您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
下面,我们将演示如何搭建一个纯注解配置的springmvc,并通过跟踪源码的方式解析随着应用服务器的启动我们的springmvc配置是如何生效的。使用web容器版本:apache-tomcat-8.5.27 。代码中一些不重要的内容未展示。
1. 编写一个简单的web应用:
maven依赖:
<groupId>per.ym</groupId>
<artifactId>mvcdemo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>mvcdemo</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.20.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>4.3.20.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<webXml>WebContent\WEB-INF\web.xml</webXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>springmvc配置类:
package per.ym.mvcdemo.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[] {RootConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[] {WebConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] {"/"};
}
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected void customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
registration.setMultipartConfig(new MultipartConfigElement("/temp/uploads"));
}
}root:
package per.ym.mvcdemo.config;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "per.ym.mvcdemo.service",
excludeFilters = {@Filter(type=FilterType.ANNOTATION, value = EnableWebMvc.class)})
public class RootConfig {
}web:
package per.ym.mvcdemo.config;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan("per.ym.mvcdemo.controller")
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
registry.jsp("/WEB-INF/views/", ".jsp");
}
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}service:
package per.ym.mvcdemo.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class HelloService {
public String hello() {
return "Hello world.";
}
}controller:
package per.ym.mvcdemo.controller;
import per.ym.mvcdemo.service.HelloService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
public class HelloWorld {
@Autowired
private HelloService service;
public HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("construct!");
}
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello() {
return service.hello();
}
}interceptor:
package per.ym.mvcdemo.interceptor;
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//目标方法运行之前执行
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return true;
}
//目标方法执行正确以后执行
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
//页面响应以后执行
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
}
}2. 原理解析
2.1. AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer剖析
在Servlet 3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,如果能发现的话,就会用它来配置Servlet容器。
Spring提供了这个接口的实现,名为SpringServletContainerInitializer,这个类反过来又会查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配置的任务交给它们来完成。Spring 3.2引入了一个便利的WebApplicationInitializer基础实现,也就是AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer。因为我们的
MyWebAppInitializer扩展了AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,当然也就实现了WebApplicationInitializer,因此当部署到Servlet 3.0容器中的时候,容器会自动发现它,并用它来配置Servlet上下文。
尽管它的名字很长,但是AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer使用起来很简便。它仅要求我们重写其中的三个方法,其他的方法是否重写则根据你的具体需求而定。
第一个方法是getServletMappings(),它会将一个或多个路径映射到DispatcherServlet上。在本例中,它映射的是“/”,这表示它会是应用的默认Servlet。它会处理进入应用的所有请求。
为了理解其他的两个方法,我们首先要理解DispatcherServlet和一个Servlet监听器,也就是ContextLoaderListene(你是否记得使用web.xml方式配置时也会有它的身影)的关系。
两个应用上下文之间的故事:
当DispatcherServlet启动的时候,它会创建Spring应用上下文,并加载配置文件或配置类中所声明的bean。在MyWebAppInitializer的getServletConfigClasses()方法中,我们要求DispatcherServlet加载应用上下文时,使用定义在WebConfig配置类(使用Java配置)中的bean。但是在Spring Web应用中,通常还会有另外一个应用上下文。另外的这个应用上下文是由ContextLoaderListener创建的。
我们希望DispatcherServlet加载包含Web组件的bean,如控制器、视图解析器以及处理器映射,而ContextLoaderListener要加载应用中的其他bean。这些bean通常是驱动应用后端的中间层和数据层组件。
