续统一启动监听
protected void processListener(MethodKafkaListenerEndpoint<?, ?> endpoint, KafkaListener kafkaListener,
Object bean, Object adminTarget, String beanName) {
String beanRef = kafkaListener.beanRef();
if (StringUtils.hasText(beanRef)) {
this.listenerScope.addListener(beanRef, bean);
}
endpoint.setBean(bean);
endpoint.setMessageHandlerMethodFactory(this.messageHandlerMethodFactory);
endpoint.setId(getEndpointId(kafkaListener));
endpoint.setGroupId(getEndpointGroupId(kafkaListener, endpoint.getId()));
endpoint.setTopicPartitions(resolveTopicPartitions(kafkaListener));
endpoint.setTopics(resolveTopics(kafkaListener));
endpoint.setTopicPattern(resolvePattern(kafkaListener));
endpoint.setClientIdPrefix(resolveExpressionAsString(kafkaListener.clientIdPrefix(), "clientIdPrefix"));
String group = kafkaListener.containerGroup();
......
// 注册已经封装好的消费端-endpoint
this.registrar.registerEndpoint(endpoint, factory);
if (StringUtils.hasText(beanRef)) {
this.listenerScope.removeListener(beanRef);
}
}KafkaListenerEndpointRegistrar#registerEndpoint
public void registerEndpoint(KafkaListenerEndpoint endpoint, KafkaListenerContainerFactory<?> factory) {
......
KafkaListenerEndpointDescriptor descriptor = new KafkaListenerEndpointDescriptor(endpoint, factory);
synchronized (this.endpointDescriptors) {
// 如果到了需要立即启动监听的阶段就直接注册并监听(也就是创建消息监听容器并启动)
if (this.startImmediately) { // Register and start immediately
this.endpointRegistry.registerListenerContainer(descriptor.endpoint,
resolveContainerFactory(descriptor), true);
}
else {
// 一般情况都先走这一步,添加至此列表,待bean后续的生命周期 统一注册并启动
this.endpointDescriptors.add(descriptor);
}
}
}
public void registerListenerContainer(KafkaListenerEndpoint endpoint, KafkaListenerContainerFactory<?> factory,
boolean startImmediately) {
......
synchronized (this.listenerContainers) {
......
// 1.创建消息监听容器
MessageListenerContainer container = createListenerContainer(endpoint, factory);
this.listenerContainers.put(id, container);
if (StringUtils.hasText(endpoint.getGroup()) && this.applicationContext != null) {
List<MessageListenerContainer> containerGroup;
if (this.applicationContext.containsBean(endpoint.getGroup())) {
containerGroup = this.applicationContext.getBean(endpoint.getGroup(), List.class);
}
else {
containerGroup = new ArrayList<MessageListenerContainer>();
this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(endpoint.getGroup(), containerGroup);
}
containerGroup.add(container);
}
// 2.是否立即启动消息监听
if (startImmediately) {
startIfNecessary(container);
}
}
}KafkaListenerEndpointRegistry#startIfNecessary
启动消息监听
private void startIfNecessary(MessageListenerContainer listenerContainer) {
if (this.contextRefreshed || listenerContainer.isAutoStartup()) {
// 启动消息监听
// 到这一步之后,消息监听以及处理都是KafkaMessageListenerContainer的逻辑
// 到此也就打通了@KafkaListener到MessageListenerContainer消息监听容器的逻辑
listenerContainer.start();
}
}这一步是实例化(此处的实例化是已经创建对象并完成了初始化操作)之后,紧接着的操作
KafkaListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#afterSingletonsInstantiated
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
this.registrar.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
// 对"注册员"信息的完善
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {
Map<String, KafkaListenerConfigurer> instances =
((ListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory).getBeansOfType(KafkaListenerConfigurer.class);
for (KafkaListenerConfigurer configurer : instances.values()) {
configurer.configureKafkaListeners(this.registrar);
}
}
if (this.registrar.getEndpointRegistry() == null) {
if (this.endpointRegistry == null) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null,
"BeanFactory must be set to find endpoint registry by bean name");
this.endpointRegistry = this.beanFactory.getBean(
KafkaListenerConfigUtils.KAFKA_LISTENER_ENDPOINT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME,
KafkaListenerEndpointRegistry.class);
}
this.registrar.setEndpointRegistry(this.endpointRegistry);
}
......
// Actually register all listeners
// 整个方法这里才是关键
// 创建MessageListenerContainer并注册
this.registrar.afterPropertiesSet();
}KafkaListenerEndpointRegistrar#afterPropertiesSet
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
registerAllEndpoints();
}KafkaListenerEndpointRegistrar#registerAllEndpoints
protected void registerAllEndpoints() {
synchronized (this.endpointDescriptors) {
for (KafkaListenerEndpointDescriptor descriptor : this.endpointDescriptors) {
// 这里是真正的创建ListenerContainer监听对象并注册
this.endpointRegistry.registerListenerContainer(
descriptor.endpoint, resolveContainerFactory(descriptor));
}
// 启动时所有消息监听对象都注册之后,便将参数置为true
this.startImmediately = true; // trigger immediate startup
}
}到此,相信大家对“spring Kafka中的@KafkaListener源码分析”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。