您好,登录后才能下订单哦!
本篇内容主要讲解“Vue+OpenLayer怎么实现测距功能”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Vue+OpenLayer怎么实现测距功能”吧!
这个库文件直接按照官网的来就可以了。 首先说一个事情哈,官网用的案例是地图使用的 EPSG:3857, 如果我们改成 EPSG:4326,测量数据不准确,切记这一点。
import 'ol/ol.css';
import Draw from 'ol/interaction/Draw';
import Map from 'ol/Map';
import Overlay from 'ol/Overlay';
import View from 'ol/View';
import { Circle as CircleStyle, Fill, Stroke, Style } from 'ol/style';
import { LineString, Polygon } from 'ol/geom';
import { OSM, Vector as VectorSource } from 'ol/source';
import { Tile as TileLayer, Vector as VectorLayer } from 'ol/layer';
import { getArea, getLength } from 'ol/sphere';
import { unByKey } from 'ol/Observable';上面是我引入的库文件,和官网基本上一样。
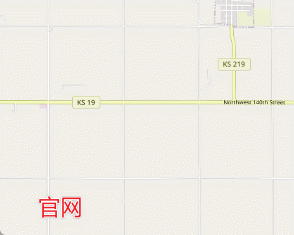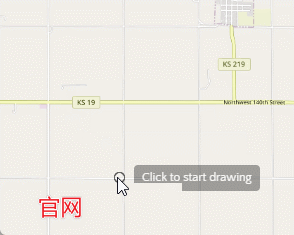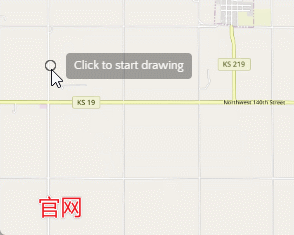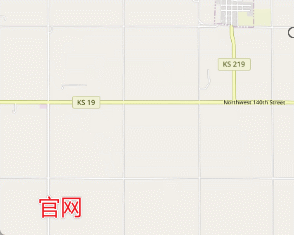
首先我们看下图官网效果,官网开始绘制或者是绘制中都在鼠标旁边有一个title文本框用来提示用户操作信息。
我们首先来实现一下这个功能。
首先说明一点哈,这是关键代码,有些参数可能用起来发现没有声明,都是全局的,自己加在全局就可以,主要是下面这一些。
var map = null var helpTooltipElement = null var feature = null; var helpTooltip = null; var draw = null; var measureTooltipElement = null; var measureTooltip = null; var listener = null; var mapMouseMove = null;
首先我们在需要实现测距功能的页面上写两个按钮,一个开始测距,一个结束测距。然后点击开始测距的时候,执行一个方法,假设是distance方法。
distance() {
let source = new VectorSource() // 首先创建一个数据源,用来放置绘制过程中和绘制结束后的线段
const layer = new VectorLayer({ // 添加一个图层,用来放置数据源,样式自己随便设置就可以了,我这里默认的官网
source: source,
style: new Style({
fill: new Fill({
color: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2)',
}),
stroke: new Stroke({
color: '#ffcc33',
width: 4,
}),
image: new CircleStyle({
radius: 7,
fill: new Fill({
color: '#ffcc33',
}),
}),
}),
});