实际上,AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer会同时创建DispatcherServlet和ContextLoaderListener。getServletConfigClasses()方法返回的带有@Configuration注解的类将会用来定义DispatcherServlet应用上下文中的bean,我们暂且把它记为context1。getRootConfigClasses()方法返回的带有@Configuration注解的类将会用来配置ContextLoaderListener创建的应用上下文中的bean,记为context2。那这两个上下文的关系是什么呢?答案是,context1会把context2设置为parent,这样,当context1中的bean需要使用到context2中的bean时就可以在其中直接获取,比如当我们把一个service层的bean注入到controller中时。
在本例中,根配置定义在RootConfig中,DispatcherServlet的配置声明在WebConfig中。稍后我们将会看到这两个类的内容。
需要注意的是,通过AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer来配置DispatcherServlet是传统web.xml方式的替代方案。如果你愿意的话,可以同时包含web.xml和AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,但这其实并没有必要。
如果按照这种方式配置DispatcherServlet,而不是使用web.xml的话,那唯一问题在于它只能部署到支持Servlet 3.0的服务器中才能正常工作,如Tomcat 7或更高版本。如果你还没有使用支持Servlet 3.0的服务器,那么在AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer子类中配置DispatcherServlet的方法就不适合你了。你别无选择,只能使用web.xml了。
2.2. 源码解析
2.2.1. 查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类
先看一下tomcat调用栈:
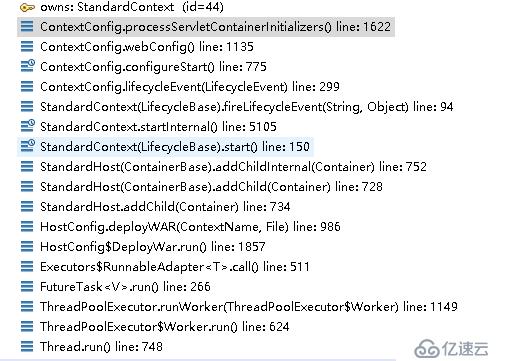
这个发生在web应用的部署过程,看这个方法名称就是处理servlet容器的初始化相关的东西。我们来看看里面是什么内容:
protected void processServletContainerInitializers() {
//类路径下查找ServletContainerInitializer的实现类
detectedScis = loader.load(ServletContainerInitializer.class);
}我们进入 loader.load(ServletContainerInitializer.class);
public List<T> load(Class<T> serviceType) throws IOException {
String configFile = SERVICES + serviceType.getName();
Enumeration<URL> resources;
if (loader == null) {
resources = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(configFile);
} else {
//类路径下查找是否有指定的文件
resources = loader.getResources(configFile);
}
while (resources.hasMoreElements()) {
//将查找到的文件里的内容读取到containerServicesFound中
parseConfigFile(containerServicesFound, resources.nextElement());
}
//使用反射创建查找到的ServletContainerInitializer的实现类
return loadServices(serviceType, containerServicesFound);
}我们看看configFile和containerServicesFound的内容都是什么

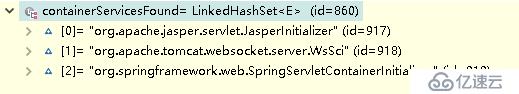
正如上述中所示的一样,在我们的spring-web-4.3.20.RELEASE.jar中的确有这个文件,其值也是我们查找到的类
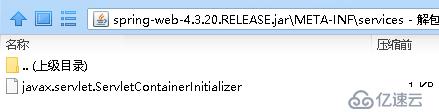
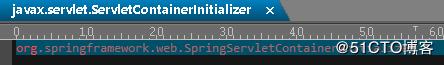
找到ServletContainerInitializer的实现类后我们返回到processServletContainerInitializers方法中,看它后续的处理
protected void processServletContainerInitializers() {
List<ServletContainerInitializer> detectedScis;
try {
WebappServiceLoader<ServletContainerInitializer> loader = new WebappServiceLoader<>(context);
//类路径下查找ServletContainerInitializer的实现类
detectedScis = loader.load(ServletContainerInitializer.class);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"contextConfig.servletContainerInitializerFail",
context.getName()),
e);
ok = false;
return;
}
for (ServletContainerInitializer sci : detectedScis) {
initializerClassMap.put(sci, new HashSet<Class<?>>());
HandlesTypes ht;
try {
//获取类上的HandlesTypes注解
ht = sci.getClass().getAnnotation(HandlesTypes.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("contextConfig.sci.debug",
sci.getClass().getName()),
e);
} else {
log.info(sm.getString("contextConfig.sci.info",
sci.getClass().getName()));
}
continue;
}
if (ht == null) {
continue;
}
//拿到注解上的value值
Class<?>[] types = ht.value();
if (types == null) {
continue;
}
for (Class<?> type : types) {
if (type.isAnnotation()) {
handlesTypesAnnotations = true;
} else {
handlesTypesNonAnnotations = true;
}
Set<ServletContainerInitializer> scis =
typeInitializerMap.get(type);
if (scis == null) {
scis = new HashSet<>();
//保存HandlesTypes注解上的value值
typeInitializerMap.put(type, scis);
}
scis.add(sci);
}
}
}看到这里是不是有点懵,HandlesTypes注解上的value用来干什么?下面,我们来看看它是用来干嘛的。
2.2.2. 查找实现WebApplicationInitializer接口的类
首先,我们看看SpringServletContainerInitializer头上的东西
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
......
}看到这里或许能猜到一些东西了吧,实际上,web容器会根据HandlesTypes注解上的value值在类路径下查找它的实现类,在SpringServletContainerInitializer上该值为WebApplicationInitializer,因此它会去查找WebApplicationInitializer的实现类,而这个实现类在我们的类路径下就有我们自己写的MyWebAppInitializer,因此它最终会找到我们的MyWebAppInitializer,而在后面调用SpringServletContainerInitializer的onStartup方法时,它将作为参数被传进去
2.2.3. WebApplicationInitializer实现类接管工作
我们在SpringServletContainerInitializer的onStartup方法中打上断点,既然springmvc是通过该类配置的,那么它肯定会在某个时候调用其中唯一的方法onStartup。
看看它的调用栈
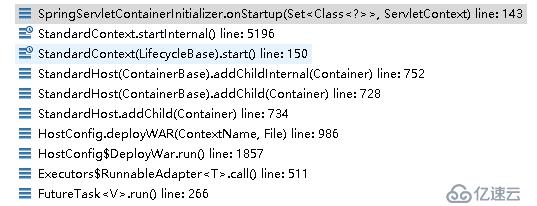
在启动standardContext时它会调用所有ServletContainerInitializer的实现类以给应用一个自身配置的机会
我们回到StandardContext.startInternal()中看看
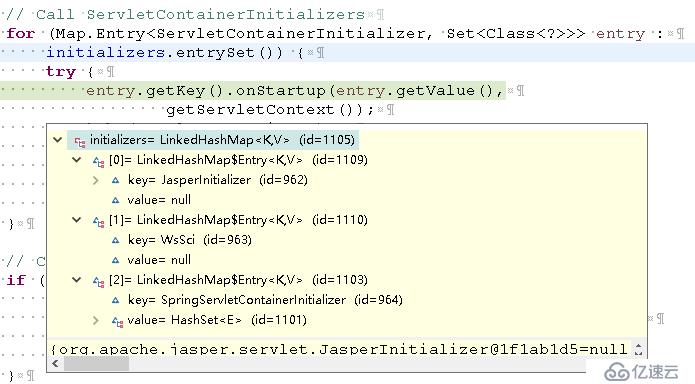
正如我们前面所看到的一样,还是它们三。进入到SpringServletContainerInitializer的onStartup()方法中
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<WebApplicationInitializer>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
//不是接口不是抽象的WebApplicationInitializer的子类
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) waiClass.newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
//调用WebApplicationInitializer实现类的onStartup方法
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}只有我们的MyWebAppInitializer

看到这里你也就应该明白了2.1中所说的内容
在Servlet 3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,如果能发现的话,就会用它来配置Servlet容器。
Spring提供了这个接口的实现,名为SpringServletContainerInitializer,这个类反过来又会查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配置的任务交给它们来完成。
2.2.4. MyWebAppInitializer开工
进入AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer#onStartup(servletContext)方法
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
//a.调用父类AbstractContextLoaderInitializer的该方法,用于注册ContextLoaderListener
super.onStartup(servletContext);
//b.注册dispatcherServlet
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}a.继续进入父类AbstractContextLoaderInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext servletContext)方法
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
//注册ContextLoaderListener
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext)方法
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
//创建spring上下文
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
//将ContextLoaderListener添加到servletContext中,这一步等同在web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}先到createRootApplicationContext()中看看
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
//获取根上下文配置类,会调用到我们自己的MyWebAppInitializer#getRootConfigClasses(),模板方法设计模式
Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
rootAppContext.register(configClasses);
return rootAppContext;
}
else {
return null;
}
}进入MyWebAppInitializer#getRootConfigClasses()
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
//使用我们的RootConfig配置类,这会使得ContextLoaderListener所加载的上下文扫 描"per.ym.mvcdemo.service"
//包下所有的组件并将其纳入到容器中
return new Class<?>[] {RootConfig.class};
}ContextLoaderListener配置完成,重新回到AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer#registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext)方法中
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
//创建dispaherServlet的spring上下文
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
//创建DispatcherServlet并传入servletAppContext,它将在servlet生命周期的init方法中被reFresh
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
//将DispatcherServlet加入到servletContext中,加上下面的几步同web.xml中配置DispatcherServlet
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
//设置DispatcherServlet随着该servlet容器启动而启动
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
//设置DispatcherServlet路径映射,将调用我们MyWebAppInitializer#getServletMappings(),即“/”
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
//获取过滤器,该方法默认为空,可重写它加入我们自己的过滤器
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
//该方法默认也为空,我们可以重写它来对DispatcherServlet进行一些额外配置,比如同MyWebAppInitializer
//中一样,配置一下用于文件上传的multipart
customizeRegistration(registration);
}到 createServletApplicationContext()中看看
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext servletAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
//获取dispaherServlet的spring上下文配置类,即MyWebAppInitializer#getServletConfigClasses中的WebConfig
Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
servletAppContext.register(configClasses);
}
return servletAppContext;