mapMouseMove = map.on('pointermove', (ev) => { // 给地图添加一个鼠标移动事件
let helpMsg = '点击开始测量' // 默认开始的操作提示文本
if (feature) { // featuer 是全局的,判断有没有点击鼠标绘制过
helpMsg = '双击结束测量' // 如果之前点击绘制了就显示双击结束
}
helpTooltipElement.innerHTML = helpMsg; // 设置dom的提示文字
helpTooltip.setPosition(ev.coordinate); // 设置位置跟着鼠标走
helpTooltipElement.classList.remove('hidden') // 让他显示出来
})
this.createHelpTooltip() // 创建那个helpTooltipElement方法
map.addLayer(layer) // 把图层添加到地图
},然后调用了一个初始化操作提示的dom元素。这个就是官网的函数,如果参数名和自己起的或者是map的指向问题需要自己根据自己的实际修改一下。
createHelpTooltip() {
if (helpTooltipElement) {
helpTooltipElement.parentNode.removeChild(helpTooltipElement);
}
helpTooltipElement = document.createElement('div');
helpTooltipElement.className = 'ol-tooltip hidden';
helpTooltip = new Overlay({
element: helpTooltipElement,
offset: [15, 0],
positioning: 'center-left',
});
map.addOverlay(helpTooltip);
},还有一点,为了好看,把官网的样式复制一下子。
<style scoped>
/deep/.ol-tooltip {
position: relative;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
border-radius: 4px;
color: white;
padding: 4px 8px;
opacity: 0.7;
white-space: nowrap;
font-size: 12px;
cursor: default;
user-select: none;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip-measure {
opacity: 1;
font-weight: bold;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip-static {
background-color: #ffcc33;
color: black;
border: 1px solid white;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip-measure:before,
/deep/.ol-tooltip-static:before {
border-top: 6px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
border-right: 6px solid transparent;
border-left: 6px solid transparent;
content: "";
position: absolute;
bottom: -6px;
margin-left: -7px;