}到这里,我们的MyWebAppInitializer的主要任务也就完成了,即向servlet容器中添加ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet
2.2.5. ContextLoaderListener创建spring上下文
由于ContextLoaderListener实现了javax.servlet.ServletContextListener接口,因此在servlet容器启动时会调用它的contextInitialized方法。
执行ContextLoaderListener#contextInitialized方法
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}在该方法中打个断点,看看tomcat是在哪里调用它的
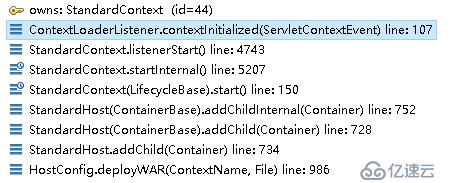
也是在StandardContext#startInternal里,到startInternal中看看
// Call ServletContainerInitializers
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer, Set<Class<?>>> entry :
initializers.entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getKey().onStartup(entry.getValue(),
getServletContext());
} catch (ServletException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.sciFail"), e);
ok = false;
break;
}
}
// Configure and call application event listeners
if (ok) {
//触发监听器
if (!listenerStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerFail"));
ok = false;
}
}在执行完ServletContainerInitializer相关操作后就立刻执行监听器的相关方法
言归正传,看看ContextLoaderListener#contextInitialized方法
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}进入父类ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext方法
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
//这个cwac就是传入ContextLoaderListener的spring上下文
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
//配置并刷新spring上下文
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
return this.context;
}
}进入configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext)
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//刷新spring上下文,这里就进入到spring的节奏里了,我们不在往下了
wac.refresh();
}2.2.6. 配置DispatcherServlet
在2.2.4,向ServletContext中添加DispatcherServlet时,我们设置了DispatcherServlet随servlet容器的启动而启动,而servlet启动时会执行它的生命周期方法init,DispatcherServlet的init方法在其父类HttpServletBean中
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
//调用子类中的方法,在FrameworkServlet中
initServletBean();
}进入FrameworkServlet#initServletBean()
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//初始化spring上下文
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//该方法默认为空
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
}先到initWebApplicationContext()中看看
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//rootContext,这个就是ContextLoaderListener加载的spring上下文
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
//这个wac就是DispatcherServlet的spring上下文
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
//设置rootContext为parent,这样当需要注入某个bean时就可以从父上下文中获取
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//配置并刷新spring上下文
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
return wac;
}设置父上下文,刷新当前上下文。到这里,我们整个init方法也就完成了
2.2.7. @EnableWebMvc是干什么的
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan("per.ym.mvcdemo.controller")
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter{看看这个@EnableWebMvc是什么样子的
//这个是关键,向spring上下文中引入DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}进入DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
@Override
protected void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
this.configurers.configurePathMatch(configurer);
}
@Override
protected void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
this.configurers.configureContentNegotiation(configurer);
}
@Override
protected void configureAsyncSupport(AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer) {
this.configurers.configureAsyncSupport(configurer);
}
@Override
protected void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
this.configurers.configureDefaultServletHandling(configurer);
}
@Override
protected void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addFormatters(registry);
}
@Override
protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addInterceptors(registry);
}
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
@Override
protected void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addCorsMappings(registry);
}
@Override
protected void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addViewControllers(registry);
}
@Override
protected void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.configureViewResolvers(registry);