left: 50%;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip-static:before {
border-top-color: #ffcc33;
}
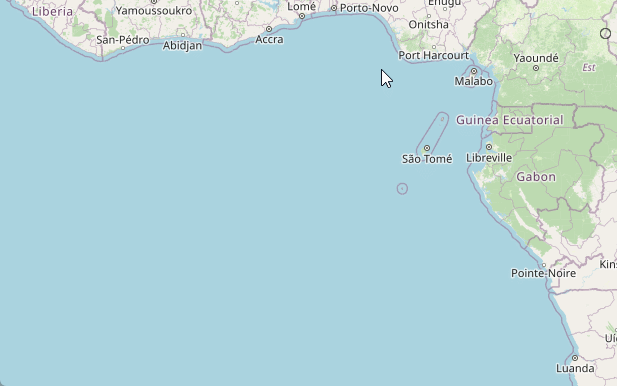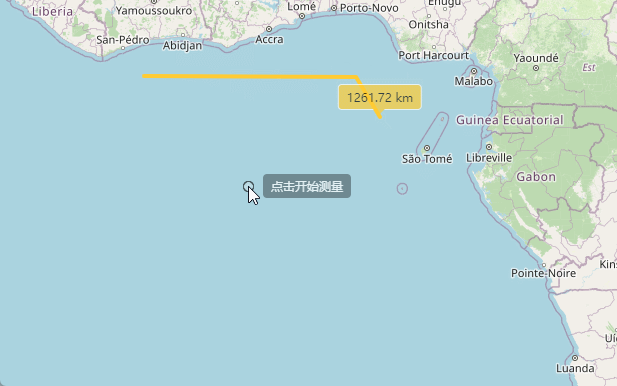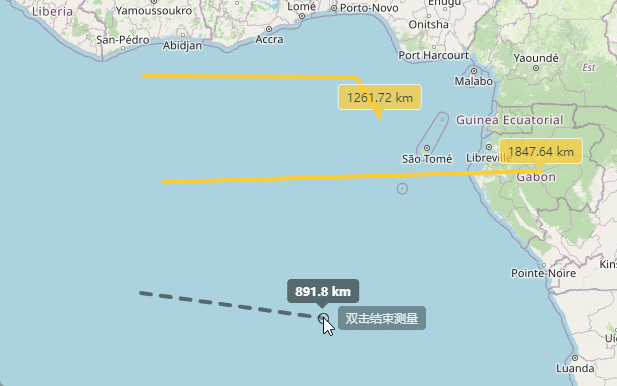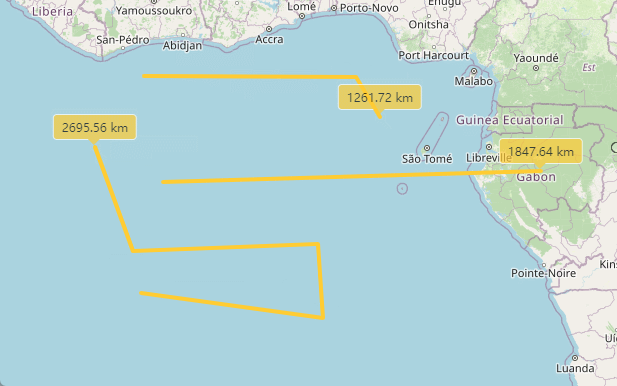
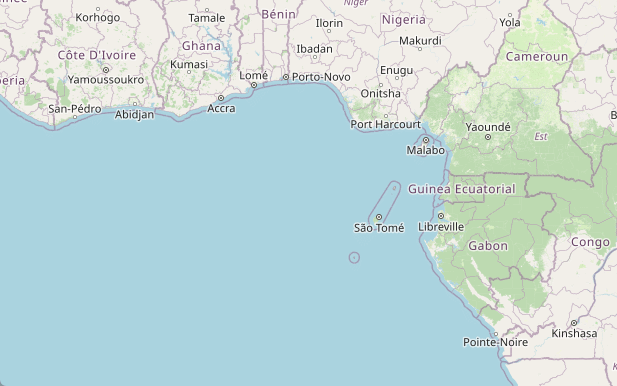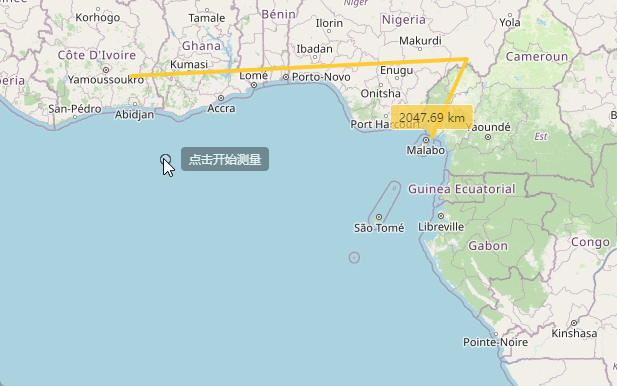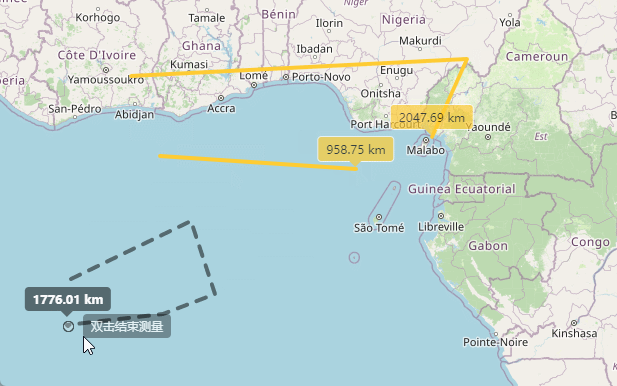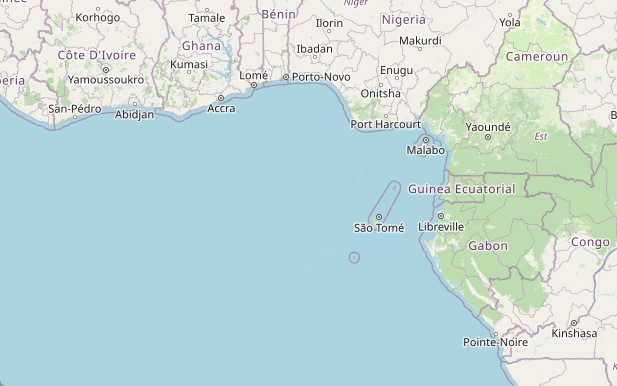
</style>然后就可以看到我们点击“开始测距”按钮之后,上面代码执行,鼠标旁边就出现一个小小的操作提示。
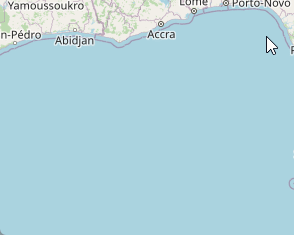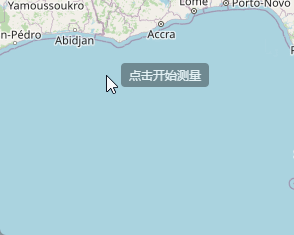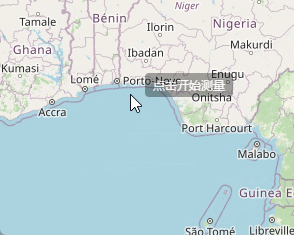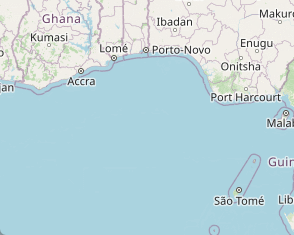
好的,通过上面的代码呢,我们成功的绘制出了提示框,然后就是鼠标绘制,代码也很简单,在map监听的pointermove方法中,继续创建一个draw进行绘制,关键代码就是下面:
draw = new Draw({
source, // 这个数据源就是我们最开始的那个数据源,这是简写,实际上是 source:source,
type: 'LineString', // 绘制线
style: new Style({ // 绘制完成之前线的样式,这是官网的样式,需要的话自己可以修改成自己想要的样子
fill: new Fill({
color: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2)',
}),
stroke: new Stroke({
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)',
lineDash: [10, 10],
width: 4,
}),
image: new CircleStyle({
radius: 5,
stroke: new Stroke({
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)',
}),
fill: new Fill({
color: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2)',
}),
}),
}),
});然后把draw绑定到地图上面。
map.addInteraction(draw); // draw 绑定到地图上面去
然后就实现了鼠标绘制线。
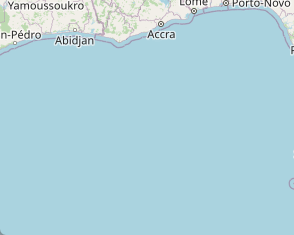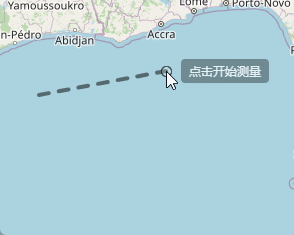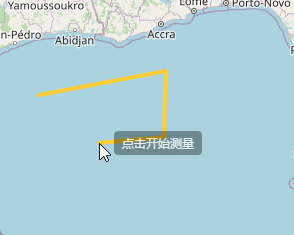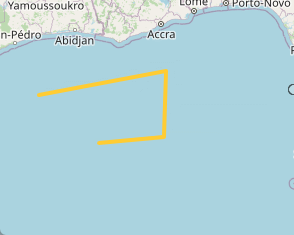
在我们点击开始测量的时候呢,在我们拖动鼠标的时候,会在上方显示出当前距离起点的距离,这个地方代码实现就是下面的样子,继续在上面的代码后面写:
// 开始监听绘制
draw.on('drawstart', (evt) => {
feature = evt.feature; // feature就是全局的
let tooltipCoord = evt.coordinate; // 鼠标当前的位置
listener = feature.getGeometry().on('change', function (evt) {
const geom = evt.target;
let output = formatLength(geom); // 距离的格式
tooltipCoord = geom.getLastCoordinate(); // 设置鼠标位置改变后的实时位置
measureTooltipElement.innerHTML = output; // 设置提示框的内容,就是距离
measureTooltip.setPosition(tooltipCoord); // 设置距离提示框的位置
});
});
// 格式化长度, 直接官网代码
const formatLength = function (line) {
const length = getLength(line);
let output;
if (length > 100) {
output = Math.round((length / 1000) * 100) / 100 + ' ' + 'km';
} else {
output = Math.round(length * 100) / 100 + ' ' + 'm';
}
return output;
};
this.createMeasureTooltip() // 创建那个距离的提示框然后上面代码调用了一个方法。
createMeasureTooltip() {
if (measureTooltipElement) {
measureTooltipElement.parentNode.removeChild(measureTooltipElement);
}
measureTooltipElement = document.createElement('div');
measureTooltipElement.className = 'ol-tooltip ol-tooltip-measure';
measureTooltip = new Overlay({
element: measureTooltipElement,
offset: [0, -15],
positioning: 'bottom-center',
stopEvent: false,
insertFirst: false,
});
this.drawElements.push(measureTooltip)
map.addOverlay(measureTooltip);
},完成上面的代码之后,我们在点击开始测量之后,会在鼠标上方实时显示当前鼠标位置距离起点的距离。
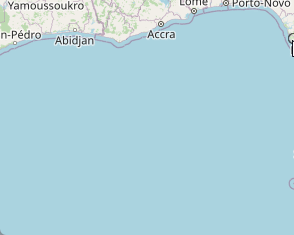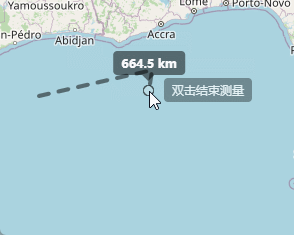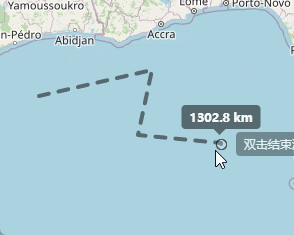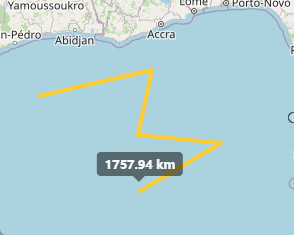
上边已经实现了点击开始测距,并且实时显示距离信息,接下来就是双击完成时候显示出总长度。
继续在之前代码后边写:
// 双击绘制完成
draw.on('drawend', () => {
measureTooltipElement.className = 'ol-tooltip ol-tooltip-static';
measureTooltip.setOffset([0, -7]);
feature = null;
measureTooltipElement = null;
this.createMeasureTooltip();
unByKey(listener);
});上边的代码基本上就是官网的代码,但是变量名不一样的地方需要稍微改一下。
通过上面的代码就实现了双击测量完成的功能。
OK,到此为止,测距功能全部完成!