}
@Override
protected void addArgumentResolvers(List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> argumentResolvers) {
this.configurers.addArgumentResolvers(argumentResolvers);
}
@Override
protected void addReturnValueHandlers(List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> returnValueHandlers) {
this.configurers.addReturnValueHandlers(returnValueHandlers);
}
@Override
protected void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
this.configurers.configureMessageConverters(converters);
}
@Override
protected void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
this.configurers.extendMessageConverters(converters);
}
@Override
protected void configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> exceptionResolvers) {
this.configurers.configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(exceptionResolvers);
}
@Override
protected void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> exceptionResolvers) {
this.configurers.extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(exceptionResolvers);
}
@Override
protected Validator getValidator() {
return this.configurers.getValidator();
}
@Override
protected MessageCodesResolver getMessageCodesResolver() {
return this.configurers.getMessageCodesResolver();
}
}该类中有很多配置方法,而这些配置方法都是调用this.configurers来进行配置的,这个configurers是通过下面这种方式注入进来的,注入的参数的类型是WebMvcConfigurer,这个时候你再看看我们的WebConfig,他继承自WebMvcConfigurerAdapter,而这个WebMvcConfigurerAdapter又实现了WebMvcConfigure。因此,这里会把我们的WebConfig注入进来并加入到this.configurers中,最终配置时就会调用我们WebConfig重写的方法,这也是我们的WebConfig为什么要继承WebMvcConfigurerAdapter并重写父类方法的原因
@Autowired(required = false)
//类型是(List<WebMvcConfigurer>,关键是这个WebMvcConfigurer
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}说到这里,那么我们WebConfig中重写的方法是在什么时候被调用的呢,DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration继承自WebMvcConfigurationSupport,在这个类里它会引入很多bean到spring上下文中,包括RequestMappingHandlerMapping、PathMatcher、HandlerMapping、BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping等等,这里我们以RequestMappingHandlerMapping为例,进行说明
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {
RequestMappingHandlerMapping mapping = createRequestMappingHandlerMapping();
mapping.setOrder(0);
//看这里,设置拦截器
mapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors());
mapping.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager());
mapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
PathMatchConfigurer configurer = getPathMatchConfigurer();
Boolean useSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseSuffixPatternMatch();
if (useSuffixPatternMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch);
}
Boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch();
if (useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
}
Boolean useTrailingSlashMatch = configurer.isUseTrailingSlashMatch();
if (useTrailingSlashMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch);
}
UrlPathHelper pathHelper = configurer.getUrlPathHelper();
if (pathHelper != null) {
mapping.setUrlPathHelper(pathHelper);
}
PathMatcher pathMatcher = configurer.getPathMatcher();
if (pathMatcher != null) {
mapping.setPathMatcher(pathMatcher);
}
return mapping;
}
到getInterceptors()方法中看看
protected final Object[] getInterceptors() {
if (this.interceptors == null) {
InterceptorRegistry registry = new InterceptorRegistry();
//看这个方法
addInterceptors(registry);
registry.addInterceptor(new ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor(mvcConversionService()));
registry.addInterceptor(new ResourceUrlProviderExposingInterceptor(mvcResourceUrlProvider()));
this.interceptors = registry.getInterceptors();
}
return this.interceptors.toArray();
}子类DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration重写这个addInterceptors(registry)方法
@Override
protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addInterceptors(registry);
}这样,他就会调用的我们WebConfig中的addInterceptors(registry)方法了
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
}而我们在WebConfig中重写的其他方法也会在创建WebMvcConfigurationSupport中定义的其他bean时被调用
然后,我们就在这里结束了吧......
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。