绘制功能完成了,就需要取消绘制,取消绘制需要在点击“取消绘制”按钮之后,取消地图绘制功能,删除界面上已经绘制过的内容。
首先我们需要删除地图上绘制过的内容,包括连线,以及弹窗。
这个地方需要注意一下,我们需要把绘制的图层,比如连线,和弹窗都保存到一个或者是几个列表里面,然后在点击按钮的时候,去遍历删除。
所以说我们要在点击测距时候加载到地图的图层之后,将创建的图层添加到一个数组存起来。
map.addLayer(layer) this.drawLayers.push(layer) // 保存起来
包括那个总距离的弹窗。
this.drawElements.push(measureTooltip) map.addOverlay(measureTooltip); // 保存起来
然后点击“取消测量”按钮的时候执行下面的代码:
// 取消绘制
cancal() {
for(let i = 0 ; i< this.drawLayers.length; i++) {
map.removeLayer(this.drawLayers[i])
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.drawElements.length; i++) {
map.removeOverlay(this.drawElements[i])
}
this.drawLayers = []
this.drawElements = []
map.removeInteraction(draw)
unByKey(mapMouseMove);
},这样就可以了。
这样就完成了!
这里分享一下全部代码,就不放资源了,下载还花钱,我也是跟人家学的,没必要都。
<template>
<div class="home">
<div class="set">
<button class="btn" @click="distance()">测距</button>
<button class="btn" @click="cancal()">取消</button>
</div>
<div id="map" ref="map"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import 'ol/ol.css';
import Draw from 'ol/interaction/Draw';
import Map from 'ol/Map';
import Overlay from 'ol/Overlay';
import View from 'ol/View';
import { Circle as CircleStyle, Fill, Stroke, Style } from 'ol/style';
import { LineString, Polygon } from 'ol/geom';
import { OSM, Vector as VectorSource } from 'ol/source';
import { Tile as TileLayer, Vector as VectorLayer } from 'ol/layer';
import { getArea, getLength } from 'ol/sphere';
import { unByKey } from 'ol/Observable';
var map = null
var helpTooltipElement = null
var feature = null;
var helpTooltip = null;
var draw = null;
var measureTooltipElement = null;
var measureTooltip = null;
var listener = null;
var mapMouseMove = null;
export default {
name: "Home",
data() {
return {
drawLayers: [],
drawElements: [],
}
},
mounted() {
this.initMap()
},
methods: {
// 初始化地图
initMap() {
map = new Map({
layers: [
new TileLayer({
source: new OSM(),
}),
],
target: 'map',
view: new View({
center: [0, 0],
zoom: 5,
maxZoom: 18,
// projection: 'EPSG:4326',
constrainResolution: true, // 设置缩放级别为整数
smoothResolutionConstraint: false, // 关闭无级缩放地图
}),
});
},
// 测距
distance() {
let source = new VectorSource()
const layer = new VectorLayer({
source: source,
style: new Style({
fill: new Fill({
color: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2)',
}),
stroke: new Stroke({
color: '#ffcc33',
width: 4,
}),
image: new CircleStyle({
radius: 7,
fill: new Fill({
color: '#ffcc33',
}),
}),
}),
});
mapMouseMove = map.on('pointermove', (ev) => {
let helpMsg = '点击开始测量'
if (feature) {
helpMsg = '双击结束测量'
}
helpTooltipElement.innerHTML = helpMsg;
helpTooltip.setPosition(ev.coordinate);
helpTooltipElement.classList.remove('hidden')
})
map.getViewport().addEventListener('mouseout', function () {
helpTooltipElement.classList.add('hidden');
});
draw = new Draw({
source,
type: 'LineString',
style: new Style({
fill: new Fill({
color: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2)',
}),
stroke: new Stroke({
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)',
lineDash: [10, 10],
width: 4,
}),
image: new CircleStyle({
radius: 5,
stroke: new Stroke({
color: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)',
}),
fill: new Fill({
color: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2)',
}),
}),
}),
});
// 开始坚挺绘制
draw.on('drawstart', (evt) => {
feature = evt.feature;
let tooltipCoord = evt.coordinate;
listener = feature.getGeometry().on('change', function (evt) {
const geom = evt.target;
let output = formatLength(geom);
tooltipCoord = geom.getLastCoordinate();
measureTooltipElement.innerHTML = output;
measureTooltip.setPosition(tooltipCoord);
});
});
// 双击绘制完成
draw.on('drawend', () => {
measureTooltipElement.className = 'ol-tooltip ol-tooltip-static';
measureTooltip.setOffset([0, -7]);
feature = null;
measureTooltipElement = null;
this.createMeasureTooltip();
unByKey(listener);
});
// 格式化长度
const formatLength = function (line) {
const length = getLength(line);
let output;
if (length > 100) {
output = Math.round((length / 1000) * 100) / 100 + ' ' + 'km';
} else {
output = Math.round(length * 100) / 100 + ' ' + 'm';
}
return output;
};
this.createHelpTooltip()
this.createMeasureTooltip()
map.addLayer(layer)
this.drawLayers.push(layer)
map.addInteraction(draw);
},
// 取消绘制
cancal() {
for(let i = 0 ; i< this.drawLayers.length; i++) {
map.removeLayer(this.drawLayers[i])
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.drawElements.length; i++) {
map.removeOverlay(this.drawElements[i])
}
this.drawLayers = []
this.drawElements = []
map.removeInteraction(draw)
unByKey(mapMouseMove);
},
createMeasureTooltip() {
if (measureTooltipElement) {
measureTooltipElement.parentNode.removeChild(measureTooltipElement);
}
measureTooltipElement = document.createElement('div');
measureTooltipElement.className = 'ol-tooltip ol-tooltip-measure';
measureTooltip = new Overlay({
element: measureTooltipElement,
offset: [0, -15],
positioning: 'bottom-center',
stopEvent: false,
insertFirst: false,
});
this.drawElements.push(measureTooltip)
map.addOverlay(measureTooltip);
},
createHelpTooltip() {
if (helpTooltipElement) {
helpTooltipElement.parentNode.removeChild(helpTooltipElement);
}
helpTooltipElement = document.createElement('div');
helpTooltipElement.className = 'ol-tooltip hidden';
helpTooltip = new Overlay({
element: helpTooltipElement,
offset: [15, 0],
positioning: 'center-left',
});
map.addOverlay(helpTooltip);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.home {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: aliceblue;
position: relative;
}
#map {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
}
.set {
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
right: 0px;
z-index: 99;
}
.btn {
margin: 10px;
}
/deep/.hidden {
display: none;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip {
position: relative;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
border-radius: 4px;
color: white;
padding: 4px 8px;
opacity: 0.7;
white-space: nowrap;
font-size: 12px;
cursor: default;
user-select: none;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip-measure {
opacity: 1;
font-weight: bold;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip-static {
background-color: #ffcc33;
color: black;
border: 1px solid white;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip-measure:before,
/deep/.ol-tooltip-static:before {
border-top: 6px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
border-right: 6px solid transparent;
border-left: 6px solid transparent;
content: "";
position: absolute;
bottom: -6px;
margin-left: -7px;
left: 50%;
}
/deep/.ol-tooltip-static:before {
border-top-color: #ffcc33;
}
</style>到此,相信大家对“Vue+OpenLayer怎么实现测距功能”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。